標識の風荷重計算の完全に機能した例 ENを使用して 1991-1-4
記事上で, EN を使用して看板の風荷重を計算する方法について説明します。 1991-1-4 オックスフォードシャーにある, イギリス. 私たちのリファレンスはENになります。 1991-1-4 構造物に対するアクション (風荷重) とBSEN 1991-1-4 国別館. 同様のデータを以下でも使用します。 に 1991-1-4 風荷重計算の例.
SkyCivは、いくつかのパラメーターを使用して風速計算を自動化します. 私たちを試してみてください 看板風荷重計算機:
構造データ
この例では, 以下のデータを使用します. のみ検討させていただきます 風源方向が 240°に等しい. しかも, の 敷地の標高は57.35mです。.
テーブル 1. 当社の風荷重計算に必要な看板データ.
| ロケーション | オックスフォードシャー, 英国 |
| 占有 | 雑多 – 看板 |
| 地形 | フラット農地 |
| 記号の水平寸法, b | 12.0 メートル |
| 記号 横 縦, h |
12.0 メートル |
| 地面から看板の上部まで, H |
50.0メートル |
| 地面から看板の重心まで, とe |
44.0 メートル |
| 看板Aの基準エリア符号 |
144.0 平方メートル. |
| 極径, d |
1.0 メートル |
| 極面タイプ |
鋳鉄 |
| 地面からポールの上部まで, とg |
38.0 メートル |
| 極Aの基準領域ポール |
38.0 メートル |
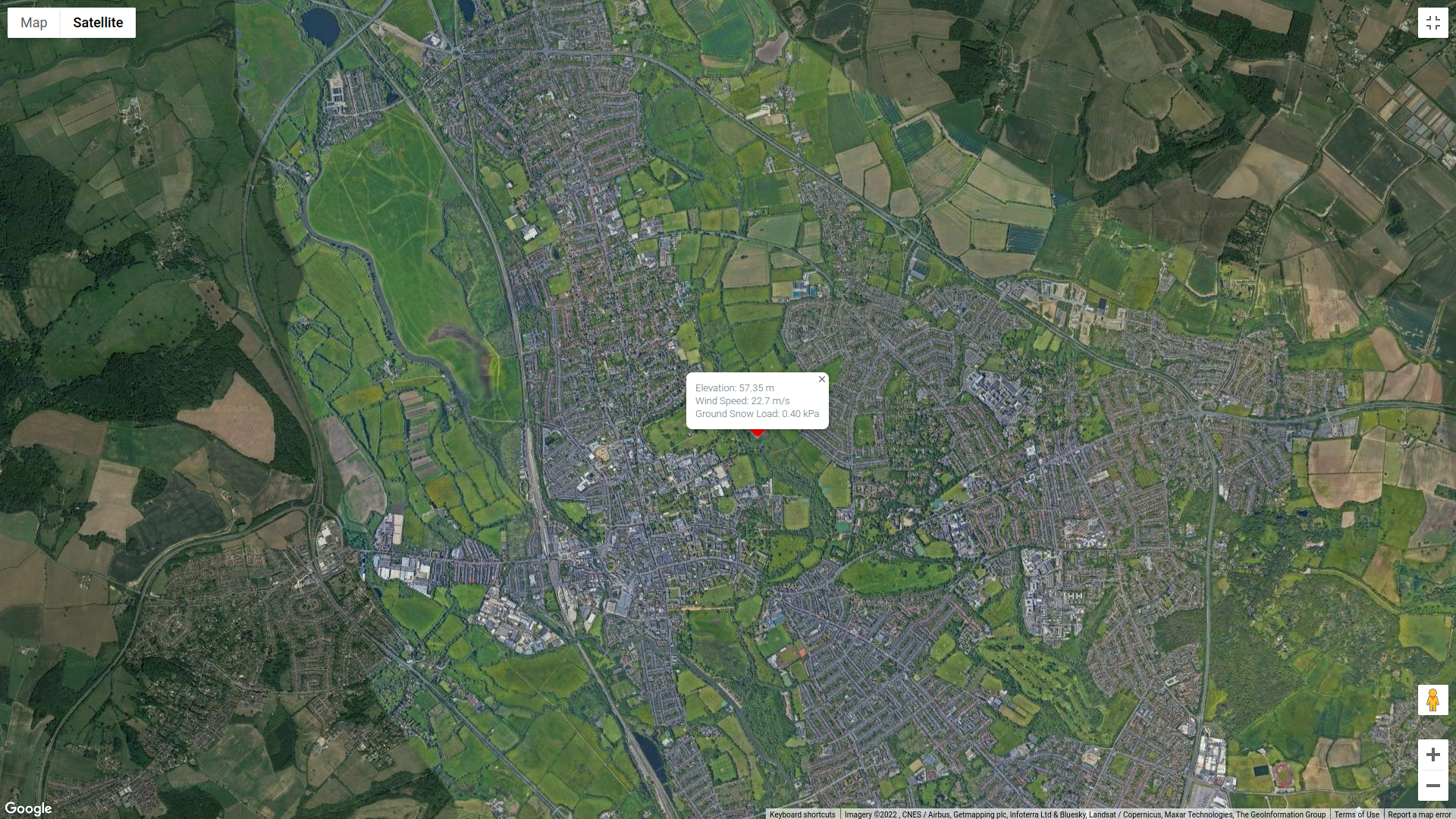
図 1. 立地 (Googleマップから).

