擁壁フーチングの安定性チェック
擁壁または壁フーチング
擁壁または壁基礎は、片側に土壌を保持することを目的とした垂直または垂直に近い構造物です。, 保持された材料の崩壊を防ぐ, 滑る, そして侵食していく. 壁基礎は、安息内部摩擦角を超えるように配置された土壌を支持します。, したがって、構造物で安定させないと崩壊する可能性があります. 壁基礎は通常、高速道路や建物などの別の構造物を建設するために急峻な地形から利用可能な平坦な土地を作り出すために使用されます。. 独立した構造物として、またはより広範な建設システムの一部として考えることができます。.
擁壁フーチング構造は基本的にコンクリート壁幹とコンクリートフーチング基礎から構成されます。. 安定性解析では 3 つの異なる土壌ゾーンが考慮されます。: パッシブ土壌, 活性土壌, および基礎土. 不動態土は、擁壁フーチングと活性土の自重が、残留土圧と適用時の外部付加に伴う圧力の作用に耐えるのに役立ちます。. 基礎構造の土は壁基礎システムの全体重量を支える役割を果たします。.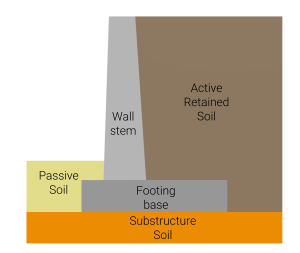
安定性の要件
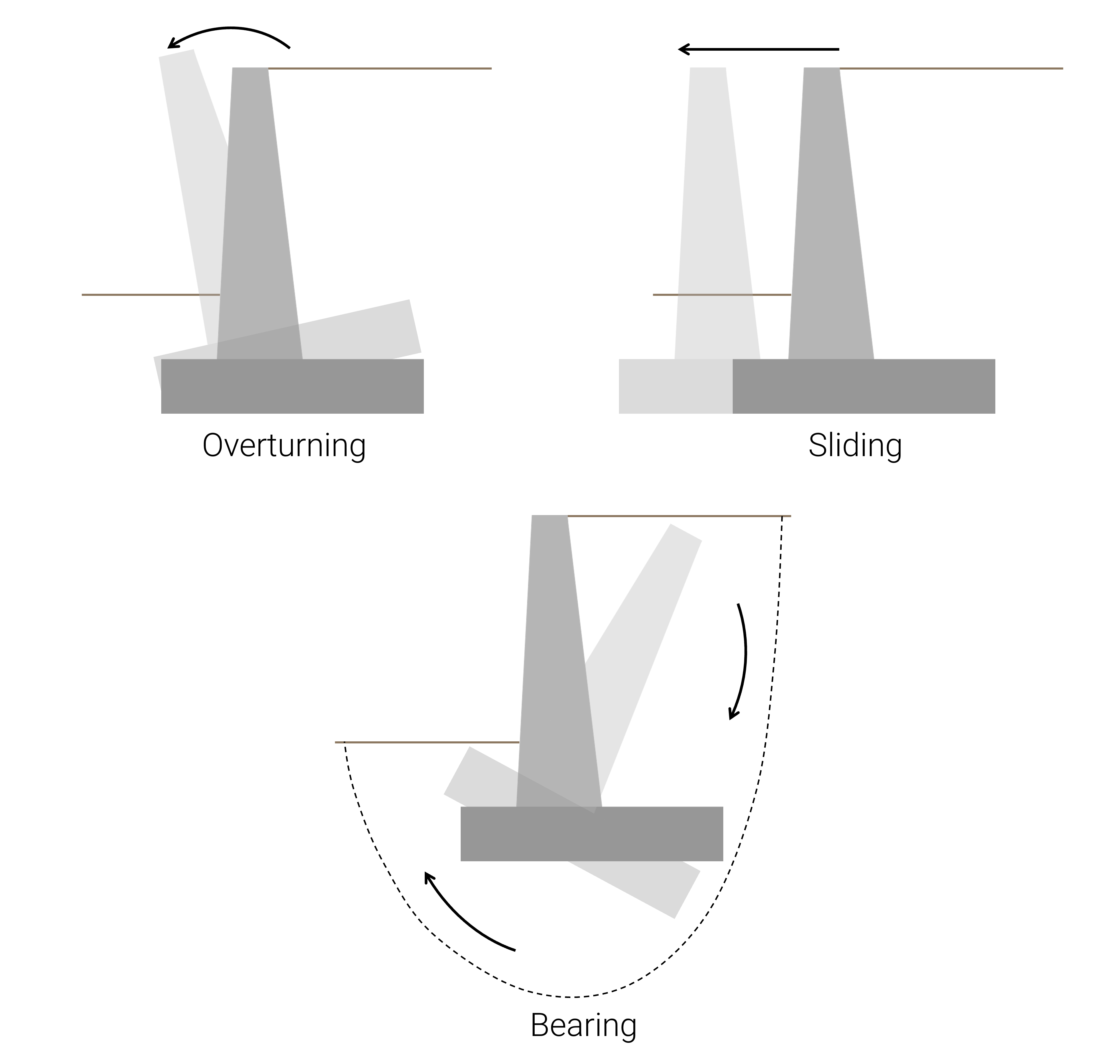
壁基礎は次のいずれかの方法で破損する可能性があります, 安定性の面で:
- かもしれない 覆す そのつま先について
- かもしれない 滑り台 その根元に沿って
- 紛失により失敗する可能性があります 支持力 基礎を支える土の
チェックを覆す
に対する安全率の計算用 転覆 つま先について (ベースの左下隅), 抵抗モーメントの合計を転倒モーメントの合計で割ります。. 擁壁フーチング転倒安全率計算用各要素, 以下にリストされています:
