基本板设计示例使用en 1993-1-8-2005, 在 1993-1-1-2005 和EN 1992-1-1-2004
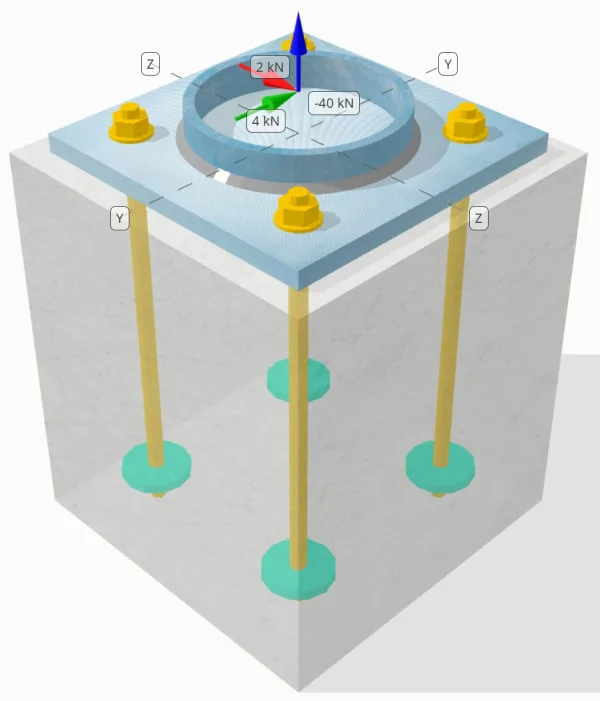
问题陈述
确定设计的列板连接是否足够 50-kN 拉力载荷, 4-kN Vy 剪切载荷, 和 2-kN Vz 剪切载荷.
给定数据
柱:
列部分: CHS193.7×10
列区域: 5770.0 平方毫米
列材料: S460
底盘:
基板尺寸: 300毫米×300毫米
基板厚度: 18毫米
底板材料: S235
灌浆:
灌浆厚度: 0 毫米
具体:
混凝土尺寸: 350毫米×350毫米
混凝土厚度: 400 毫米
混凝土材料: C35/45
破裂或无裂缝: 破裂
锚:
锚直径: 16 毫米
有效嵌入长度: 350 毫米
嵌入式板直径: 70 毫米
嵌入式板厚度: 10 毫米
锚材料: 4.8
焊缝:
焊接类型: 鱼片
焊缝尺寸: 7毫米
填充金属分类: E42
锚数据 (从 SkyCiv计算器):
SkyCiv 免费工具中的模型
立即使用我们的免费在线工具对上面的底板设计进行建模! 无需注册.
笔记
此设计示例的目的是演示涉及并发剪切和轴向载荷的容量检查的分步计算. 一些必需的检查已经在前面的设计示例中讨论过. 请参阅每个部分提供的链接.
分步计算
检查一下 #1: 计算焊接容量
完整的 拉伸载荷 受到抵制 整个焊缝断面, 而 剪切载荷分量 仅分布到总焊缝长度的一部分. 这部分是通过投影来确定的 90° 扇区 从柱的中心到其圆周. 因此, 只要 总周长的一半 旨在抵抗剪切载荷.
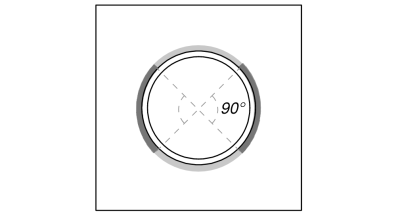
我们首先计算 总焊接长度 和 焊缝的一部分 90°投影范围内.
\(L_{焊接,满的} = pi d_{上校} = pi 次 193.7\ \文本{毫米} = 608.53\ \文本{毫米}\)
\(L_{焊接} = frac{\pi d_{上校}}{2} = frac{\pi times 193.7\ \文本{毫米}}{2} = 304.26\ \文本{毫米}\)
下一个, 我们计算 合成剪切载荷.
\(V_r = \sqrt{(v_y)^ 2 + (v_z)^ 2} = sqrt{(4\ \文本{千牛})^ 2 + (2\ \文本{千牛})^ 2} = 4.4721\ \文本{千牛}\)
然后我们计算 普通的 和 剪应力, 考虑到假设的负载分布.
