What Member Fixities mean and how they are identified in Structural 3D
Member End Fixities control how members are connected to each other or to the end nodes and include conditions such as a fixed, appuntato, o collegamento a molla.
Questa impostazione Membro controlla il modo in cui l'estremità del membro si connette al relativo nodo finale, e quindi come i membri si connettono tra loro. Un codice di fissità è a 6 codice carattere che specifica il 6 degrees of freedom for translation and rotation.
Member-end fixity codes accept ‘F’ (Fisso) and ‘R’ (Rilasciato) valori. This code refers to the member end’s connection to its end node for each of the 6 degrees of freedom in the following order:
- Local x-axis Translation
- Local y-axis Translation
- Local z-axis Translation
- Local x-axis Rotation
- Local y-axis Rotation
- Local z-axis Rotation
NOTA: Member-end fixities are with respect to the member’s local axis system rather than the global axis system.
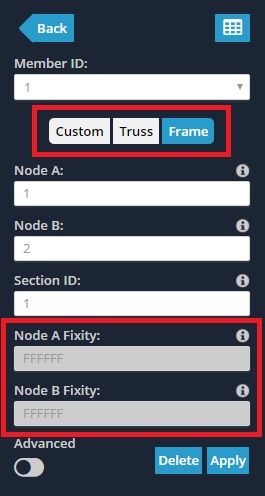
Telaio members have a fully fixed, rigid connection specified by a fixity code of ‘FFFFFF’.
travatura members have a hinged connection denoted by a code of ‘FFFFRR’.
To specify custom values, ensure that the costume button is selected. This enables the end fixity fields to be edited.
How to tell Member End Fixity while looking in the model space
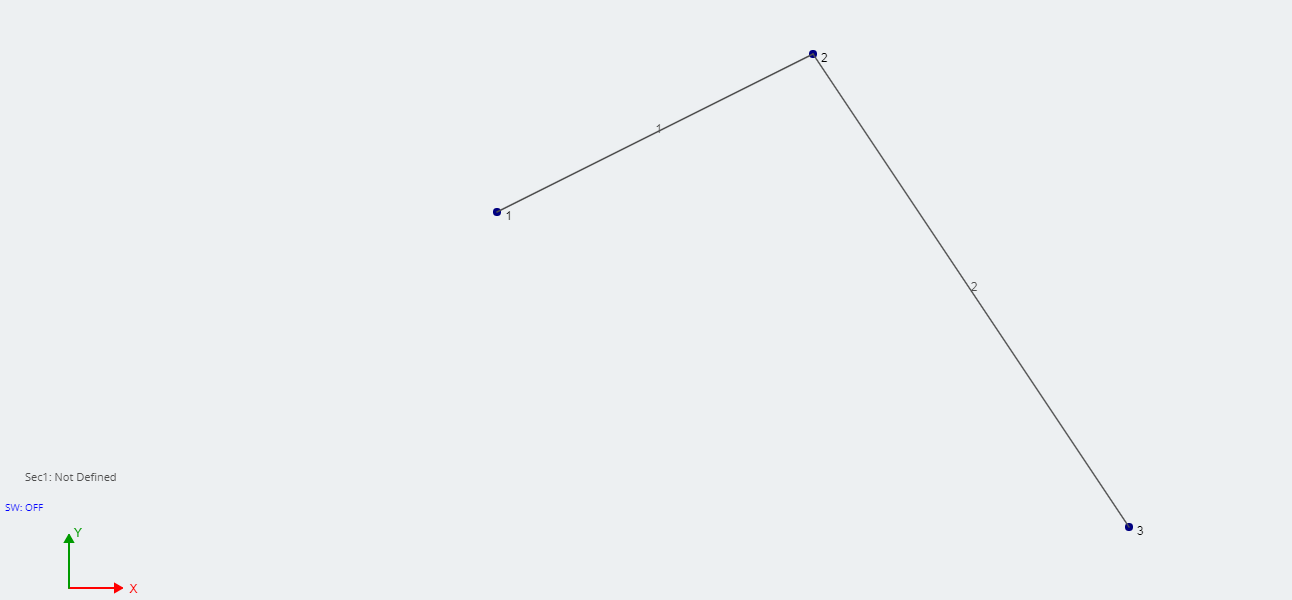
When modeling with members, it is convenient to know the members’ end fixity without having to click on each member individually. Per impostazione predefinita, when members are modeled they have fully fixed, o Telaio, end fixities (FFFFFF). The member looks like a single line between nodes:

When any of the degrees of freedom are released, the member will have a small dot near the end of the member (as shown below circled in red). Per esempio, for members with pinned, o travatura, end fixities (FFFRRR), the member would look like this:

Further Explanation
For more information on member fixities, SkyCiv has a technical article (including a video) nel nostro blog, CREDIAMO IN UN SOFTWARE MIGLIORE how to model member fixities:
Esempio: How to model pin connections or hinges
In questo esempio, creeremo una semplice connessione pin, come una cerniera. Inizia creando 3 nodi e unendoli con 2 aste. In questo esempio node, 2 sarà il cardine.
