The upcoming analysis will encompass both geometric and material nonlinearity. It also offers real-time tracking of the load-displacement curve, enabling an in-depth investigation of the member’s capacity while optimizing computational time. The results will provide insights into the member’s capacity, its deformed state, and its failure status.
Βήμα 1. Model Parts
Go to the ‘Main Parts’ menu and select the ‘PROFILE’ tab. To input the sections’ geometry, import a DXF file stored locally on your PC. The DXF file can be received from εδώ
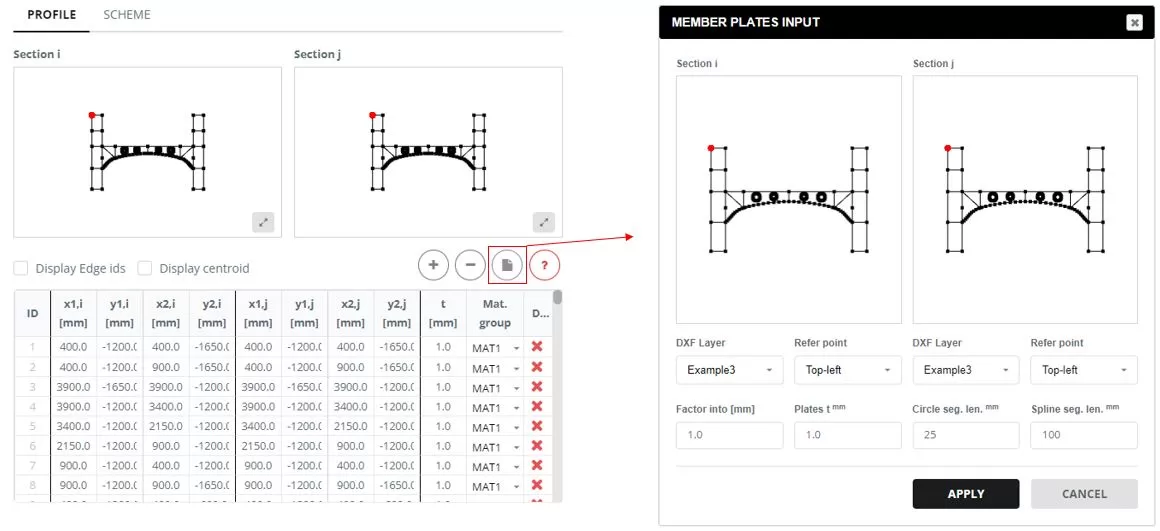
Navigate to the ‘SCHEME’ αυτί. When you click on the ‘Updated plate t’ column cell, a popup window will appear. In this window, update the thickness for all edges to t=0 mm.
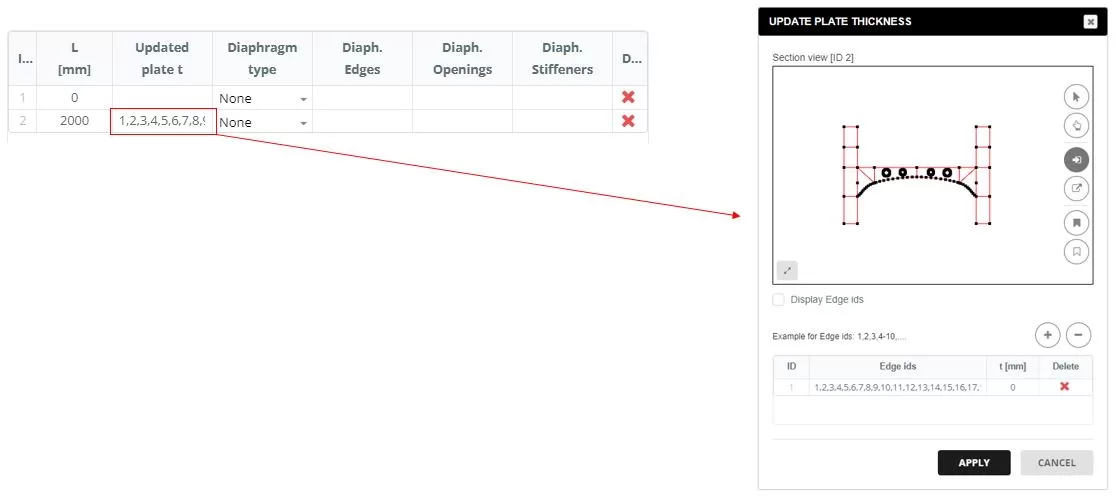
Add diaphragms to the sections, selecting the ‘Polygon’ τύπος. The edges for the diaphragm are defined in a popup window that appears when you click on the ‘Diaphragm Edges’ column cell. In the ‘DIAPHRAGM INPUT’, select the edges that form the diaphragm shape and input the thickness (τ).
