Τύπος ανάλυσης
Linear Static – static analysis, takes into account elastic material properties
Γραμμικός λυγισμός – γραμμική ανάλυση ευστάθειας για επιλεγμένο αριθμό ιδιοτρόπων.
Geometry Nonlinear Static – iterative analysis, takes into account elastic material properties and geometry nonlinearity (μεγάλες μετατοπίσεις)
Γεωμετρία + Υλικό Μη Γραμμικό Στατικό – η επαναληπτική στατική ανάλυση λαμβάνει υπόψη τη μη γραμμικότητα του υλικού και της γεωμετρίας (μεγάλες μετατοπίσεις)
Γεωμετρία + Μη γραμμικό υλικό - Δυναμική - επαναληπτική δυναμική ανάλυση λαμβάνει υπόψη τη μη γραμμικότητα του υλικού και της γεωμετρίας (μεγάλες μετατοπίσεις)

Στατικές ρυθμίσεις
Συντελεστής γενικού φορτίου – ο συντελεστής θα πολλαπλασιαστεί με όλες τις τιμές φορτίου στο μοντέλο για ανάλυση
Χρονική περίοδος και χρονική αύξηση – ρυθμίσεις ανάλυσης επανάληψης. Αυτές οι ρυθμίσεις για τις περισσότερες περιπτώσεις ανάλυσης έχουν ρυθμιστεί σωστά και μπορούν να χρησιμοποιηθούν από προεπιλογή.
Δυναμικές ρυθμίσεις
Χρονική περίοδος και χρονική αύξηση – ρυθμίσεις ανάλυσης επανάληψης.
Βήματα εξόδου αποτελεσμάτων – για την καταγραφή των αποτελεσμάτων κατά την ανάλυση
Damping – Rayleigh damping, alternatively termed proportional damping, represents a variant of viscous damping allocated throughout the elements. This approach constructs a damping matrix, δηλώνεται ως , through a linear amalgamation of the mass matrix and the stiffness matrix
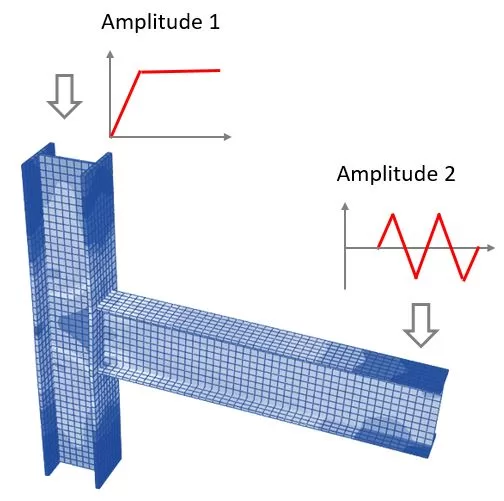
Πλάτος Φορτίου
In nonlinear finite element analysis, the load-time function is a critical feature that defines how loads are applied over time. The software provides the capability to assign varying load intensities at different instances, which is especially useful in simulating real-world conditions where loads are not constant.
To enhance this functionality, the software allows the definition of two amplitude options for the loads. These amplitude options enable users to specify a pattern or a sequence of load values that change over the course of the analysis.
The first amplitude option can define the initial ramp-up of the load, allowing for a gradual increase from zero to the maximum load value, reflecting a more realistic application of force or pressure on the structure. The second amplitude option can describe a subsequent phase, such as a holding pattern, cyclic loading, or a decrease to simulate the removal of the load.
If you only need to deal with a single load amplitude, where all applied loads follow the same function, use ‘Amplitude 1’ as an example. The program will ignore the second amplitude if it is not used.