図 2. 看板寸法.
設計風圧を決定する式は次のとおりです。:
基本風速用:
\({v}_{b} = {c}_{あなたへ} {c}_{シーズン} {c}_{代替} {v}_{b,地図}\) (1)
どこ:
\({v}_{b}\) =基本風速(m / s)
\({c}_{あなたへ}\) = 方向係数
\({c}_{シーズン}\)=季節要因
\({c}_{代替}\)= 高度係数:
\({c}_{代替} = 1 + 0.001あ \) ために \( z ≤ 10 \) (2)
\({c}_{代替} = 1 + 0.001あ ({10/と}^{0.2}) \) ために \( と > 10 \) (3)
\({v}_{b,地図}\) = BS EN の図 NA.1 に示されている基本風速の基本値 1991-1-4 国別館
\( あ \) = 平均海抜からのメートル単位のサイトの高度
基本速度圧力用:
\({q}_{b} = 0.5 {⍴}_{空気} {{v}_{b}}^{2} \) (4)
どこ:
\({q}_{b}\) = Paでの設計風圧
\({⍴}_{空気}\) = 空気の密度 (1.226kg /立方メートル)
\({v}_{b}\)=基本風速(m / s)
ピーク圧力用:
\({q}_{p}(と) = 0.5 {c}_{e}(と){q}_{b} \) カントリー地形のサイト用 (5)
\({q}_{p}(と) = 0.5 {c}_{e}(と){c}_{e,T}{q}_{b} \) 町の地形のサイト用 (6)
どこ:
\({c}_{e}(と)\) = 露出係数
\({c}_{e,T} \) = 街の地形の露出補正係数
看板・ポールにかかる風力を計算するには:
\({F}_{w} = {c}_{s}{c}_{d}{c}_{f}{q}_{p}({と}_{e}){あ}_{参照} \) (7)
どこ:
\( {c}_{s} {c}_{d} \) = 構造的要因
\({c}_{f} \) = 構造の力係数
\({q}_{p}({と}_{e}) \) = 基準高さにおけるピーク速度圧力 \({と}_{e} \)
\({あ}_{参照} = b h) = 構造の参照領域
地形カテゴリ
BS ENに基づく 1991-1-4 国別館, 英語の地形カテゴリ 1991-1-14 に集約されました 3 カテゴリ: 地形カテゴリー 0 海と呼ばれます; 地形カテゴリー I および II は田舎の地形として考慮されています。, 地形カテゴリ III および IV は町の地形として考慮されています.
240°からの風を考慮, 風上地形の地形カテゴリは次のように分類できます。 街の地形.
方向性と季節性の要因, \({c}_{あなたへ}\) & \({c}_{シーズン}\)
方程式を計算するには (1), 方向と季節要因を決定する必要があります, \({c}_{あなたへ}\) & \({c}_{シーズン}\). BS ENの表NA.1より 1991-1-4 国別館, 風源方向が240°なので, 方向係数の対応する値, \({c}_{あなたへ}\), に等しい 1.0.
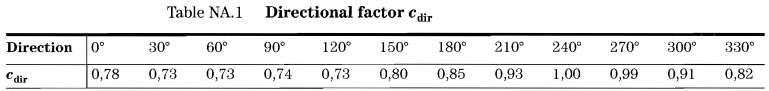
一方, 季節要因に関して保守的なケースを検討したいと思います, \({c}_{シーズン}\), 私たちはそうします に設定 1.0.
