Using the SkyCiv Load Generator for ASCE 7 Snow Load Calculations
To calculate the snow load pressures for a structure using SkyCiv Load Generator, the process is to define first the code reference. However, only users with a Professional Account or who purchased the standalone Load Generator module will be able to use this calculation. You can purchase the standalone module thru this link.
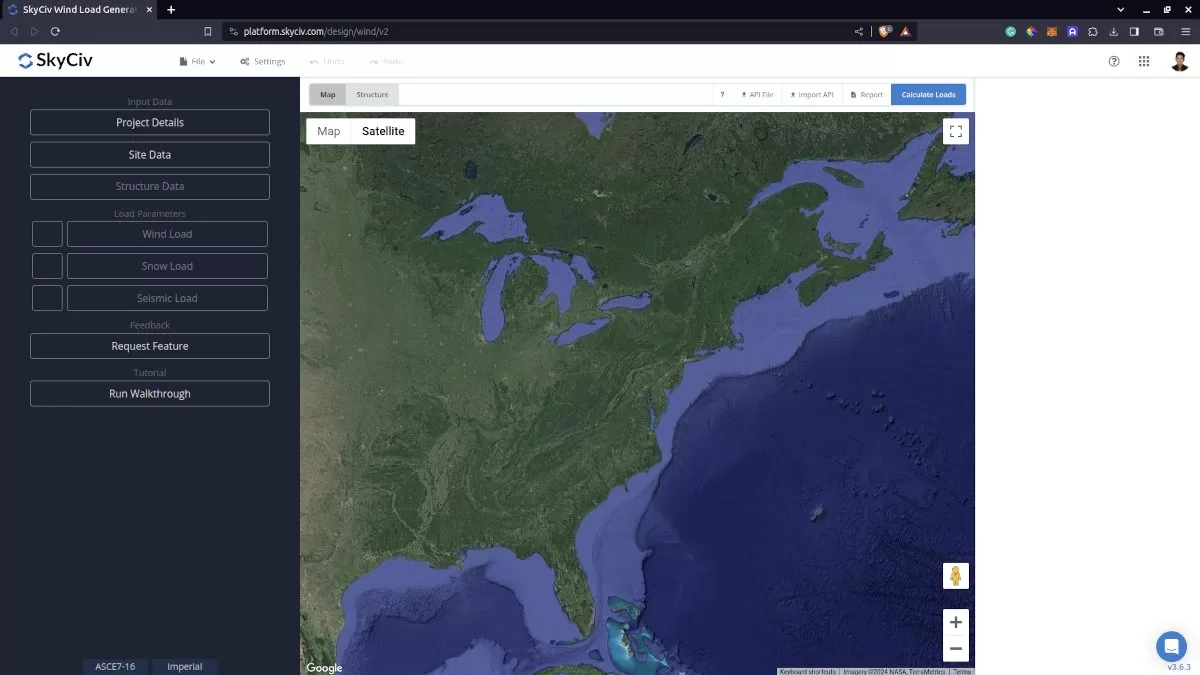
Figure 1. SkyCiv Load Generator UI
Site Data
Users can get the ground snow load by location from the SkyCiv snow map database. Using the ASCE 7-10 or ASCE 7-16, you just need to define the Risk Category of the structure and put the address located in the USA:
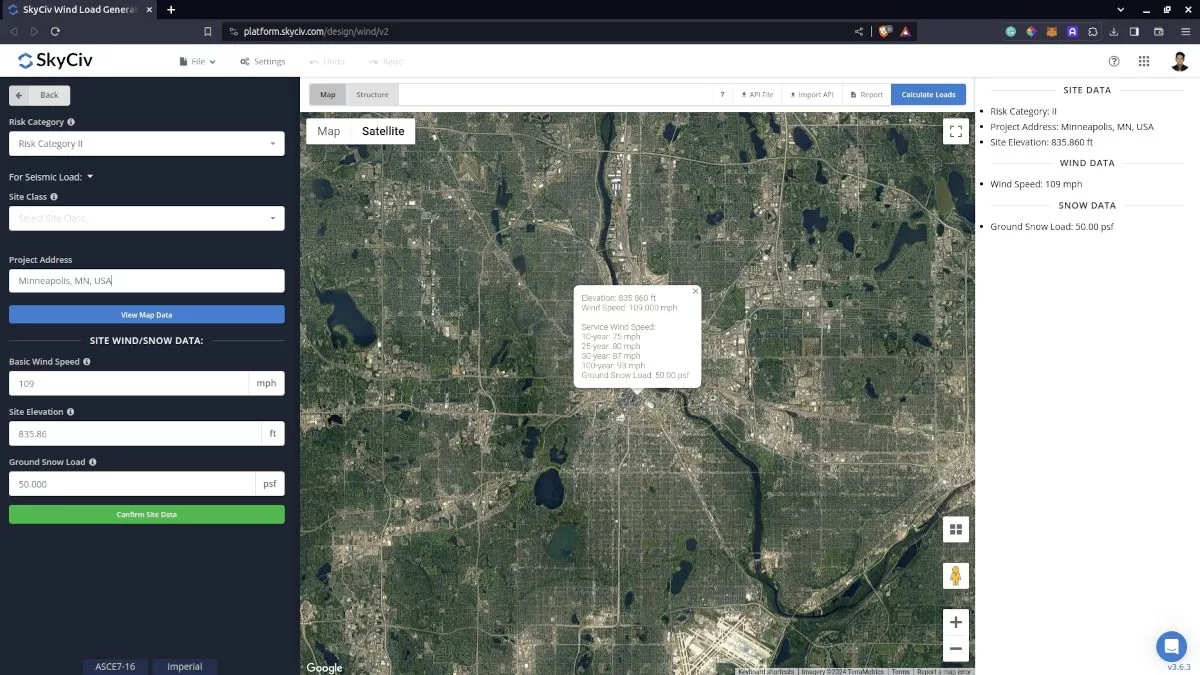
Figure 2. Site data of SkyCiv Load Generator
SkyCiv has digitalized the map as per the paperback standard. This means, you can simply enter in the site location and the software will automatically pull the ground snow load based on this input. There is a limit to how many times the ground snow load can be obtained on the free tool. The ground snow load values are derived from Section 7.2 of ASCE 7 utilizing the ground elevation of the structure taken from Google Maps API.