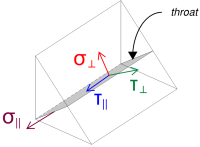
\( \sigma_{\人} = frac{n_x}{L_{焊接,满的}\,a\,\sqrt{2}} = frac{40\ \文本{千牛}}{608.53\ \文本{毫米} \次 4.95\ \文本{毫米} \次 sqrt{2}} = 9.39\ \文本{兆帕} \)
\( \你的_{\人} = frac{n_x}{L_{焊接,满的}\,a\,\sqrt{2}} = frac{40\ \文本{千牛}}{608.53\ \文本{毫米} \次 4.95\ \文本{毫米} \次 sqrt{2}} = 9.39\ \文本{兆帕} \)
\( \你的_{\平行} = frac{电压}{L_{焊接}\,一个} = frac{4.4721\ \文本{千牛}}{304.26\ \文本{毫米} \次 4.95\ \文本{毫米}} = 2.9693\ \文本{兆帕} \)
在那之后, 我们计算 综合压力 使用 在 1993-1-8:2005 情商. (4.1).
\(F_{w,ED1} = sqrt{(\sigma_{\人})^ 2 + 3\大的((\你的_{\人})^ 2 + (\你的_{\平行})^2\big)}\)
\(F_{w,ED1} = sqrt{(9.39\ \文本{兆帕})^ 2 + 3\大的((9.39\ \文本{兆帕})^ 2 + (2.9693\ \文本{兆帕})^2\big)}\)
\(F_{w,ED1} = 19.471\ \文本{兆帕}\)
与此同时, 我们确定 母材上的应力 使用相同的方程.
\(F_{w,ED2} = \sigma_{\人} = 9.39\ \文本{兆帕}\)
下一个, 我们计算 焊接能力. 我们首先确定 极限拉伸强度 (fu) 的 较弱的材料, 然后使用 在 1993-1-8:2005 情商. (4.1) 以获得 角焊缝电阻 和 贱金属电阻.
\(f_u = \min\!\剩下(F_{ü,\文本{上校}},\ F_{ü,\文本{BP}},\ F_{ü,w}\对) = 分钟!\剩下(550\ \文本{兆帕},\ 360\ \文本{兆帕},\ 500\ \文本{兆帕}\对) = 360\ \文本{兆帕}\)
\(F_{w,路德1} = frac{f_u}{\beta_w\,(\伽玛_{M2,\text{焊接}})} = frac{360\ \文本{兆帕}}{0.8 \次 (1.25)} = 360\ \文本{兆帕}\)
\(F_{w,路数2} = frac{0.9\,f_u}{\伽玛_{M2,\text{焊接}}} = frac{0.9 \次 360\ \文本{兆帕}}{1.25} = 259.2\ \文本{兆帕}\)
以来 19.471 兆帕 < 360 兆帕, 焊接容量是 充足的.
检查一下 #2: 计算由于张力负载而导致的基本板弯曲屈服能力
底板弯曲屈服能力的设计示例已在底板拉伸设计示例中讨论过. 请参阅此链接以了解分步计算.
检查一下 #3: 计算张力的混凝土突破能力
混凝土因拉力荷载而破裂的能力的设计示例已在张力底板设计示例中讨论过. 请参阅此链接以了解分步计算.
检查一下 #4: 计算锚推拉力
锚杆拉拔能力的设计示例已在张力底板设计示例中讨论过. 请参阅此链接以了解分步计算.
检查一下 #5: 计算Y方向的侧面井喷容量
Y 方向侧面防喷能力的设计示例已在张力底板设计示例中讨论过. 请参阅此链接以了解分步计算.
检查一下 #6: 计算Z方向的侧面井喷容量
Z 方向侧面防喷能力的设计示例已在张力底板设计示例中讨论. 请参阅此链接以了解分步计算.
检查一下 #7: 计算锚孔处底板承载力 (vy剪)
压缩和剪切底板设计实例中已经讨论了 Vy 剪切锚孔中底板承载能力的设计实例. 请参阅此链接以了解分步计算.
检查一下 #8: 计算锚孔处底板承载力 (VZ剪)
压缩和剪切底板设计示例中已经讨论了 Vz 剪切锚孔中底板承载能力的设计示例. 请参阅此链接以了解分步计算.
检查一下 #9: 计算混凝土破碎能力 (vy剪)
剪切力底板设计实例中已经讨论了因 Vy 剪切而导致混凝土破裂破坏能力的设计实例. 请参阅此链接以了解分步计算.
检查一下 #10: 计算混凝土破碎能力 (VZ剪)
剪切力底板设计实例中已经讨论了因 Vz 剪切而导致混凝土破裂破坏能力的设计实例. 请参阅此链接以了解分步计算.