高度係数 \({c}_{代替}\)
高度係数については, \({c}_{代替}\), 式のみを使用します (2) サイト標高を使用したより保守的なアプローチ \( あ \) 57.35mに等しい. したがって:
\({c}_{代替} = 1 + 0.001(57.35) = 1.05735\)
基本的な風速と風圧, \({v}_{b}\) & \({q}_{b}\)
英国の風速マップは、BS EN の国家付録の図 NA.1 から取得できます。 1991-1-4.
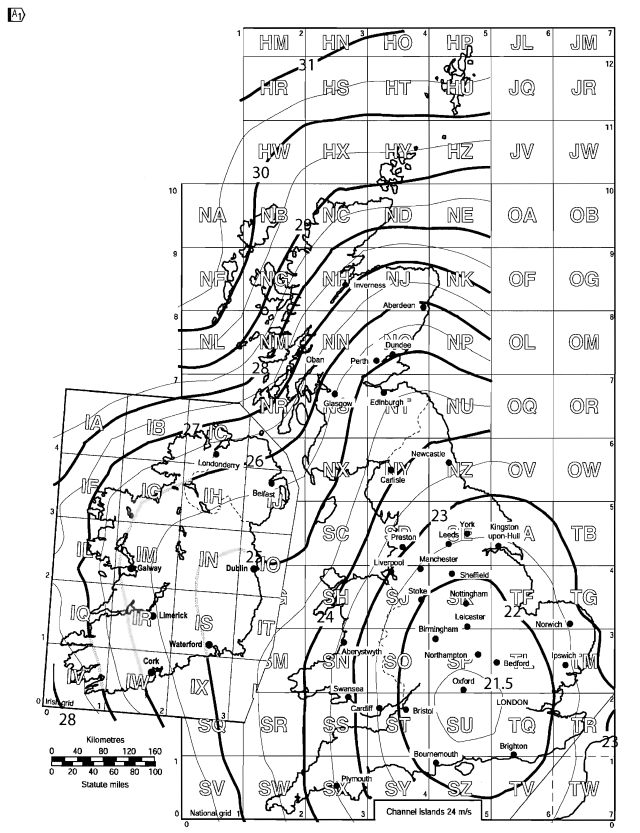
図 5. BS EN の図 NA.1 に基づく英国の基本風速 1991-1-4 国別館.
当サイトの場所について, オックスフォードシャー, イングランド, 計算された \( {v}_{b,地図} \) に等しい 22.7 MS.
\( {v}_{b} = {c}_{あなたへ} {c}_{シーズン} {c}_{代替} {v}_{b,地図} = (1.0)(1.0)(1.05735)(22.7) \)
\( {v}_{b} = 24.0 MS \)
基本風圧を計算できます, \( {q}_{b,0} \), 方程式を使用して (4):
\( {q}_{b} = 0.5(1.226)({24}^{2}) = 353.09 上手 \)
SkyCivが風域の検出を自動化し、わずかな入力で対応する風速値を取得. 私たちを試してみてください SkyCiv Free Wind Tool
地形学的要因 \({c}_{の}(と)\)
この構造の場合, 地形は比較的平らで、240°からの風が吹く, の
高度係数, \({c}_{代替}\), 式のみを使用します (2) サイト標高を使用したより保守的なアプローチ \( あ \) 57.35mに等しい. したがって:
最高速度圧力, \({q}_{p}(と)\)
私たちの構造にとって, 地形カテゴリはタウン地形に分類されるため, ピークも同様, ピーク速度圧力, \({q}_{p}(と)\), 方程式を使用して解くことができます (6):
\({q}_{p}(と) = {c}_{e}(と){c}_{e,T}{q}_{b} \)
どこ:
\({c}_{e}(と)\) = BS EN の図 NA.7 に基づく暴露係数 1991-1-4 国別館
\({c}_{e,T} \) = BS EN の図 NA.8 に基づく街の地形の露出補正係数 1991-1-4 国別館
暴露係数を決定するには, \({c}_{e}(と)\) , 看板用に, 私たちは計算する必要があります \(と – {h}_{ディス}\) 風上から海岸線までの距離 (km). 簡単にするために, 変位高さを設定します, \({h}_{ディス}\), に 0. のために \(と \) 値, 検討させていただきます \(z = 38.0\) そして \(z = 44.0\). しかも, 風上から海岸線までの距離は100km以上. したがって, BS ENの図NA.7を使用 1991-1-4 国別館:
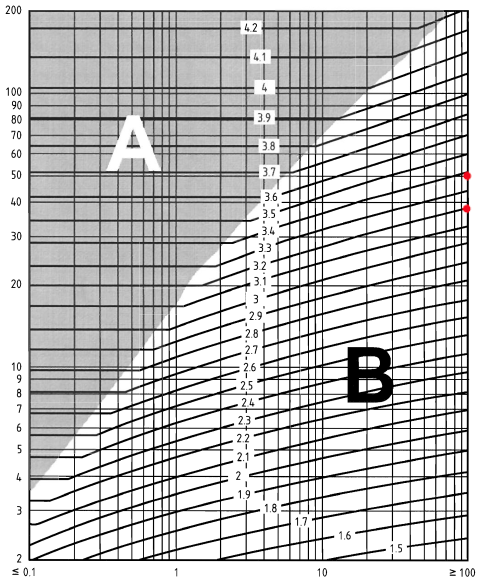
図 6. BS ENの図NA.7 1991-1-4 国別館.