Site Input Parameters for Snow Load Calculation
Risk Category – Used in determining the ground snow load pg value
Project Address – Used for getting the nearest ground snow load based on the Risk Category selected
Ground Snow Load – the ground snow load to be used in calculating the design snow pressure. This is automatically determined based on Risk Category and Project Address and can be modified by the user
Once the parameters above are completed, we can click the “Confirm Site Data” to check if our input is okay (will change the font color of the button from white to green). After this, we can now proceed to the Structure Data section.
Structure Data
Next step is to define first the Structure you are analyzing. Currently, only Building structure is supported in ASCE 7.
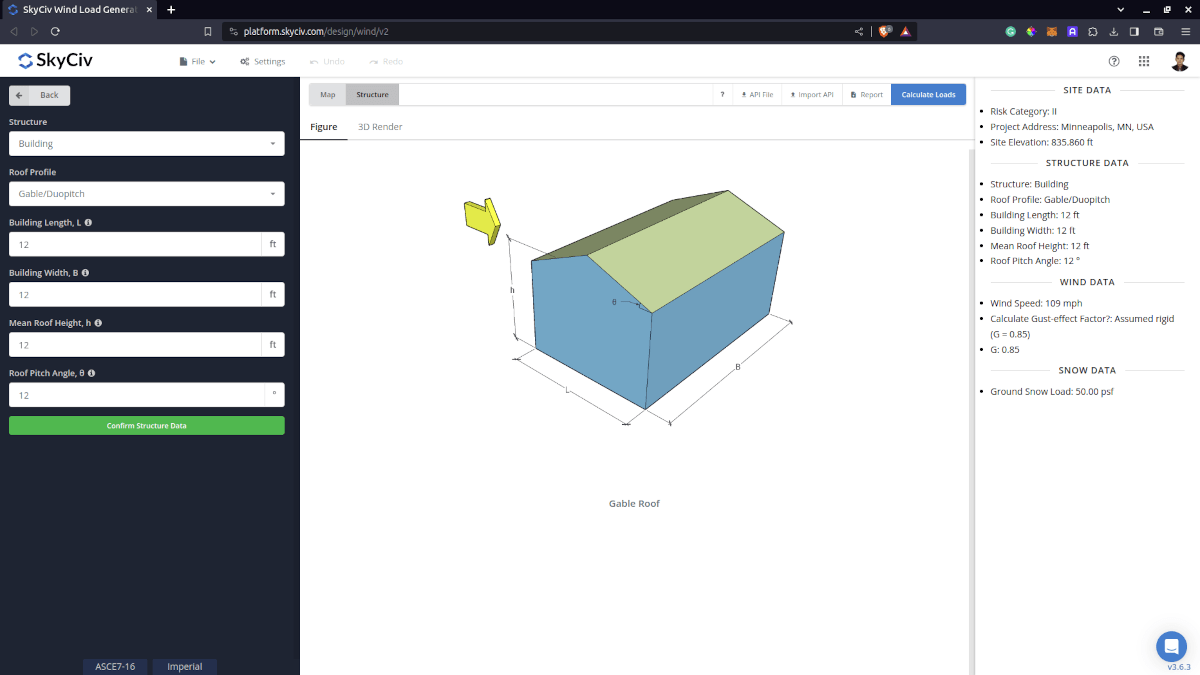
Figure 3. Structure data input for buildings.
Structure Input Parameters for Snow Load Calculation
Roof Profile – Used in pressure coefficient values based on the selected roof profile and roof pitch angle
Building Length – the dimension parallel to the wind direction as defined in ASCE 7. Used in calculation of pressure coefficients
Building Width – the dimension perpendicular to the wind direction as defined in ASCE 7. Used in calculation of pressure coefficients
Mean Roof Height – the dimension of the structure from ground to the middle height of the sloping roof. Used in calculation of velocity pressure
Roof Pitch Angle – the roof slope in degree. Used in calculation of pressure coefficients. Use our pitch roof calculator if you need to determine this.
Once the parameters above are completed and validated (clicking Confirm Structure Data), we can now proceed to the Snow Load Parameters section.
