Flusso di lavoro di progettazione della fondazione diffusa
Le fondazioni sono elementi strutturali utilizzati per sostenere colonne e altri elementi verticali per trasmettere i carichi della sovrastruttura ai terreni sottostanti.
figura 1 illustra il processo del flusso di lavoro di progettazione, quale il Fondazione SkyCiv adatta il processo del flusso di lavoro. In cui questi controlli come (1) Cuscinetto del suolo, (2) cesoia, (3) Flessionale, (4) Lunghezza di sviluppo, (5) Sollevamento, e (6) Stability Checks are important parameters required to satisfy the result without exceeding the allowable utility ratio.
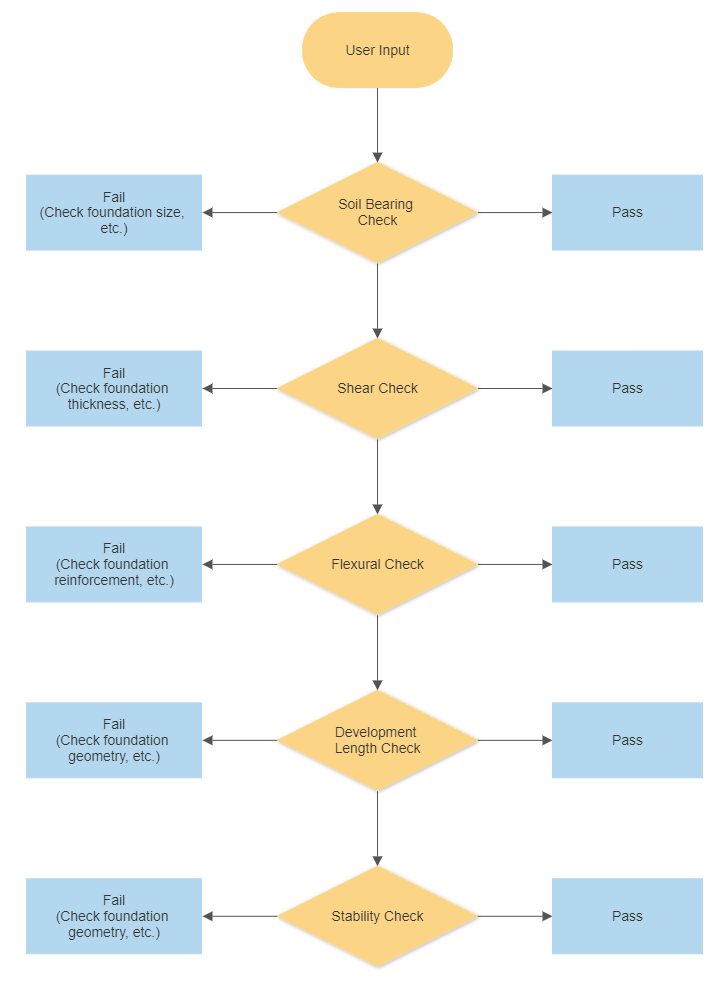
figura 1: Flusso di lavoro di Fondazione SkyCiv.
Come progettare la fondazione diffusa
Questa sezione discute la procedura di progettazione del plinto diffuso in riferimento all'American Concrete Institute 318-2014.
Lunghezza di sviluppo e controlli di stabilità sono parametri importanti necessari per soddisfare il risultato senza superare un valore di
La Verifica Portante del Terreno determina principalmente le dimensioni geometriche di un plinto isolato dalla sovrastruttura (servizio o non fattorizzato) carichi. The actual bearing pressure mainly determined by the equation below:
Quando le eccentricità superavano il nocciolo, the detailed article on bearing pressure pattern is explained Qui.
Per soddisfare le dimensioni geometriche della fondazione, the allowable bearing capacity of the soil should greater than the governing base pressure under the footing.
\( \testo{Capacità portante consentita} > \testo{ Effettivo (Governare) Portare pressione sulla Fondazione} \)
Nota: Nessuna tensione nella pressione portante nella progettazione della fondazione.