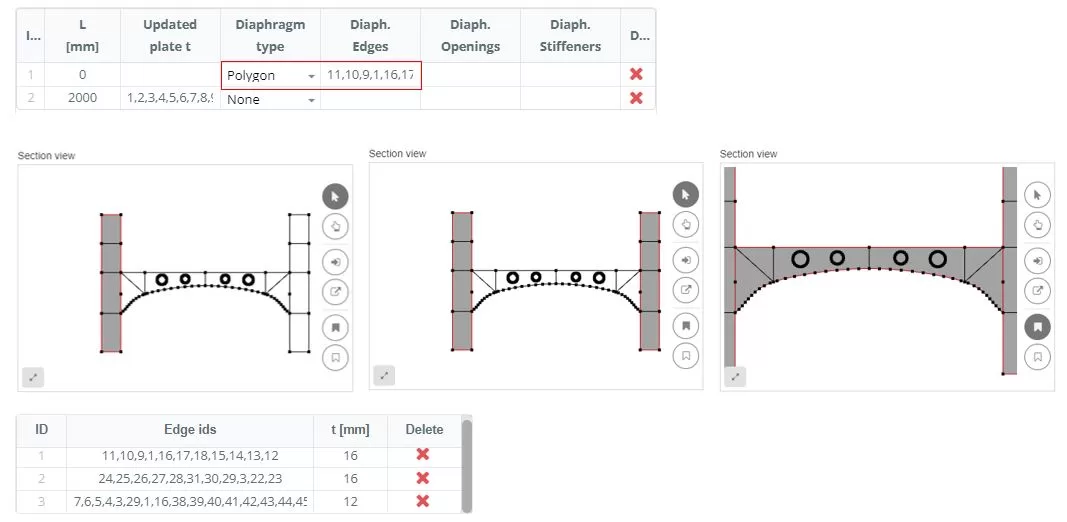
Add diaphragms to the sections, selecting the ‘Polygon’ τύπος. The edges for the diaphragm are defined in a popup window that appears when you click on the ‘Diaphragm Edges’ column cell. In the ‘DIAPHRAGM INPUT’, select the edges that form the diaphragm shape and input the thickness (τ).