Snow Data
To proceed with our snow load calculation, we need to check the checkbox first beside the Snow Load button. By default, this is checked when the site snow data has been defined.
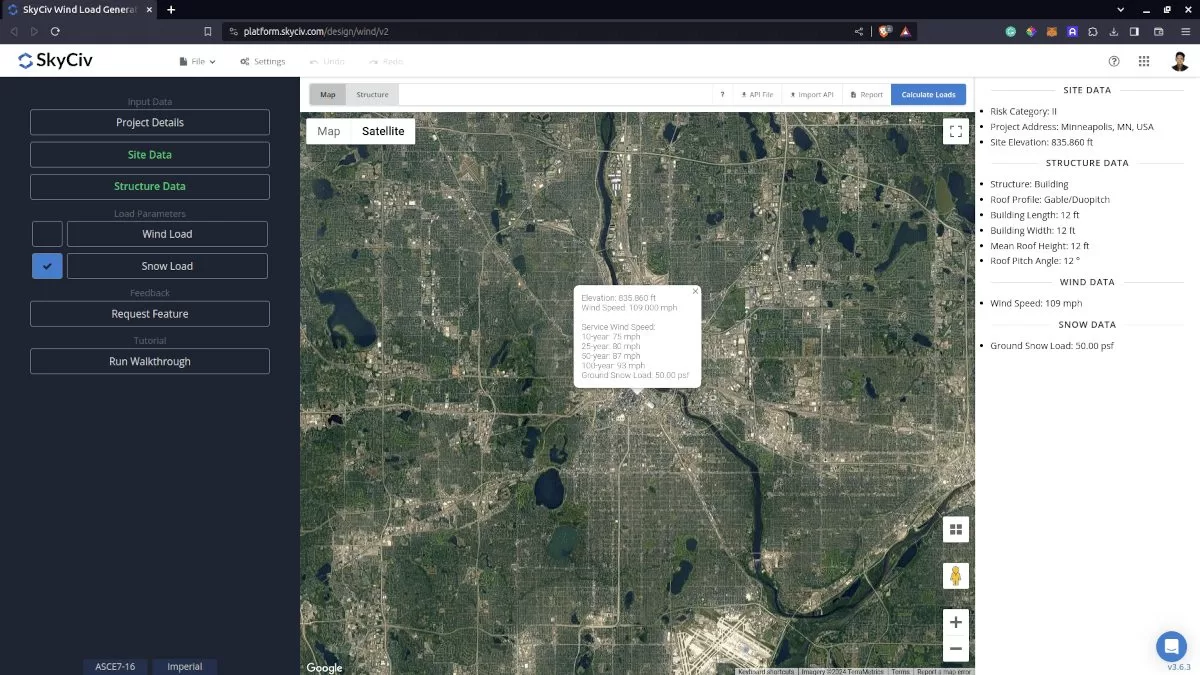
Figure 4. Checkbox for Snow Load Data.
Snow Input Parameters
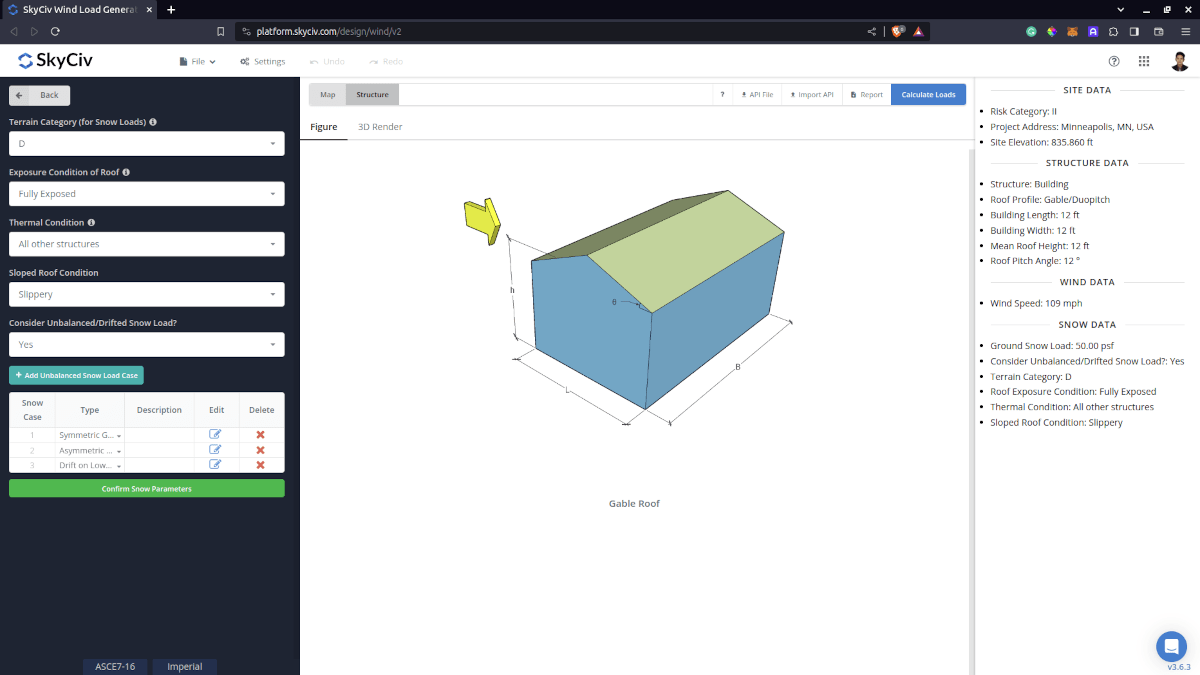
Figure 5. Snow Load Input Parameters.