- 抵抗する瞬間: 右に位置するすべての下向きの力と、ベースの左端の角の上にあるすべての右向きの力にレバーを掛けて、合成荷重の重心に到達します。.
- ステムウォール重量
- 基礎フーチング重量
- 活性土壌重量
- 受動的土壌重量 (含まれている場合)
- 転倒モーメント計算例
- 有効土圧の鉛直成分 (裏込めが傾斜している場合)
- 追加料金合力圧力の垂直成分 (裏込めが傾斜している場合)
- パッシブ土壌圧力 (含まれている場合)
- 転覆の瞬間: ベースの左端の角の上にあるすべての左方向の力にレバーを掛けて、結果として生じる荷重の重心までの荷重.
- 有効土圧の水平成分
- サーチャージ合成圧力の水平成分
転倒モーメントの計算例はこちら ここに, 転倒チェックは 無料の SkyCiv 壁基礎計算機
スライディングチェック
滑りに対する安全率の計算に, 水平抵抗荷重の合計 (右を指して) 左向きの荷重の合計で割られます。.
- 転倒モーメント計算例:
- フーチング基礎と下部工土との摩擦による水平力
- パッシブ土壌圧力 (含まれている場合)
- 滑り荷重:
- 有効土圧の水平成分
- サーチャージ合成圧力の水平成分
スライディングの計算例はこちら ここに, スライドチェックは、 無料の SkyCiv 壁基礎計算機
支持力のチェック
支持力の破壊に対する安全率の計算用, 基礎土の最大許容圧力は、擁壁フーチングベース上の土の反力の台形分布を考慮した合計垂直荷重によって加えられる最大圧力で除算されます。.
SkyCiv 壁基礎計算機
SkyCiv 擁壁計算ツールを使用すると、カンチレバーと重力壁の両方の安定性チェックを簡単に実行できます。, テーパーステムまたは欄干を使用する可能性あり, 傾斜した埋め戻しを使用する, 受動的土圧の寄与を含むか無視する.
製品開発者
ベン (民事)