Model Details and Parameters
Find the stress distribution in a square plate due to the effects of a circular hole at the center under an in-plane uniform line load. Only a quarter model may be analyzed due to symmetry.
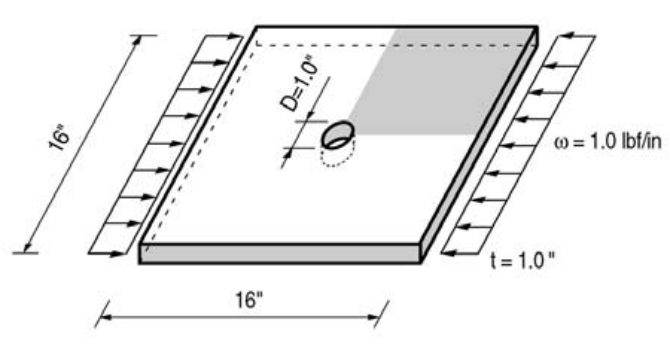
Structural geometry
- Analysis Type
2-D static analysis - Dimension
Length: 8.0 in
Width: 8.0 in
Thickness: 1.0 in
Radius of the hole: 0.5 in - Plate Type
Mindlin Plane Stress - Material
Structural Steel
Young’s Modulus: 1 psi
Poisson’s Ratio: 0.1 - Element Property
Plate Thickness: 1 in - Boundary Supports
Nodes 1 – 9: Constrain Dy, Rx, Ry and Rz (symmetric about X-axis)
Nodes 64 – 72: Constrain Dx, Rx, Ry and Rz (symmetric about Y-axis) - Loads
Node 9 : 0.5265 lbf, Node 73 : 1.657 lbf, Node 74 : 2.543 lbf, Node 75 : 2.343 lbf, Node 76 : 0.9305 lbf
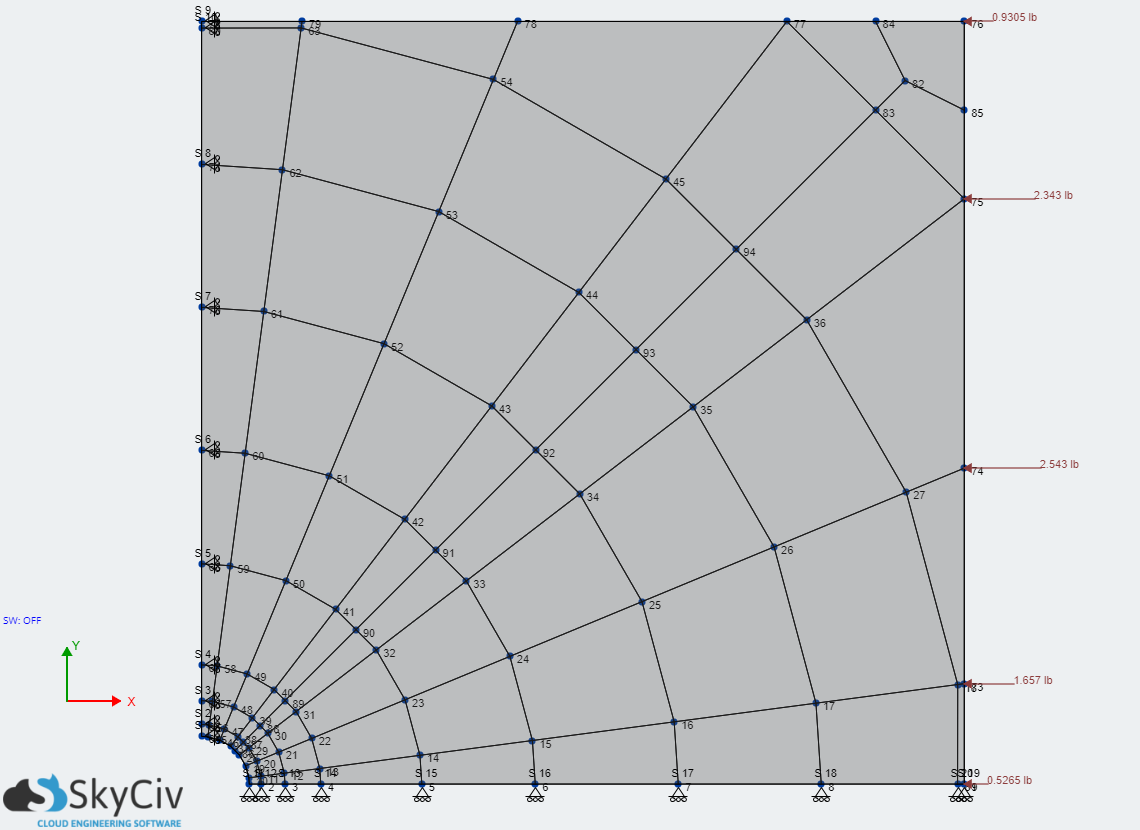
Analysis model
Results
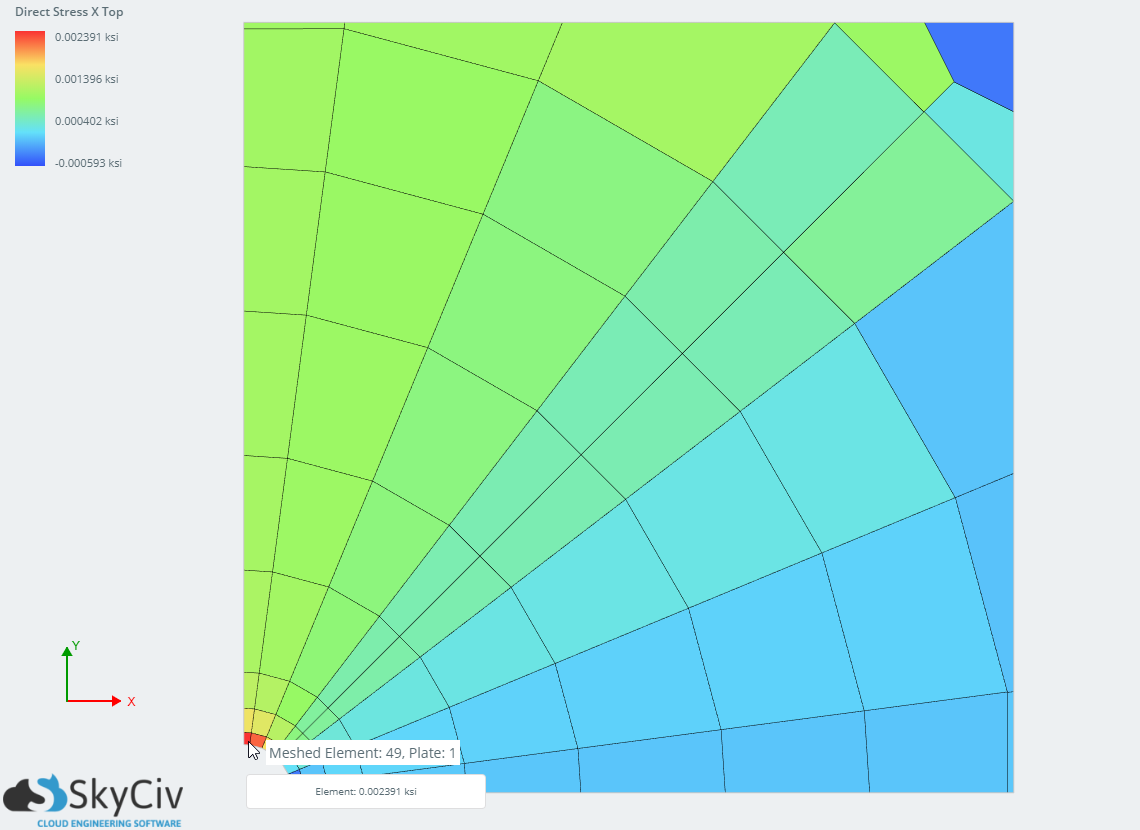
Direct Stress X Stress of the structure (Element 49)
Comparison of Results
| Result | Location | SkyCiv | Theoretical | Difference 1 | Third-Party 2 | Difference 2 |
| Direct Stress X Stress of the structure (ksi) | Element 49 Top | 0.002391 | 0.002332 | 2.55% | 0.002369 | 0.93% |
Reference
Timoshenko, S. and Goodier, J. N., “Theory of Elasticity”, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1951, pp 78-80
Extra Considerations
- This verification model was created and checked on 26 April 2020. Since this date, the plate solver and S3D software may have been further improved to achieved greater accuracy.
- Plates are not exact elements like beam and frame elements and therefore the mesh plays a huge role in the results. Always try to use a structured mesh when it is possible to do so.
- Results between software will never be exactly the same since different elements are used and the nature of plates are approximate