Terrain Category for Snow Loads
This parameter is used in calculating Exposure Factor, Ce. Options for this factor are the following:
- B, C, or D (from Section 26.7 of ASCE 7)
- Above the treeline in windswept mountainous areas
- In Alaska, in areas where trees do not exist within a 2-mile (3-km) radius of the site
Exposure Condition of Roof
Like the Terrain Category for Snow Loads, this parameter is also used in calculating Exposure Factor, Ce. The option for this selection and their corresponding definition from ASCE 7 are the following:
- Sheltered: “Roofs located tight in among conifers that qualify as obstructions. Obstructions within a distance of 10 x height of the obstruction above the roof level provide shelter.”
- Fully Exposed: “Roofs exposed on all sides with no shelter afforded by terrain, higher structures, or trees. Roofs that contain several large pieces of mechanical equipment, parapets that extend above the height of the balanced snow load (hb), or other obstructions are not in this category. If the only obstructions are a few deciduous trees that are leafless in winter, the “fully exposed” category shall be used.”
- Partially Exposed: “All roofs except as indicated above.”
Thermal Condition
This parameter is used in getting the Thermal Factor, Ct. The options for this are the following:
- Structures kept just above freezing and others with cold, ventilated roofs in which the thermal resistance (R-value) between the ventilated space and the heated space exceeds 25 °F × h × ft2/Btu (4.4 K × m2/W)
- Unheated and open-air structures
- Structures intentionally kept below freezing
- Continuously heated greenhouses with a roof having a thermal resistance (R-value) less than 2.0 °F × h × ft2/Btu (0.4 K × m2/W)
- All other structures
Sloped Roof Condition
This parameter is used in getting the Roof Slope Factor, Cs. This parameter has two options: “Slippery” and “Other cases.”
Consider Unbalanced/Drifted Snow Load Case?
This parameter is a “Yes” or “No” to calculate for Unbalanced Snow Load Case. Upon selecting “No,” the balanced snow load case shall only be calculated. On the other hand, upon selecting “Yes,” the unbalanced snow load case table will show. There are three options for ASCE 7:
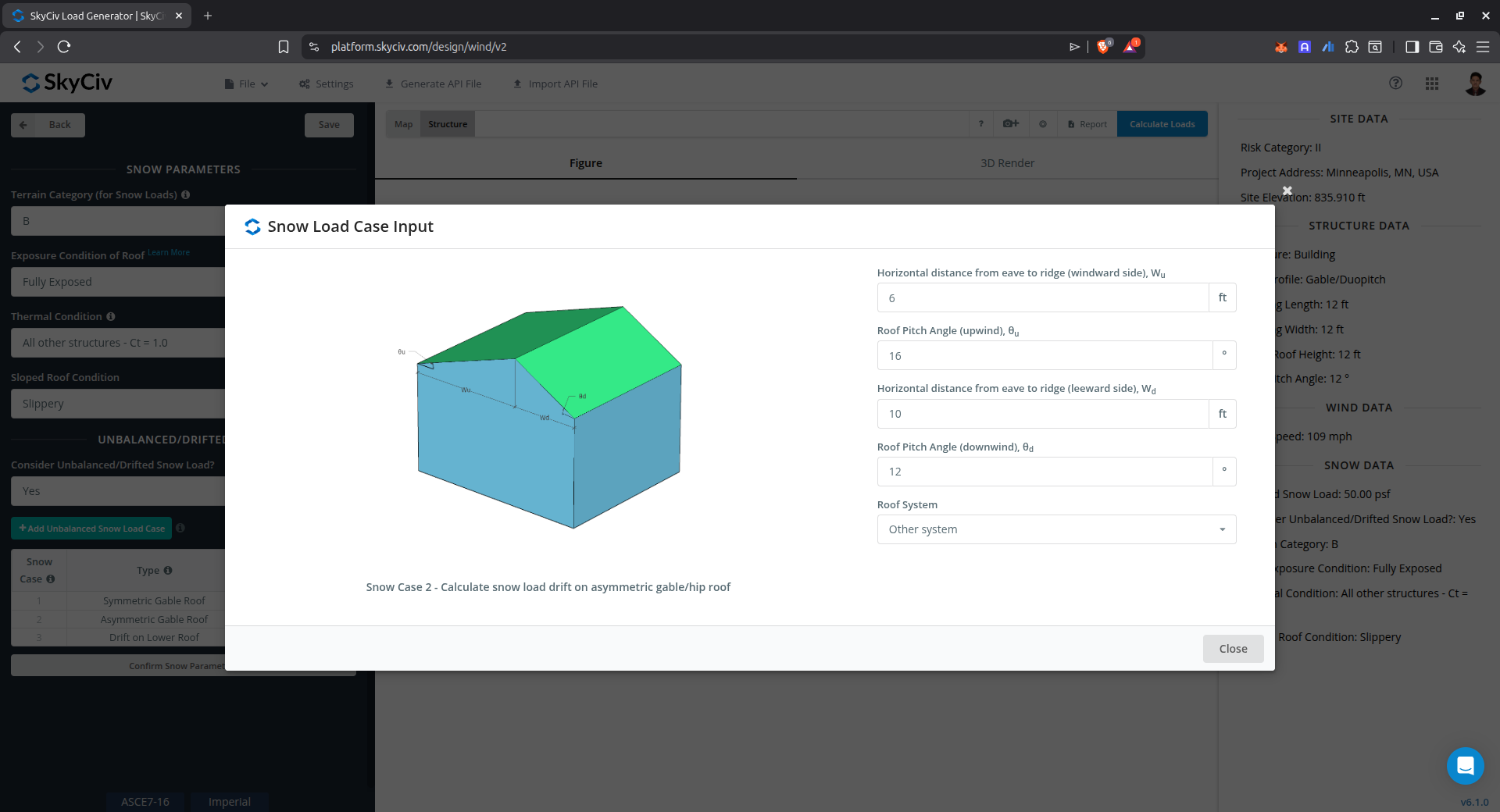
Snow Load Drift on Symmetric Gable Roof
This case is used to calculate the snow load drift on a symmetric gable roof.