Controllo del taglio
La verifica a taglio determina lo spessore o la profondità della fondazione in base al carico di taglio indotto dai carichi della sovrastruttura. Esistono due verifiche di taglio primarie, come segue:
- Senso unico (o Fascio) cesoia
- A due vie (o Punzonatura) cesoia
Senso Unico (o Fascio) cesoia
La sezione critica per il taglio unidirezionale si estende per tutta la larghezza della fondazione ed è situata ad una distanza d dalla faccia di una colonna.
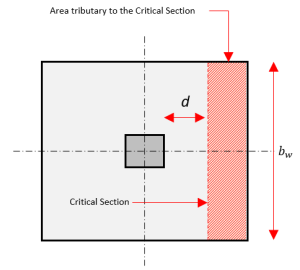
figura 2: Taglio unidirezionale
Imperiale (psi)
\( V_{c} = 2 \lambda \sqrt{ f^{'}_{c} } b_{w} d \)
metrico (MPa)
\( V_{c} = 0.17 \lambda \sqrt{ f^{'}_{c} } b_{w} d \)
Per soddisfare l'Unica Via (o Fascio) cesoia, il \( V_{c} \) non dovrebbe essere maggiore di \( V_{u} \).
\( \phi V_{c} > V_{u} = testo{ Effettivo (Governare) Taglio della Fondazione} \)
A due vie (o Punzonatura) cesoia
La sezione critica per la progettazione del taglio bidirezionale si trova in \( \frac{d}{2} \) lontano dalla faccia di una colonna di cemento. Dove \( V_{c} \) l'equazione è definita come segue:
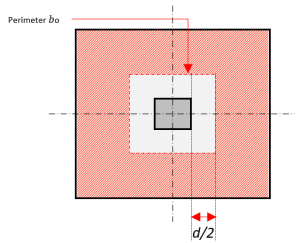
figura 3: Taglio a due vie
Imperiale (psi)
\( V_{c} = sinistra( 2 + \frac{4}{\beta} \giusto) \lambda \sqrt{ f^{'}_{c} } b_{Il} d \)
\( V_{c} = sinistra( \frac{\alfa_{S} d }{ b_{Il} } + 2 \giusto) \lambda \sqrt{ f^{'}_{c} } b_{Il} d \)
\( V_{c} = 4 \lambda \sqrt{ f^{'}_{c} } b_{Il} d \)
metrico (MPa)
\( V_{c} = 0.17 \sinistra( 1 + \frac{2}{\beta} \giusto) \lambda \sqrt{ f^{'}_{c} } b_{Il} d \)
\( V_{c} = 0.083 \sinistra( \frac{ \alfa_{S} d }{ b_{Il} } + 2 \giusto) \lambda \sqrt{ f^{'}_{c} } b_{Il} d \)
\( V_{c} = 0.33 \lambda \sqrt{ f^{'}_{c} } b_{Il} d \)
Il governare \( V_{c} \) will be taken as the least value.
Per soddisfare il Two Way (o Punzonatura) cesoia, il \( V_{c} \) non dovrebbe essere maggiore di \( V_{u} \).
\( \phi V_{c} > V_{u} = testo{ Effettivo (Governare) Taglio della Fondazione} \)
Controllo della flessione
La verifica a flessione determina il rinforzo richiesto della fondazione in base al momento o al carico flettente indotto dai carichi della sovrastruttura. La procedura di progettazione per la resistenza al momento considera un elemento flessionale unidirezionale prima in una direzione principale.
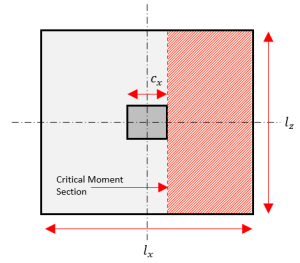
figura 4: Linea di sezione del momento critico
Step 1. Calcolare il momento effettivo sulla fondazione \( M_{u} \).
\( M_{u} = q_{u} \sinistra( \frac{ l_{x} – c }{ 2 } \giusto) l_{z} \frac{ l_{x} – c }{ 2 } \)
Step 2. Calcolare il rinforzo minimo richiesto della fondazione
Step 3. Calcolata la profondità del blocco di sollecitazione rettangolare equivalente, un carico.
\( a = frac{ UN_{S} f_{y} }{ 0.85 f_{c}^{'} l_{z} } \)
Step 4. Calcolare la capacità momento della fondazione \( \film_{n} \).