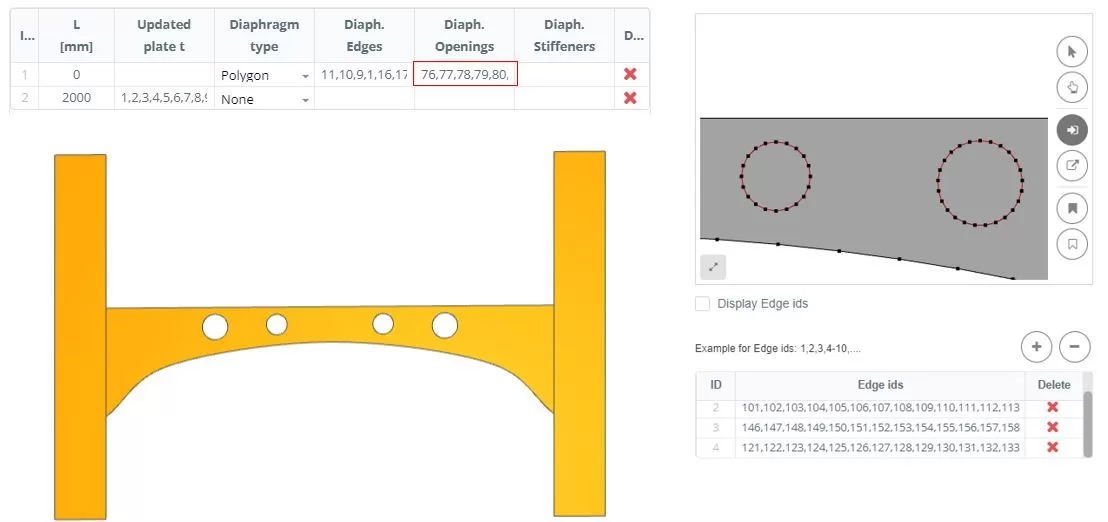
Add diaphragms to the sections, selecting the ‘Polygon’ τύπος. The edges for the diaphragm are defined in a popup window that appears when you click on the ‘Diaphragm Edges’ column cell. In the ‘DIAPHRAGM INPUT’, select the edges that form the diaphragm shape and input the thickness (τ).
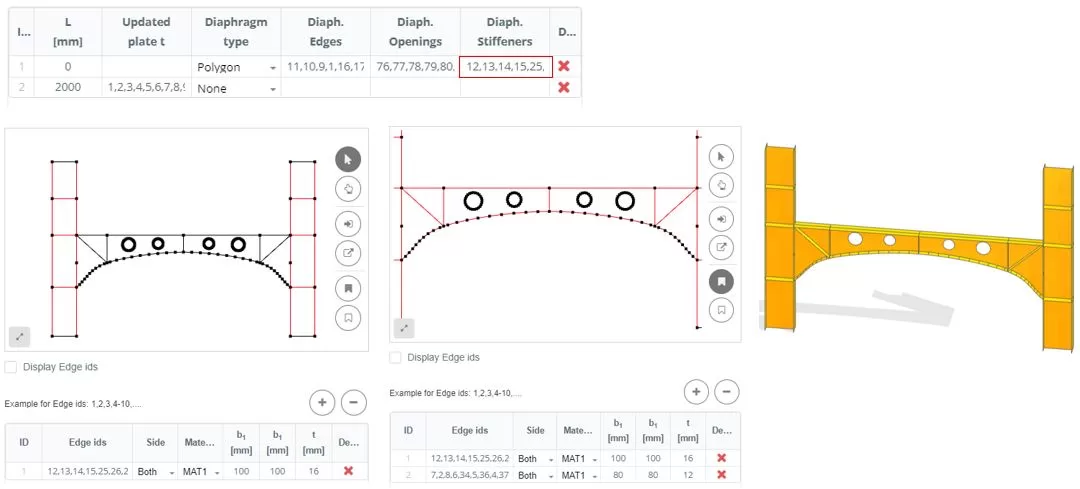
Βήμα 2. Πλέγμα
Navigate to the ‘Meshing’ μενού. Set the FE element size to 50 χιλ, by frame set sub-mesh to the beam edges and then click the ‘Generate’ κουμπί.