したがって:
\({c}_{e}(38.0) = 3.2\)
\({c}_{e}(44.0) = 3.3\)
一方, 露出補正係数 \( {c}_{e,T} \) 看板の場合はBS ENの図NA.8から決定できます。 1991-1-4 国別館. 1kmに相当する町の地形内の距離を使用, 露出補正係数を取得できます \( {c}_{e,T} \):
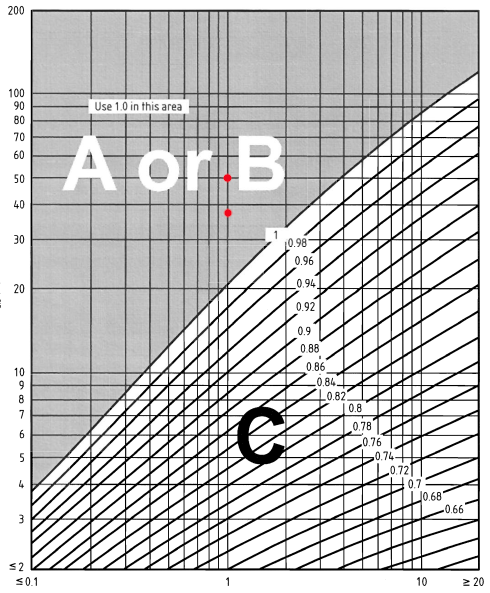
図 7. BS ENの図NA.8 1991-1-4 国別館.
したがって:
\({c}_{e,T}(38.0) = 1.0\)
\({c}_{e,T}(44.0) = 1.0\)
上記の値を使用する, ピーク速度圧力を計算できます, \({q}_{p}(と)\), ために \(z = 38.0\) そして \(z = 50.0\):
\({q}_{p}(44.0) = (3.3)(1.0)(353.09) = 1165.20 上手 \)
\({q}_{p}(38.0) = (3.2)(1.0)(353.09) = 1129.89 上手 \)
構造的要因, \( {c}_{s}{c}_{d} \)
弊社の看板用に, 構造因子には簡略化した値を使用します, \({c}_{s}{c}_{d}\), に等しくなる 1.0 セクションに基づく 6 または 1991-1-4.
力係数, \( {c}_{f}\), 看板用
看板用, 力係数, \({c}_{f}\), に等しい 1.8 セクションに基づく 7.4.3 または 1991-1-4.
風力, \( {F}_{w,看板} \), 看板を演じる
看板に働く力は次の式で計算できます。 (7) セクションに基づく 5.3(2) または 1991-1-4.
\({F}_{w,看板} = {c}_{s}{c}_{d}{c}_{f}{q}_{p}({と}_{e}){あ}_{参照,看板} = (1.0)(1.8)(1165.20上手)(12.0メートル)(12.0メートル)\)
\({F}_{w,看板} = 302019.84 N)
なお、看板の重心に作用する風力の水平離心率は3.0mが推奨されています。.
風力計算はすべて、EN 用 SkyCiv Load Generator を使用して実行できます。 1991 (看板とポールの風荷重計算機). ユーザーはサイトの場所を入力して、風速と地形データを取得できます, ソーラー パネルのパラメータを入力し、設計風圧を生成します. スタンドアローン版で, このプロセスを合理化し、看板やポールの詳細な風荷重計算レポートを取得できます。!
風力, \( {F}_{w,ポール} \), ポールに作用する
同様に, ポールに作用する力は、次の式を使用して計算できます。 (7) セクションに基づく 5.3(2) または 1991-1-4.