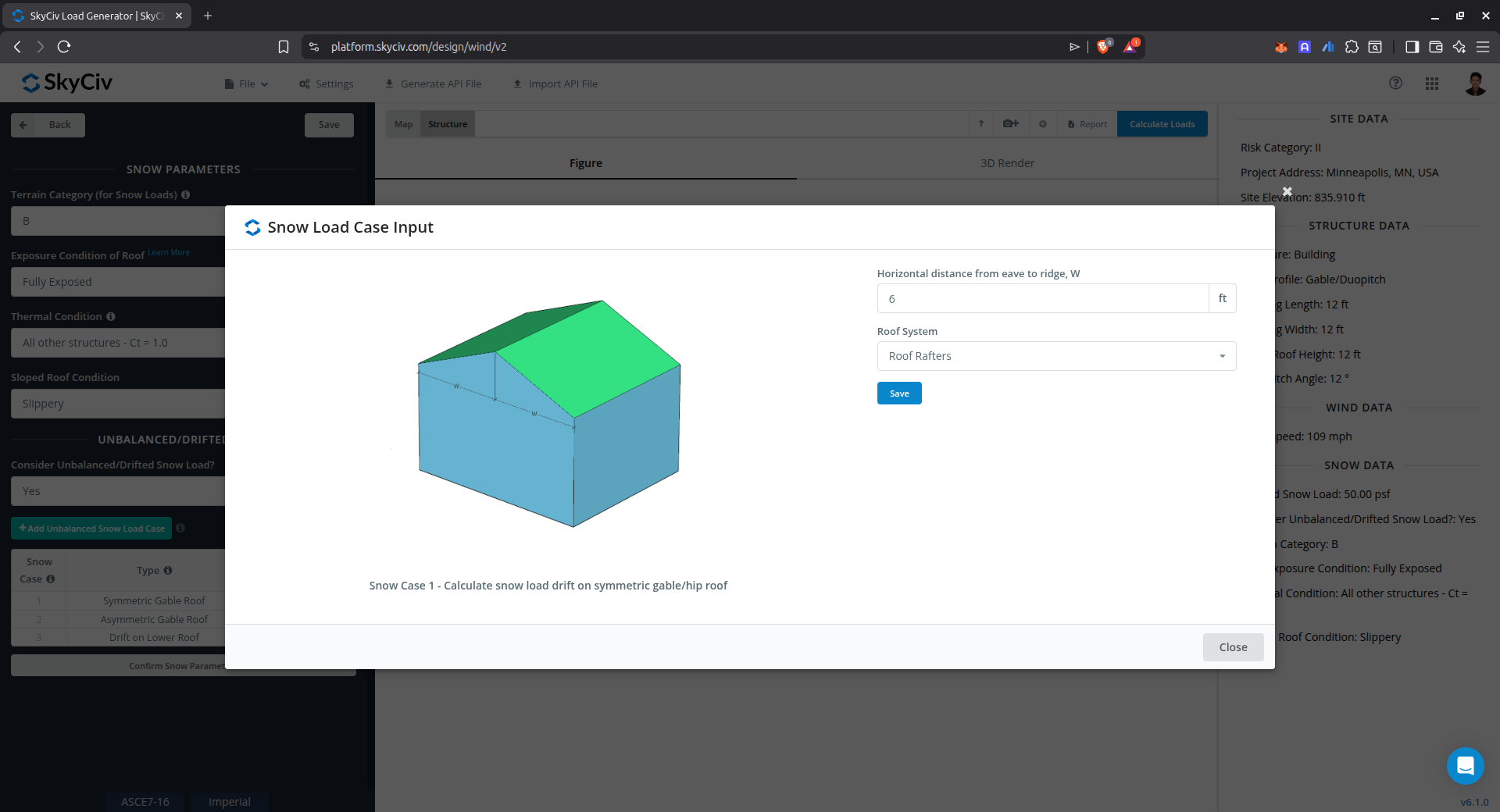
Snow Load Drift on Asymmetric Gable Roof
This case is used to calculate the snow load drift on an asymmetric gable roof as shown below.