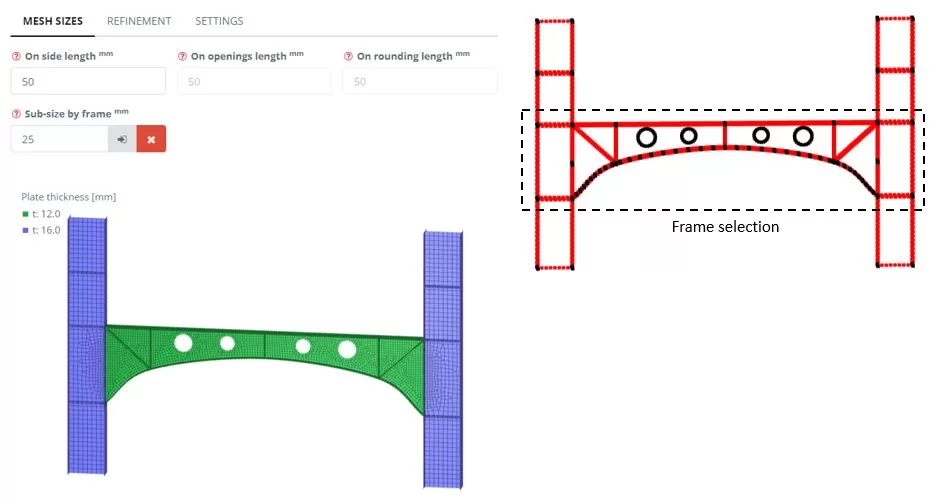
Βήμα 3. Boundaries and Load
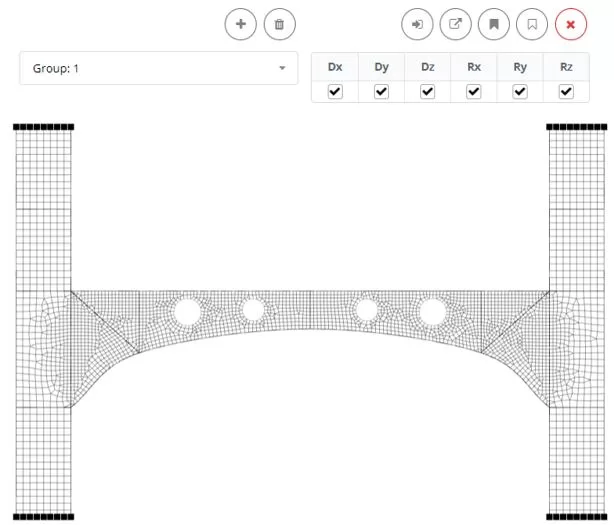
Go to the ‘Boundaries’ > ‘Nodes (Εθιμο)‘ menu. Add a new boundary group named ‘Group: 1’. Select the nodes and apply fixed constrains
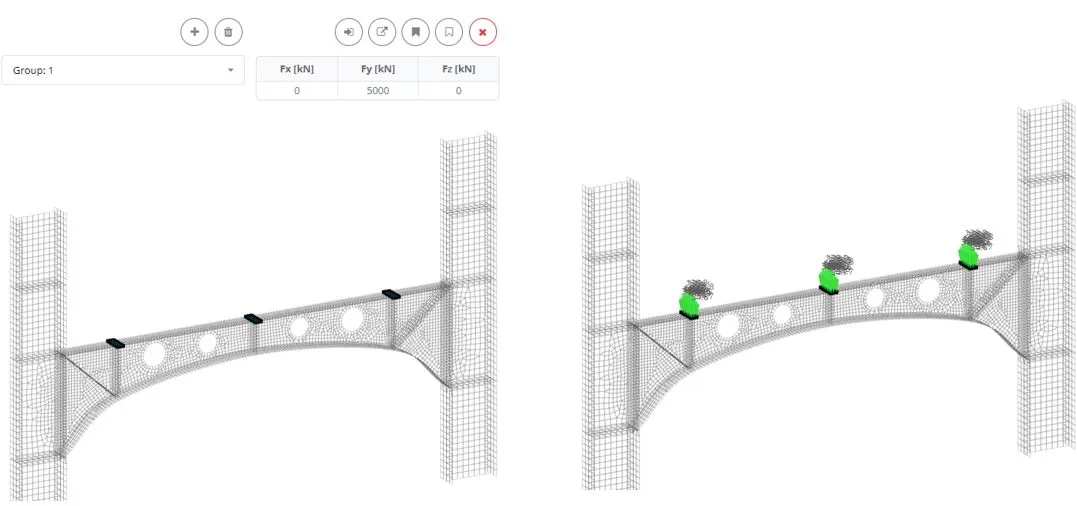
Go to the ‘Loads > ‘Force Area (Εθιμο)‘ menu. Add a new Load group named ‘Group: 1’. Select the elements above vertical stiffeners, and then assign a load Fy of 5000 ΚΝ