\({F}_{w,ポール} = {c}_{s}{c}_{d}{c}_{f}{q}_{p}({と}_{g}){あ}_{参照,ポール}\) (8)
どこ:
\({c}_{f} = {c}_{f,0}{ψ}_{λ} \)
\({あ}_{参照,ポール} = {と}_{g}d \)
注意:
\(ψ_{λ} \) 実効細さに基づいて計算されます, \( λ \), 使用する 図 7.36 セクションの 7.13 または 1991-1-4
\({c}_{f,0}\) レイノルズ数に基づいて計算されます \( R_{e} \) =建物またはその他の構造物の場所での地面からの高さ 7.28 または 1991-1-4
どこ:
\( {と}_{g} \) 地面からのポールの高さ (m)
\( d \) ポールの直径はメートルです
\( n = 0.000015 平方メートル/秒 \) 空気の動粘度です
\( v({と}_{g}) = (2{q}_{p}({と}_{g})/r)^{0.5} \) (9)
\( {R}_{e} = v(z_{g})d/n \) (10)
次のセクションでこれらのパラメータについて詳しく説明します
レイノルズ数, \( {R}_{e} \), ポール用
上記の計算値を使用する, 計算できます \( v({と}_{g}) \) 式を使用する (9):
\( v({と}_{g}) = (2{q}_{p}({と}_{g})/r)^{0.5} = (2(1129.89)/(1.226))^{0.5} \)
\( v({と}_{g}) = 42.93 MS)
したがって, レイノルズ数 \( R_{e} \) ポール用, 式を使用する (10) です:
\( {R}_{e} = v({と}_{g})d/ν = (42.93)(1.0)/(0.000015) \)
\( {R}_{e} = 2862000 \)
力係数, \( {c}_{f0} \), フリーエンドフローなし
使用したポールの材質は鋳鉄です。 同等の表面粗さ \( k \) に等しい 0.2 テーブルに基づく 7.13 または 1991-1-4.
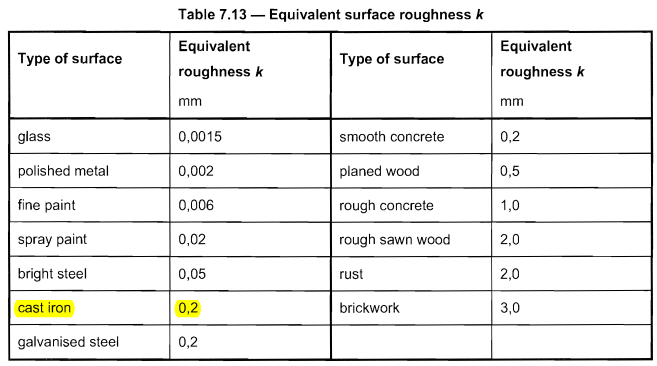
図 8. テーブル 7.13 または 1991-1-4 同等の粗さの場合 \( k \).
力係数 \( {c}_{f0} \) 図の式を使用して決定できます 7.28 英語の 1991-1-4 と \( k/d = 0.2\):
\( {c}_{f0}= 1.2 + {0.18ログ(10 K D)}/{1 + 0.4ログ({R}_{e}/{10}^{6}} = 1.2 + {0.18ログ(10 (0.2)}/{1 + 0.4ログ((2862000)/{10}^{6}}\)
\( {c}_{f0} = 1.246 \)
効果的な細さ, \( λ \)
効果的な細さ, \( λ \), ポールの場合はNo.4表から決定できます。 7.16 または 1991-1-4.
\( λ = 最大(0.7 {と}_{g}/d, 70) \) ために \( {と}_{g} \) > 50メートル
\( λ = 最大({と}_{g}/d, 70) \) ために \( {と}_{g} \) < 15メートル
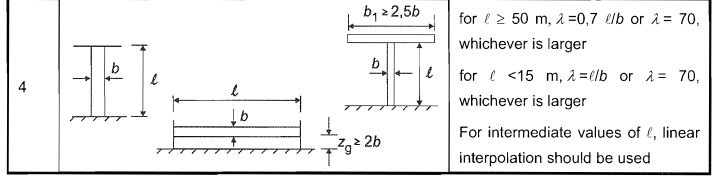
図 9. テーブル 7.16 または 1991-1-4 実効細さの計算用 \( λ \).