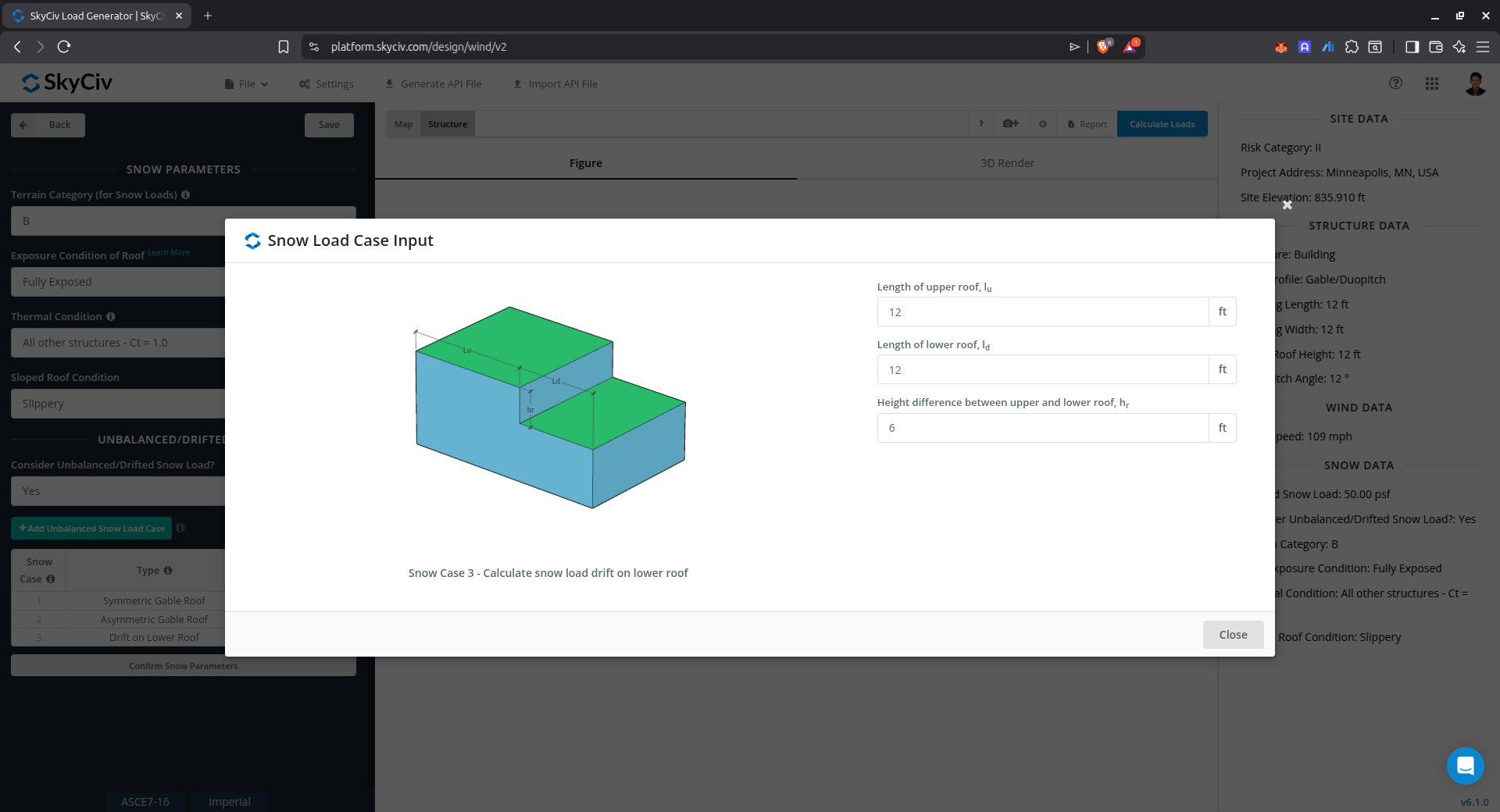
Snow Load Drift on Lower Roof
This case is used to calculate the snow load drift on the lower roof levels and can also be used in obtaining drift on parapet walls for windward and leeward cases.
After all these parameters are defined, the next step is to click the Calculate Loads on the upper right side of the UI.
Results
The snow load results will show the parameters in calculating the balanced snow load as shown below. The summarized results are shown on the right side of the screen. Other results are shown on the detailed report.