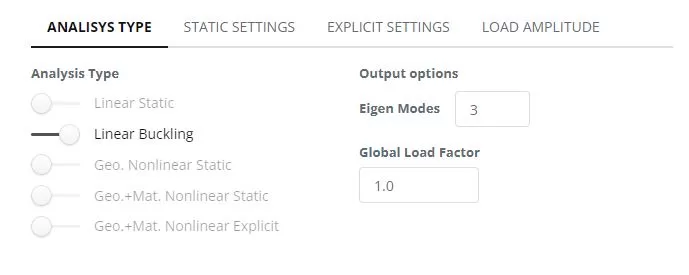
Βήμα 4. Ανάλυση Γραμμικής Λυγισμού
Navigate to the ‘Analysis‘ menu. Select Linear Buckling. Click ‘Perform Analysis’ button.
Βήμα 5. Imperfection from buckling mode
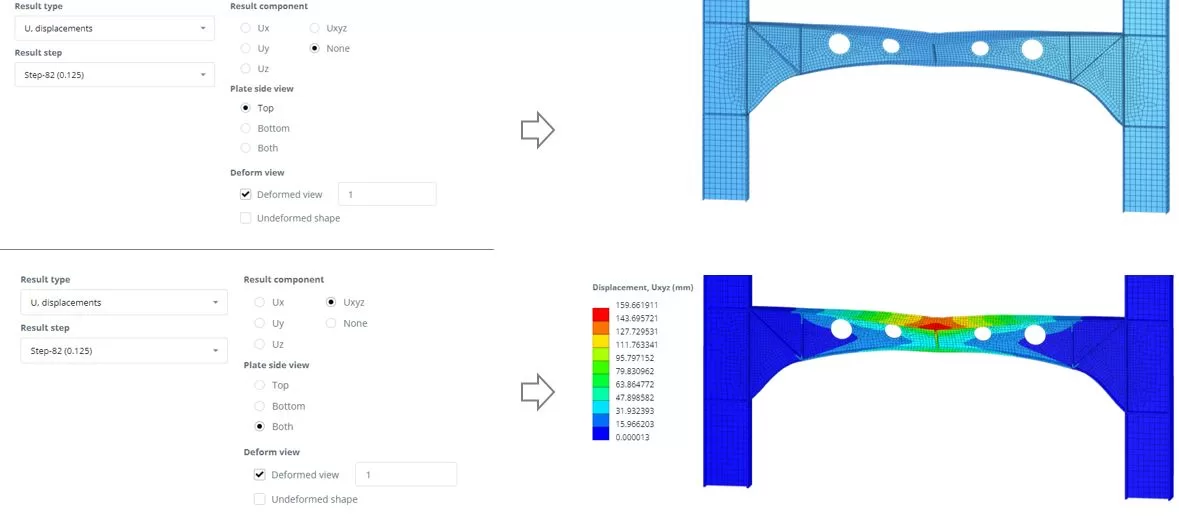
Navigate to the ‘Results’ μενού, choose your preferred results options, and click ‘Display’ to view the deformed state of the model. Click ‘Set Imperf.’. Navigate to the ‘Imperfections‘ > ‘From buckling’ menu, set scaling to 5 χιλ.