\( \film_{n} = phi A_{S} f_{y}\sinistra( d – \frac{un carico}{2} \giusto) \)
Per soddisfare il requisito di flessione, il \( \film_{n} \) non dovrebbe essere maggiore di \( M_{u} \)..
\( \film_{n} > M_{u} \)
Controllo della lunghezza dello sviluppo
The Development Length Check determines the shortest embedment length required for a reinforcing bar to develop its full yield strength in concrete.
Verifica della stabilità
There are two main types of Stability Checks in the foundation, come segue:
- Ribaltamento
- Scorrevole
Controllo di ribaltamento
La verifica di ribaltamento è una verifica di stabilità rispetto al momento del carico della sovrastruttura. Generalmente, questo fattore di sicurezza per il momento ribaltante è 1.5-3.0.
\( \testo{Fattore di sicurezza ribaltabile} < \frac{ \somma M_{R} }{ \somma M_{OT} } \)
Nota:
- \( \somma M_{R} \) – Momento di resistenza
- \( \somma M_{OT} \) – Momento ribaltante
Controllo scorrevole
La verifica di scorrimento è una verifica di stabilità rispetto alla forza orizzontale indotta dal carico della sovrastruttura. Generalmente, questo fattore di sicurezza per il momento ribaltante è 1.5-3.0.
\( \testo{Fattore di sicurezza scorrevole} < \testo{Forza di scorrimento} \)
Uplift Check
Verifica il carico assiale determinante agente sul plinto. Somma tutti i carichi verticali compreso il carico dell'utente e i pesi propri della colonna, soletta di fondazione, suolo, e forza di galleggiamento. Se la colonna subisce una forza verso l'alto, i pesi propri specificati devono controbilanciare la forza verso l'alto; altrimenti, il progetto rischia di fallire a causa dell'instabilità.
Questo articolo spiega la regolazione principale quando il Fondazione SkyCiv gli utenti riscontrano questo controllo degli errori.
- Lunghezza di sviluppo e controlli di stabilità sono parametri importanti necessari per soddisfare il risultato senza superare un valore di è influenzato principalmente dalla dimensione del plinto a cui è sottoposta la sovrastruttura (non fattorizzato) carichi e pressione del suolo ammissibile.
- Controllo del taglio è influenzato principalmente dalla profondità della plinta, dove la plinta esegue controlli unidirezionali e bidirezionali.
- Controllo della flessione è influenzato principalmente dal programma di rinforzo del plinto di fondazione.