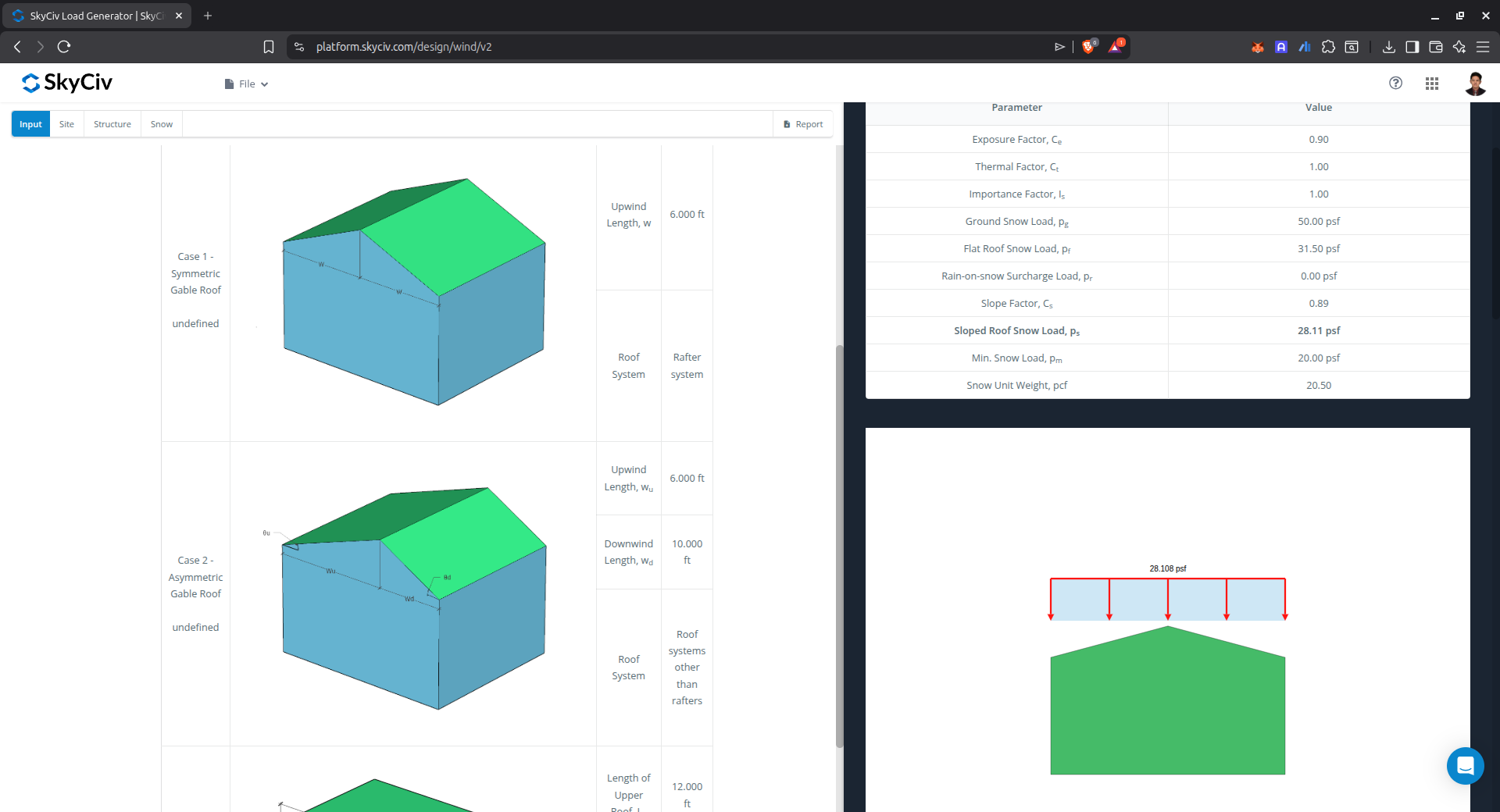
Figure 9. Snow load parameters that are used in the calculation and the calculated balanced snow load.
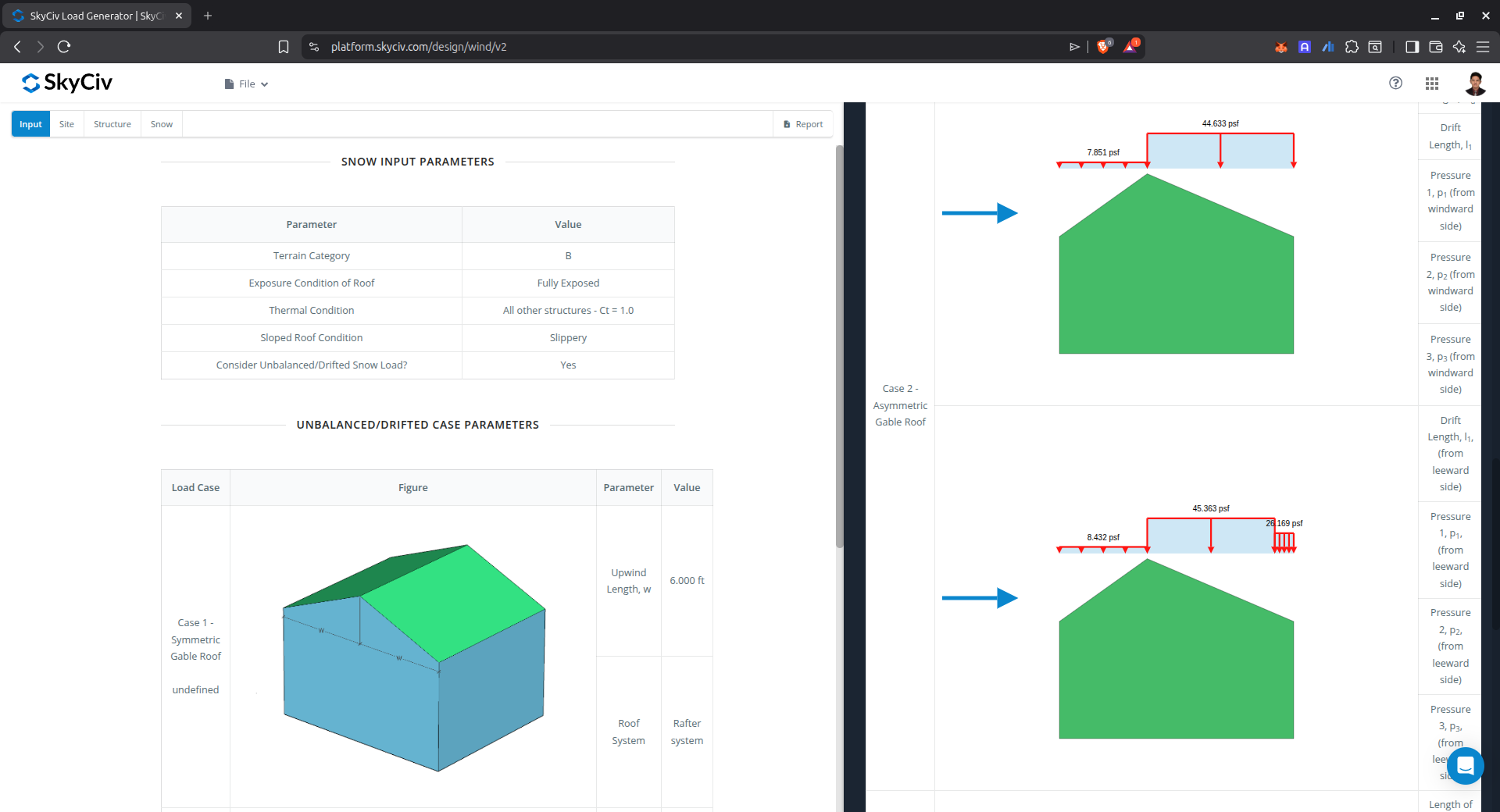
Figure 10. Unbalanced snow load results.
Detailed Calculation
The detailed snow load calculations can be accessed only by Professional account users and those who