以来 \( {と}_{g} \) 38.0mに等しい, の値を補間する必要があります \( λ \) 50m用と15m用:
\( {と}_{g} = 38\)
\( {λ}_{50メートル} = 最大(0.7 (38), 70) = 70 \)
\( {λ}_{15メートル} = 最大((38), 70) = 70 \)
したがって:
\( λ = 70 \)
最終影響係数, \( {ψ}_{λ} \)
最終影響係数, \( {ψ}_{λ} \), 図を使用して取得できます 7.36 または 1991-1-4 固さ比が必要 \( ファイ \) 効果的な細さ \( λ \). 固さ比を仮定します \( ファイ \) に等しい 1.0 パイプ柱には穴が開いていないため、.
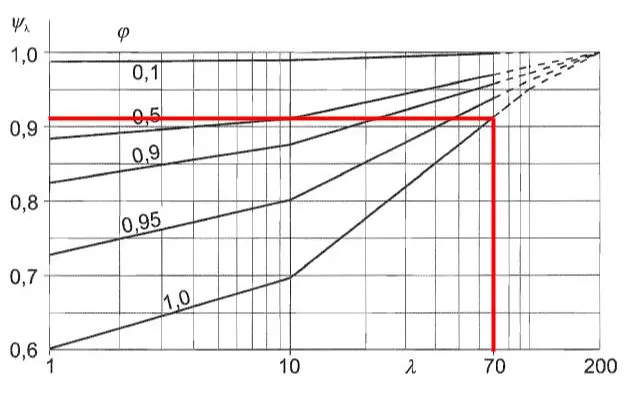
図 10. 対応する最終効果係数 \( {ψ}_{λ} \) 図に基づく看板を支えるポール用 7.36 または 1991-1-4.
図から 10, 最終効果要因は次のとおりであると推測できます。 \( {ψ}_{λ} \) 極は次と等しいため 0.910.
上記の計算されたパラメータから,すでに計算できます 風力, \( {F}_{w,ポール} \):
\({c}_{f} = {c}_{f,0}{ψ}_{λ} = (1.246)(0.910) = 1.134\)
\({F}_{w,ポール} = {c}_{s}{c}_{d}{c}_{f}{q}_{p}({と}_{e}){あ}_{参照,ポール} = (1.0)(1.134)(1129.89)(38.0×1.0) \)
\({F}_{w,ポール} = 48689.22 N \)
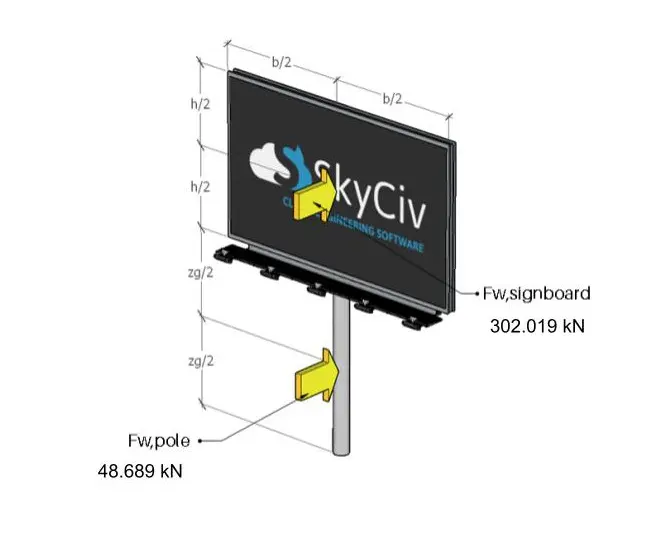
図 11. 看板やポールに働く風力.
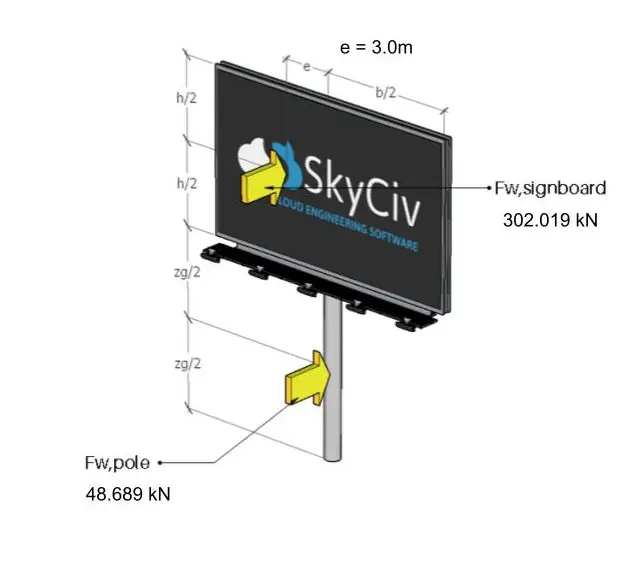
図 12. 偏心ケースの看板・ポールに作用する風力.