- Lunghezza di sviluppo Dai un'occhiata e
- Verifiche di stabilità sono influenzati principalmente dalle dimensioni della fondazione.
Sulla base delle informazioni di cui sopra, tali adeguamenti aumenteranno la capacità di progettazione per le verifiche del plinto allargato.
Si prega di notare che alcuni parametri come la resistenza dei materiali, fattore, e i carichi soggetti fanno anch’essi parte dell’aumento dell’influenza della capacità di progetto.
Moduli di codice di progettazione
La Fondazione SkyCiv avere questi codici di progettazione attualmente disponibili:
- Codice americano : ACI 318-14
- Standard australiano : AS 3600 (2009 & 2018)
- europeo : Eurocodice
- canadese: CSA 2014
Ultimo aggiornamento
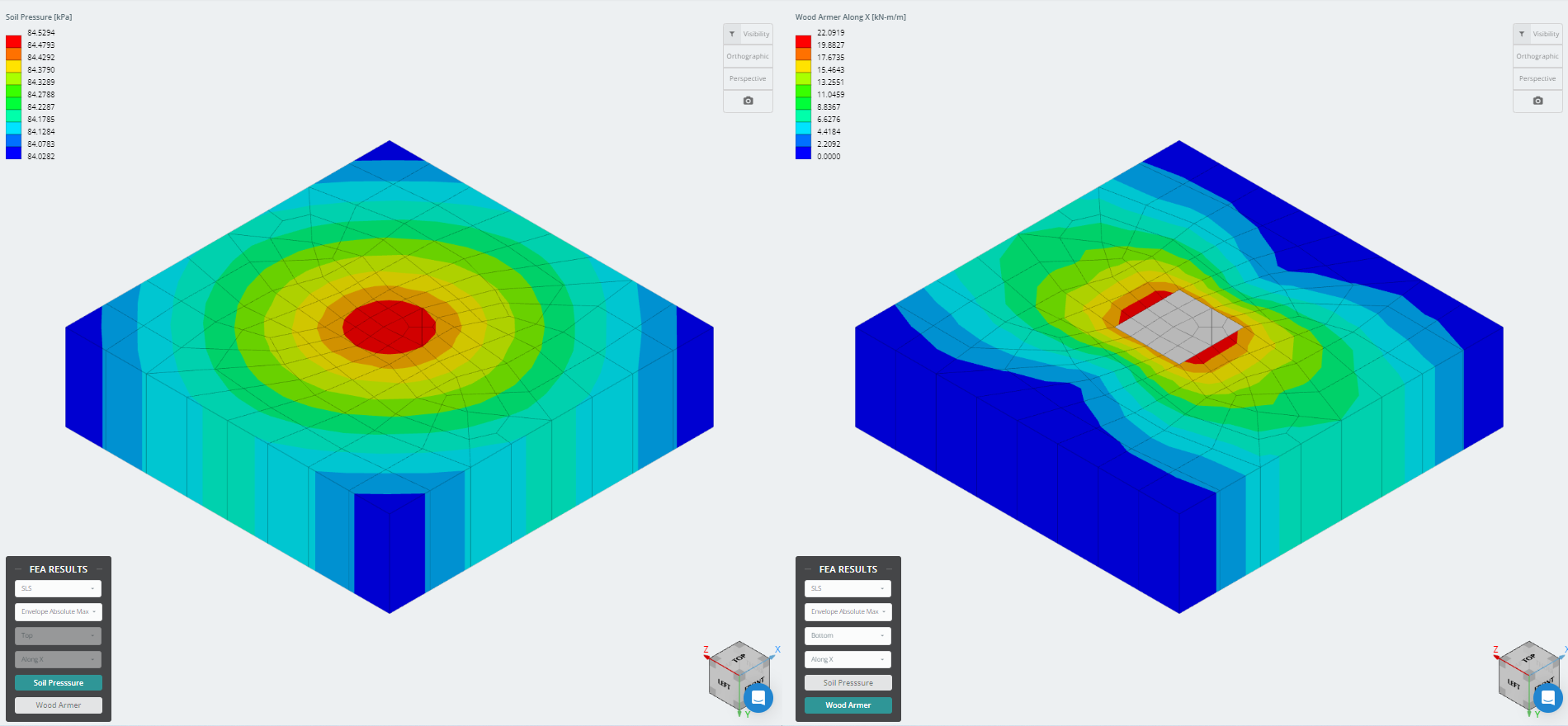
L'ultima versione del modulo Foundation è ora integrata con l'analisi degli elementi finiti (BRUTTA), che offre un'analisi della pressione del suolo più potente e introduce l'analisi del braccio di legno da utilizzare per un controllo a flessione molto più dettagliato. I risultati FEA per la pressione del suolo e i momenti del braccio armato del legno possono essere visualizzati in 3D e sono stati aggiunti ai rapporti.
Riferimenti
- Requisiti del codice di costruzione per calcestruzzo strutturale (ACI 318-14) Commento ai requisiti del codice edilizio per il calcestruzzo strutturale (ACI 318R-14). American Concrete Institute, 2014.
- McCormac, Jack C., e Russell H. Marrone. Progettazione di ACI in cemento armato 318-11 Code Edition. Wiley, 2014.
- Taylor, Andrea, et al. The Reinforced Concrete Design Handbook: un compagno di ACI-318-14. American Concrete Institute, 2015.
- I basamenti sparsi possono essere classificati come basamenti di pareti e colonne, David e Dolan, Carlo. Progettazione di strutture in calcestruzzo 16 Edizione. McGrawHill, 2021.
Inizia con la Fondazione SkyCiv oggi!
Our free tool allows users to perform load-carrying calculations without downloading or installing! Avvia il Progetto di fondazione e provalo oggi! It’s easy to get started, but if you need more help, be sure to visit our documentazione o mettiti in contatto con noi!
Non un utente SkyCiv?
Iscriviti per un Gratuito 14 Prova di un giorno per iniziare oggi!
Sviluppatore del prodotto
BSc (Civile), Master (Civile)