purchased the standalone load generator module. All the parameters and assumptions used in the calculation are displayed on the report to make it transparent to the user. You can download a sample detailed calculation thru the following links:
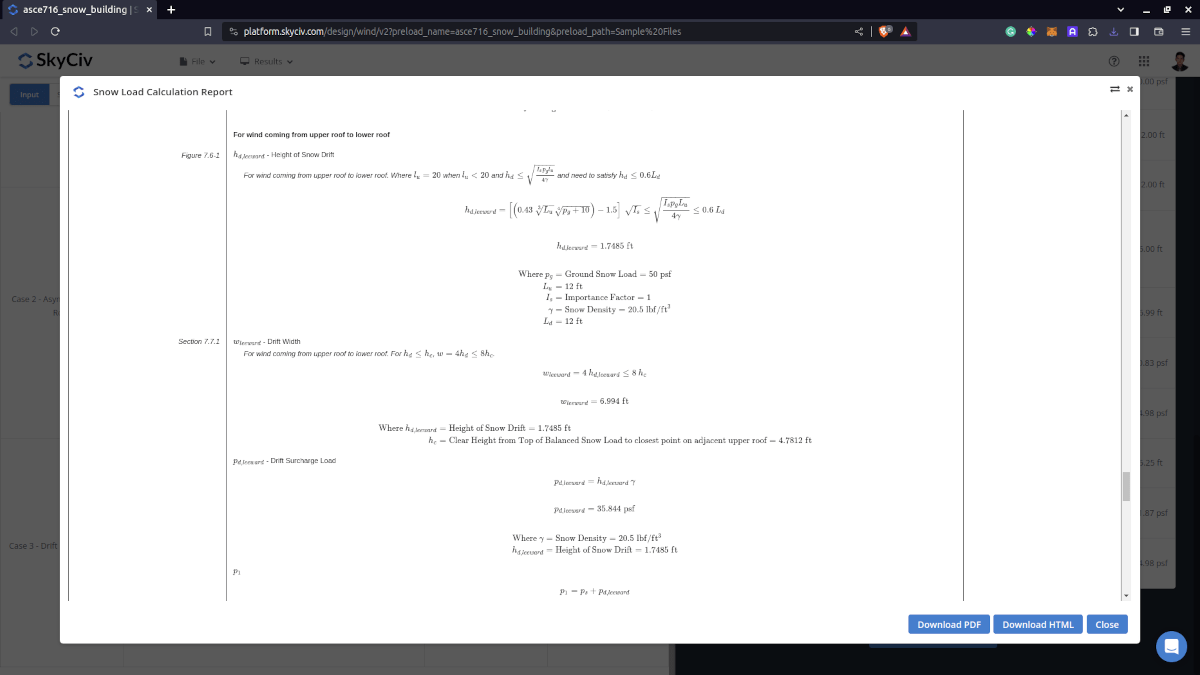
For additional resources, you can use these links for reference:


