Continuous Members vs. Normal Members – when to use each
前書き
This article will explore an in-depth look at how members (または要素) connect to each other via nodes and how this is handled in the SkyCiv Solver. Nodes mark a point of connectivity between members, they are the separation of the stiffness matrices.
Members can be a number of different types. 実際には, Structural 3D actually has a current total of 6 メンバーの種類. 現時点では, we will look into the two types of members as these are fundamental member types for modeling in general. There are two main member types in Structural 3D: 通常メンバーと継続メンバー. This discussion will be more in-depth with how they are both handled by the SkyCiv solver, as well as the advantages of using one from the other.
Normal Members
Normal members are elements that are treated ‘normally’ in the sense that the members are analyzed in the traditional sense.
伝統的に, 有限要素解析 (醜い) solvers work by using the direct stiffness method. Based on the applied loads and stiffness of the elements in the structure, the displacement of the structure can be solved as shown in the following equation:
\(Q=KD\)
どこ:
\(Q=\) vector of stiffness
\(K=\) グローバル剛性マトリックス (各部材の剛性マトリックスから組み立て)
\(D=) vector of unknown nodal displacements which are unknown and to be solved
SkyCiv Structural 3D applies these formulas to the model and obtains the results from every node and member.
継続的
Continuous members in Structural 3D are a type of member that allows for connectivity between two nodes to a node(s) メンバーへのノード接続を持たない. Node connections occur when a node is assigned to connect two or more members.
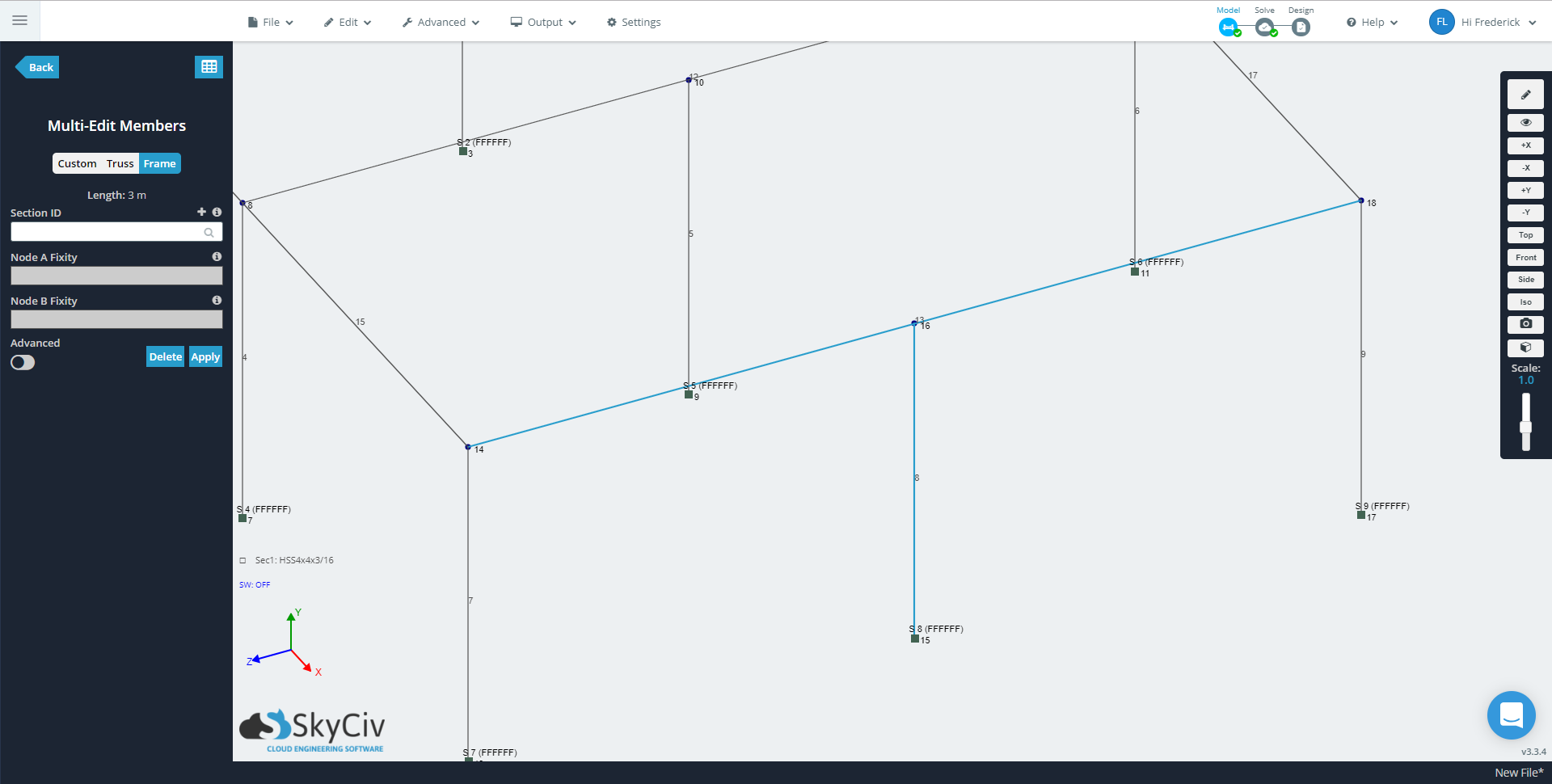
In the case shown below, the nodes are clearly not connected as the two members do not share a common node. Realistically they should be connected because the node of the second member (カラム) is along the path of the first member (ビーム).