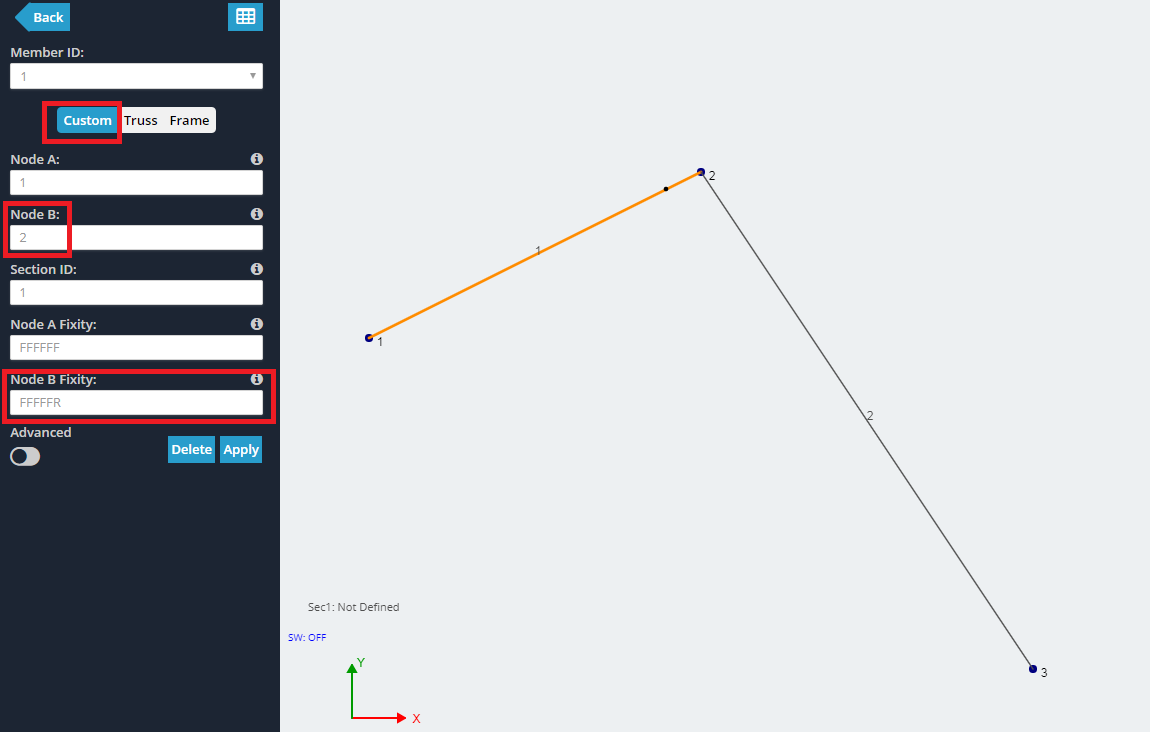
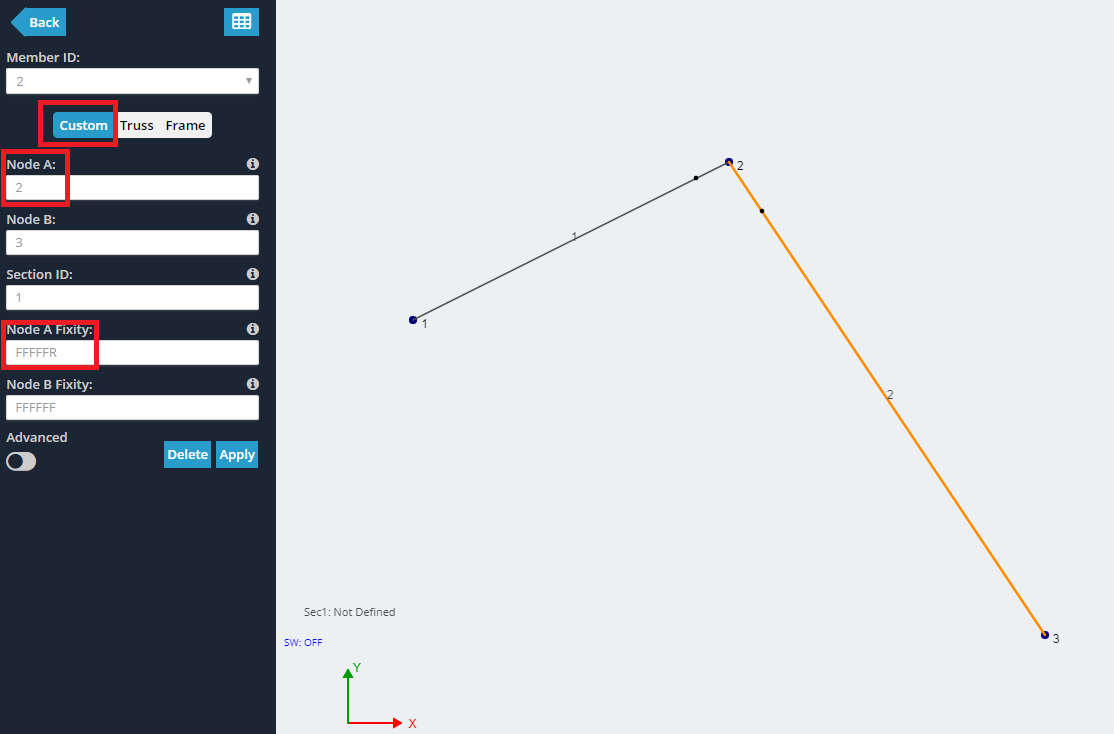
Maggiori informazioni
Per maggiori informazioni, SkyCiv has a further explanation on how to model a hinge, utilizzando il software di analisi strutturale.
video: Spiegazione dei gradi di libertà e dei codici di fissità