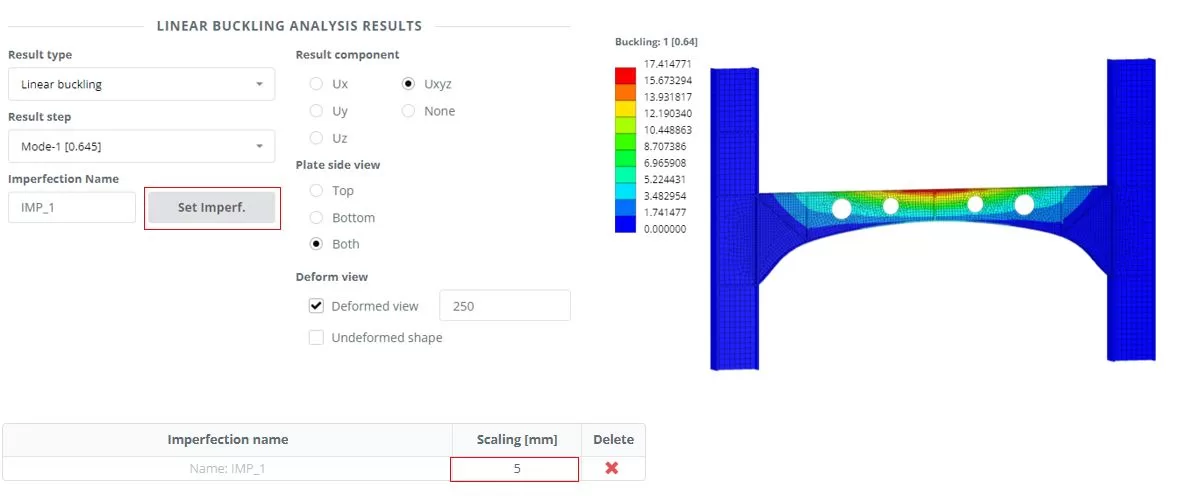
Βήμα 6. Μη γραμμική ανάλυση
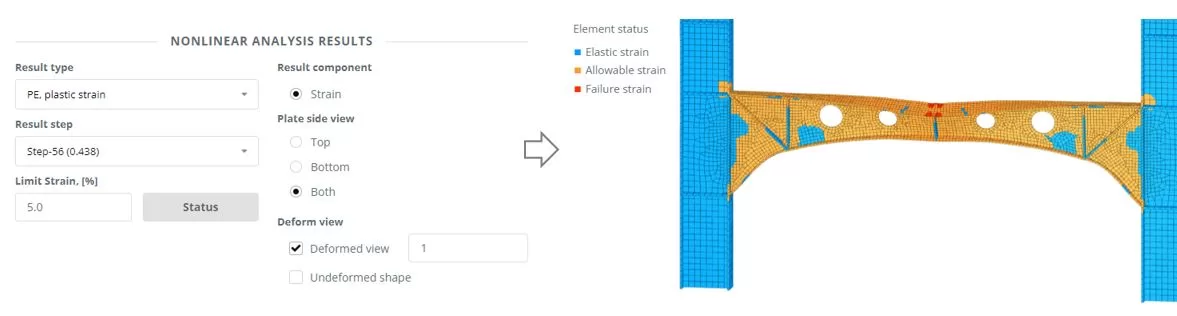
Navigate to the ‘Analysis‘ menu. Select Nonlinear Explicit including geometry and material nonlinearity. Click ‘Perform Analysis’ button.