The member deflecting the largest in the image below is selected as a ‘Normal’ メンバー, therefore it does not recognize the column along its length. Changing the member to ‘Continuous’ 意志 “connect” the long member to the column, which is the case for the other two members showing limited deflection.
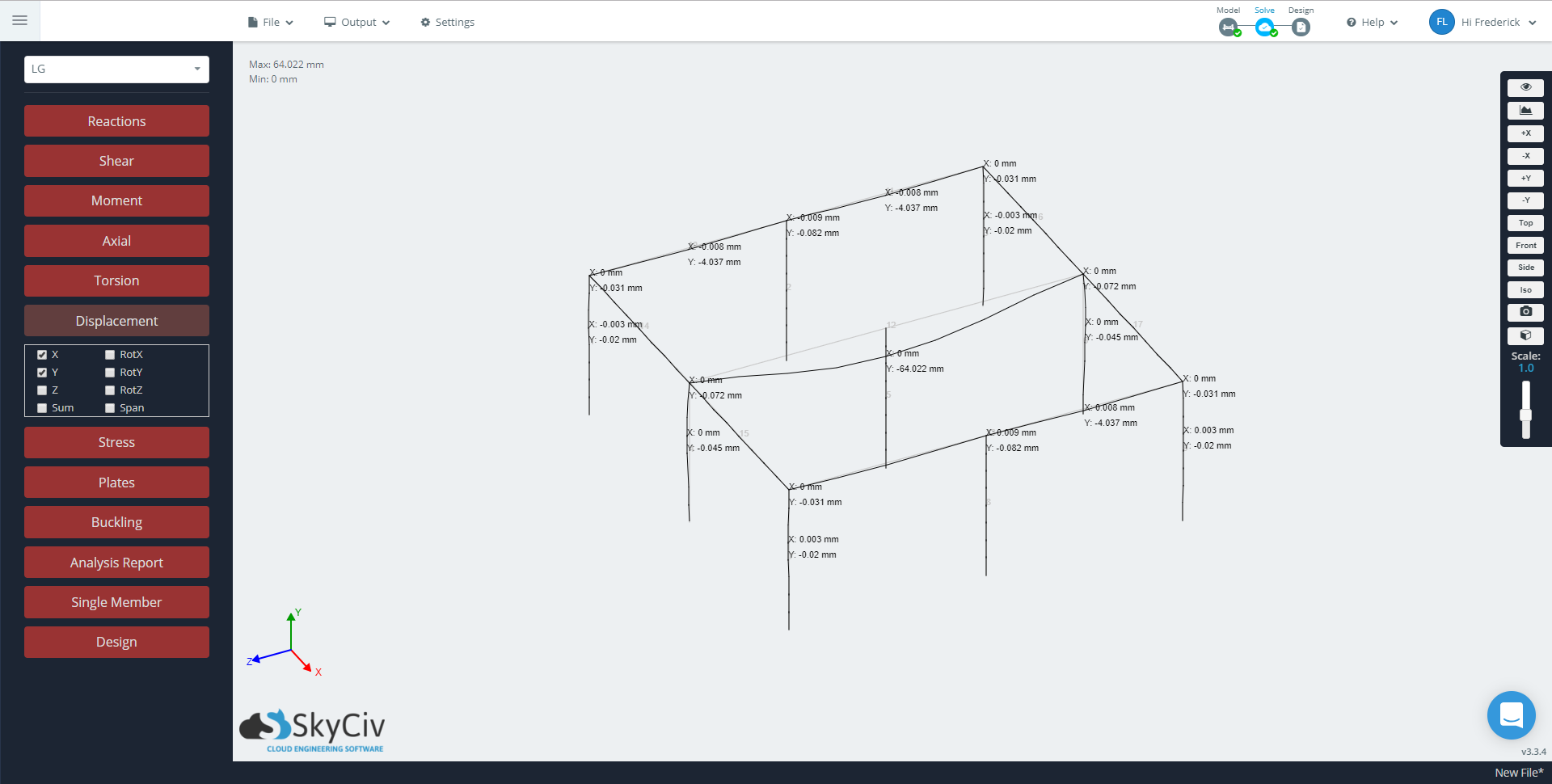
Advantages and Disadvantages of each Member Type
Normal Members
Models built with normal members are more likely to be compatible with third-party structural analysis software. As other programs may not support continuous members in the way that Structural 3D implements it, the results provided may not be correct.
It is important to check that there are no continuous members in the model before exporting it.