SkyCiv Load Generator
地上高として, 数回クリックして入力するだけで、看板やポールの風荷重を取得できます. スタンドアロン版を購入するか、Professional アカウントにサインアップする場合, 看板プロジェクトの詳細な風レポートを生成できるようになります。!
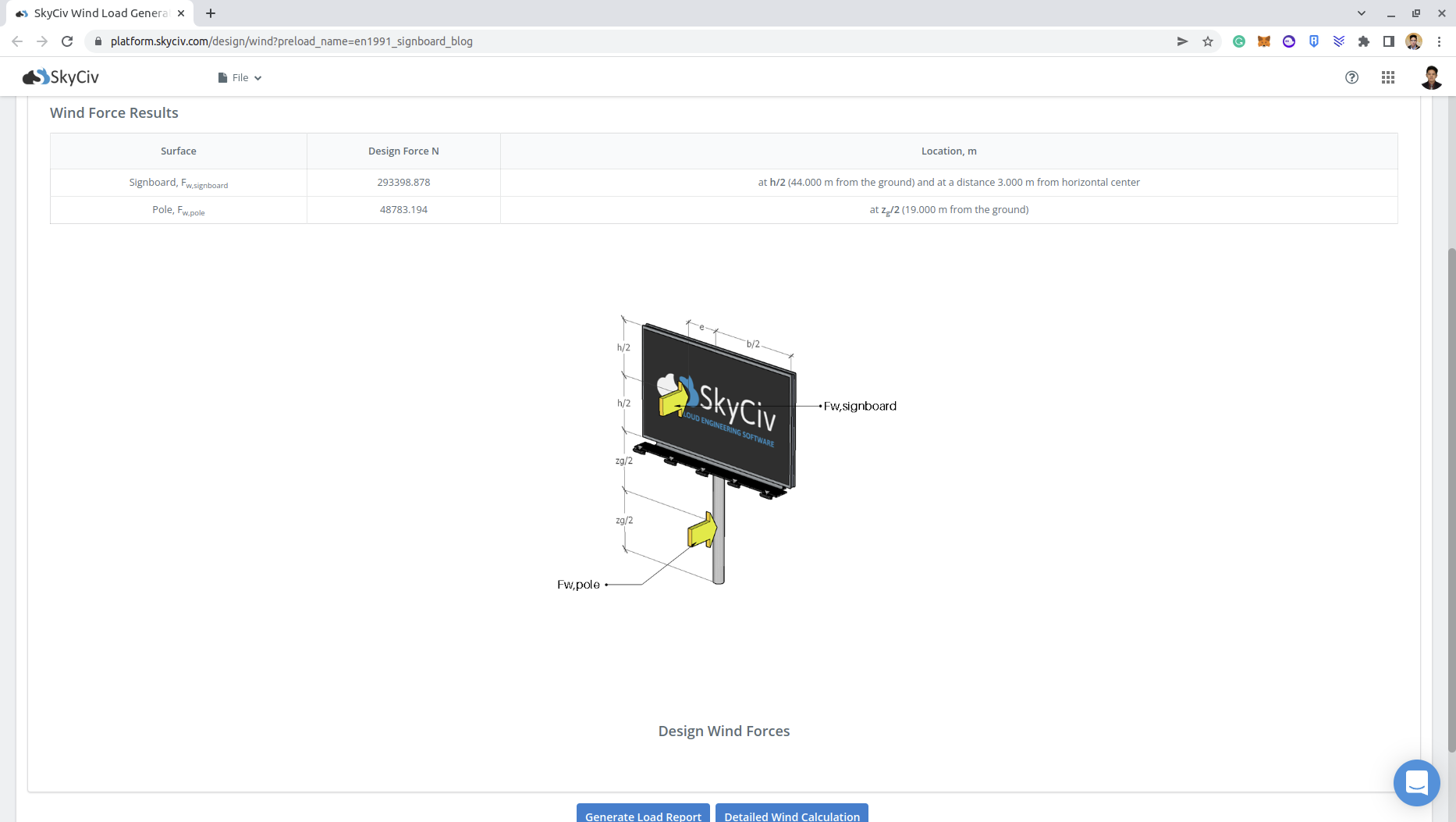
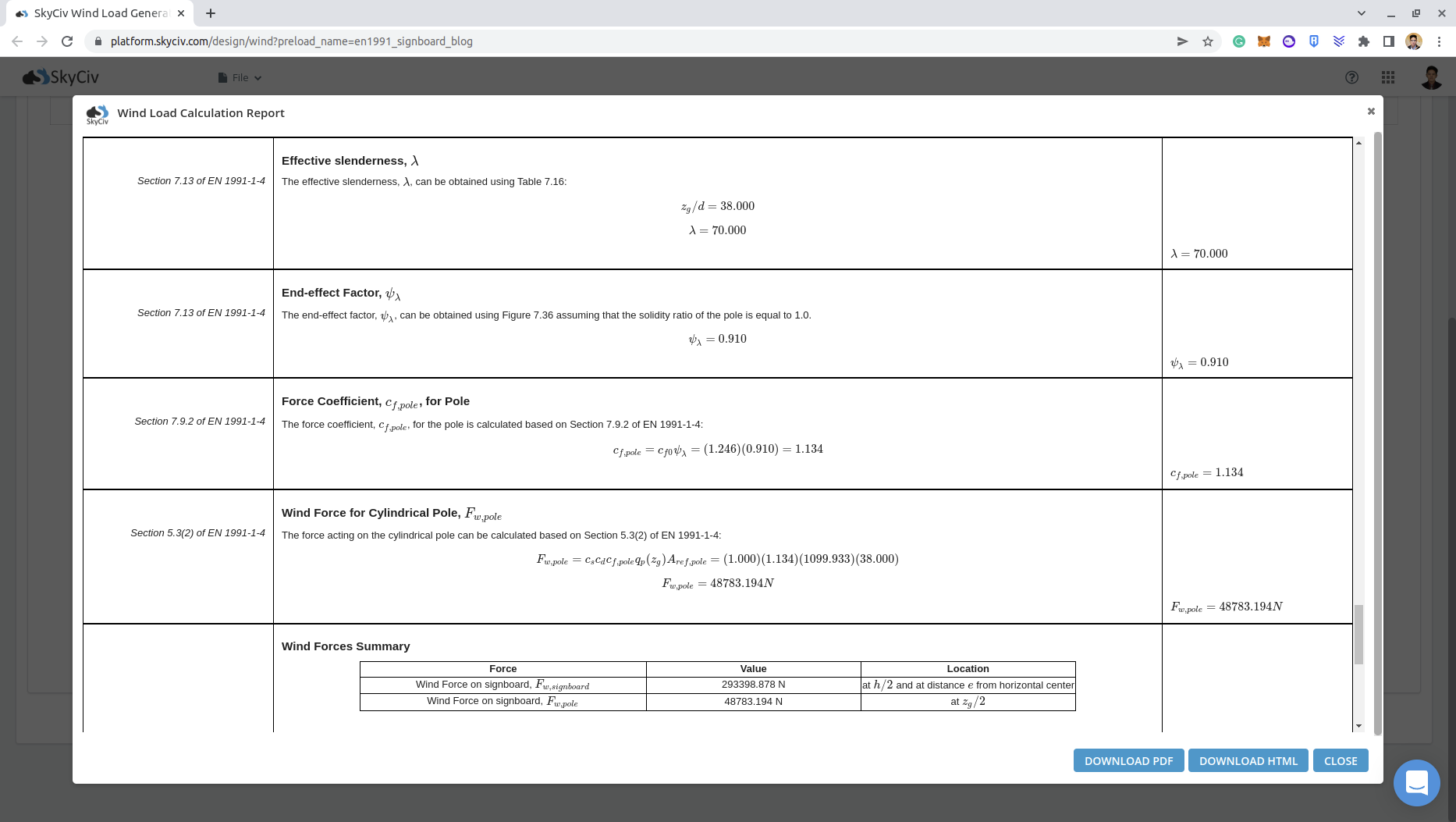
これらのリンクから看板の詳細な風荷重レポートを確認できます。:
構造エンジニア, 製品開発
MS土木工学
参考文献:
- に, B. (2005). ユーロコード 1: 構造物に対するアクション-パート1–4: 一般的なアクション-風のアクション.
- BSI. (2005). BS EN 1991-1-4: 2005+ A1: 2010: ユーロコード 1. 構造物に対するアクション. 一般的なアクション. 風のアクション.