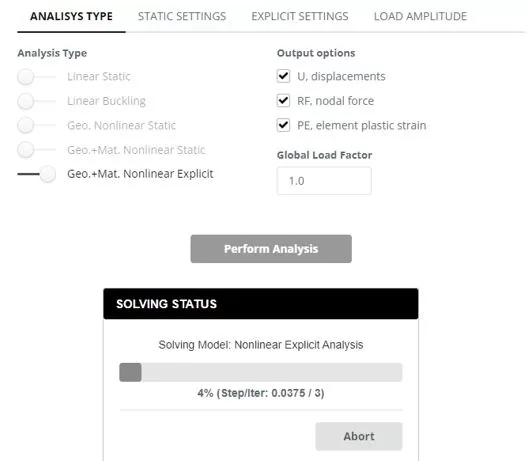
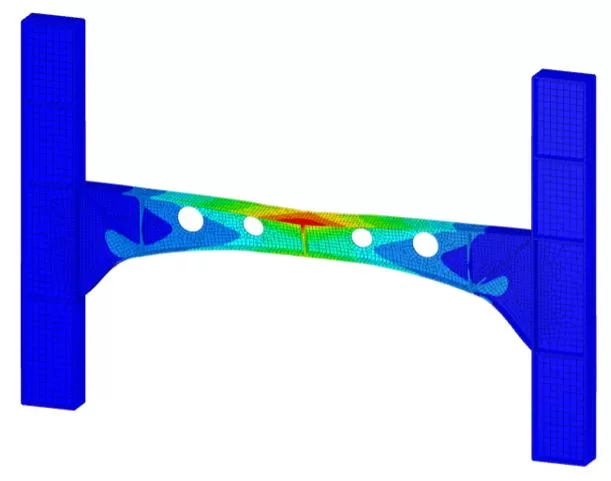
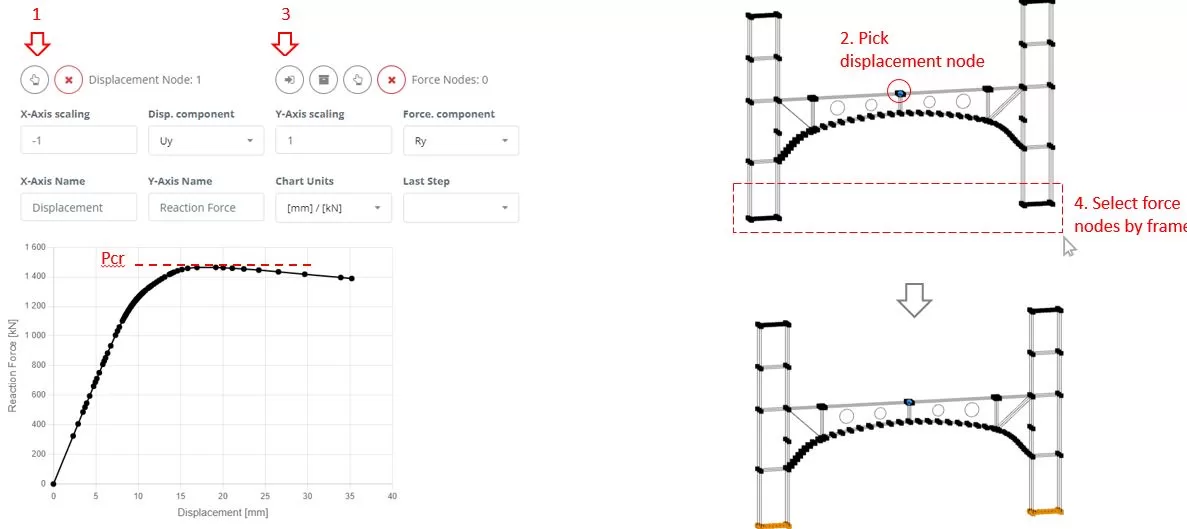
While the analysis is in progress, navigate to ‘Chart’ menu. Πρώτα, select a node to measure the Uy displacement (βήματα 1 και 2). Τότε, using frame selection, choose nodes from which to extract the Ry reaction forces (βήματα 3 και 4). Monitor the chart’s changes to identify the critical force (Pcr) that leads the structure to failure. Terminate the ongoing analysis once the failure state is detected.
Βήμα 7. Αποτελέσματα
Navigate to the ‘Results’ μενού, choose your preferred results options, and click ‘Display’ to view the deformed state of the model.