In terms of analysis, as the member is broken into simple members, the number of evaluation points in the model is more as opposed to continuous members which carry the same number of evaluation points across two or more spans, making the results less detailed. One can increase the number of evaluation points in the General Solver Settings, but as this controls the evaluation points for all members, the analysis could be longer. This can be a disadvantage when working with large and complex structures.
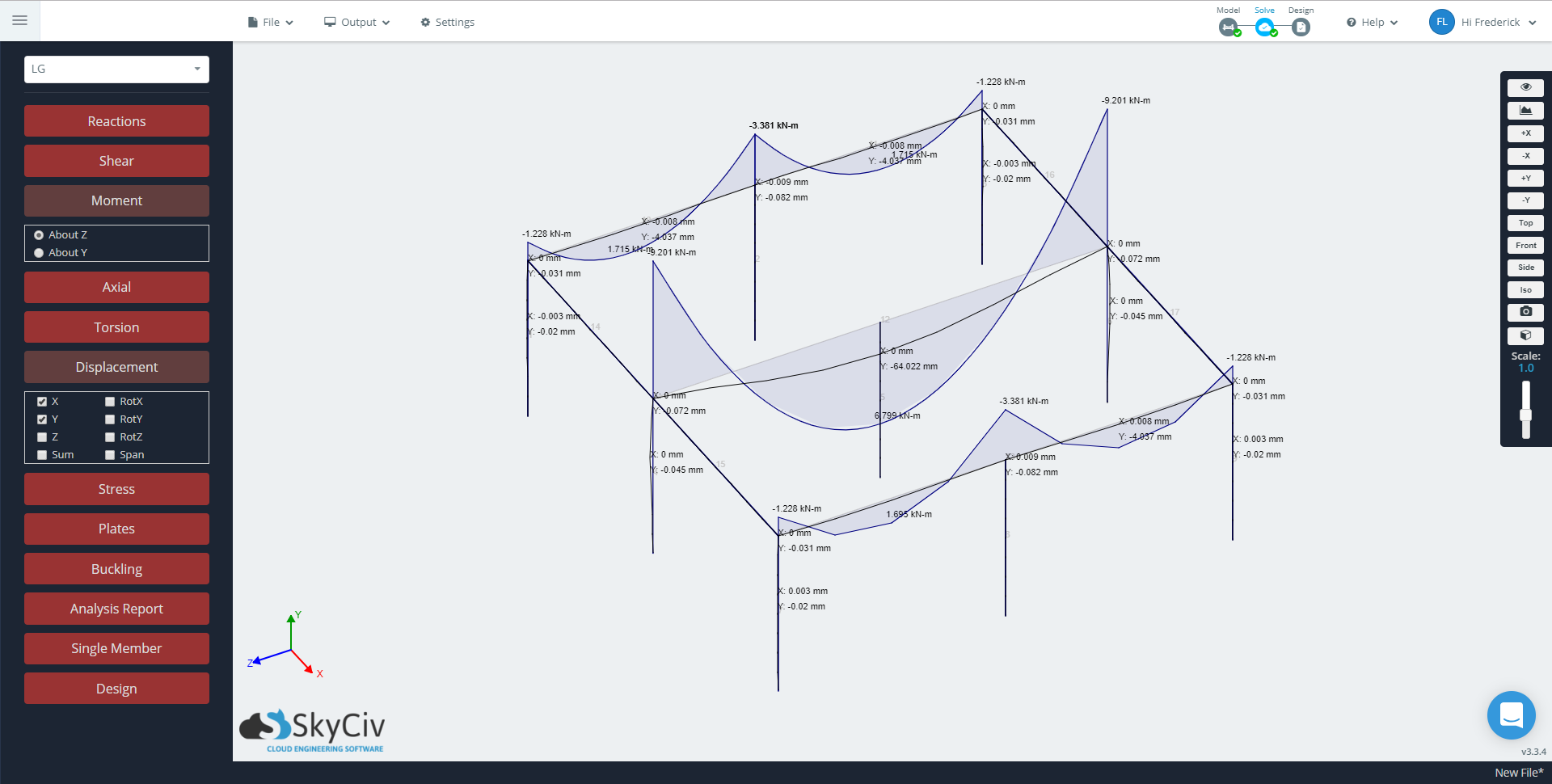
継続会員
Continuous members, 一方で, are very useful when it comes to increasing the efficiency in modeling. Continuous members reduce the number of members required to make a similar model with normal members. This directly impacts the amount of loads that will be present in your project. 例えば, Loading a continuous member with a distributed load vs loading each normal member with a distributed load.
With respect to analysis, reducing the amount of members reduces the clutter and makes it easier to interpret and present the results. Having fewer members reduces the amount of subsequent model elements in your project, making it easier to see member behavior. 例えば, with continuous members, you can check the behavior over a larger span, 同じスパン上の通常のメンバーの組み合わせではなく.
デザインに関しては, 連続部材は、モノリシックに動作することを意図しているため、鉄筋コンクリート梁に最適です. スパンは通常、中間で断面を変更しないため, また、特定のスパンに必要な鋼材セクションを特定するのにも役立ちます. 例えば, continuous members are almost always recommended when designing girders or members that frame into them, つまり, floor or roof framing.