检查一下 #11: 计算撬出容量
混凝土撬出能力的设计示例已在剪切底板设计示例中讨论过. 请参阅此链接以了解分步计算.
检查一下 #12: 计算锚杆剪切能力
的效果 拉力负荷 在此检查中考虑锚杆能力,如果 剪切力通过杠杆臂作用. 然而, 在这个例子中, 剪切作用 无杠杆臂. 因此, 锚杆上的剪应力和拉应力之间的相互作用将在 交互检查.
用于逐步计算无杠杆臂的剪切能力, 请参考此链接.
SkyCiv 底板设计软件可以执行所有必要的检查,以确定剪切载荷是否在有杠杆臂的情况下作用. 你可以 尝试免费工具 今天.
检查一下 #13: 计算锚钢相互作用校核
我们使用 在 1992-4:2018 桌子 7.3 情商. (7.54) 评估 剪应力和拉应力之间的相互作用 在锚杆上. 将拉应力和承载力以及剪应力和承载力代入方程, 结果 互动价值 是:
\(一世_{整数} = 左(\压裂{N_{埃德}}{N_{路,s}}\对)^ 2 + \剩下(\压裂{V_{埃德}}{V_{路,s}}\对)^2)
\(一世_{整数} = 左(\压裂{10\ \文本{千牛}}{49.22\ \文本{千牛}}\对)^ 2 + \剩下(\压裂{1.118\ \文本{千牛}}{38.604\ \文本{千牛}}\对)可以假设为 0.042117\)
以来 0.042 < 1.0, 锚杆钢失效相互作用校核为 充足的.
检查一下 #14: 计算混凝土失效相互作用检查
SkyCiv 还使用一些参数自动计算地面雪荷载 交互检查 需要用于 具体失败 同时承受剪切和拉伸载荷. 为了这, 我们用 在 1992-4:2018 桌子 7.3 情商. (7.55) 和 情商. (7.56).
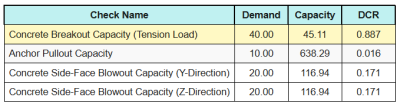
这是所有结果的比率 拉伸检查.
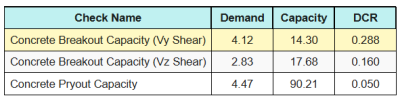
这是所有结果的比率 剪切检查.
第一, 我们检查使用 情商. (7.55) 并将结果与 最大交互限制 1.0.
\(一世_{\文本{案例1}} = 左(\剩下(\压裂{N_{埃德}}{N_{路}}\对)^{1.5}\对) + \剩下(\剩下(\压裂{V_{埃德}}{V_{路}}\对)^{1.5}\对)\)
\(一世_{\文本{案例1}} = 左(\剩下(\压裂{40}{45.106}\对)^{1.5}\对) + \剩下(\剩下(\压裂{4.1231}{14.296}\对)^{1.5}\对) = 0.99\)
下一个, 我们检查使用 情商. (7.56) 并将结果与 最大交互限制 1.2.
\(一世_{\文本{案例2}} = frac{N_{埃德}}{N_{路}} + \压裂{V_{埃德}}{V_{路}} = frac{40}{45.106} + \压裂{4.1231}{14.296} = 1.1752\)
以来 0.99 < 1.0 和 1.175 < 1.2, 的 混凝土失效相互作用检查 是 充足的.
设计概要
的 SkyCiv底板设计软件 可以自动为此设计示例生成逐步计算报告. 它还提供了执行的检查及其结果比率的摘要, 一目了然地使信息易于理解. 以下是示例摘要表, 报告中包括.
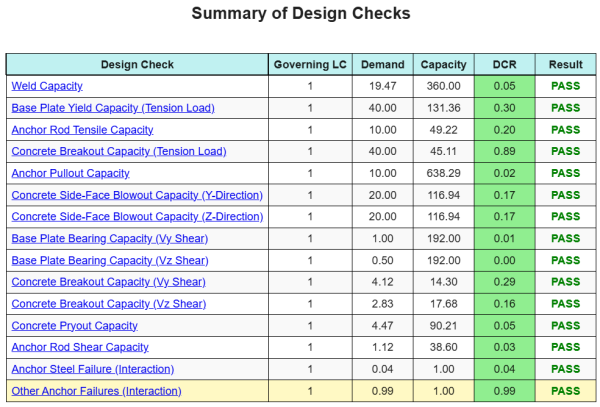
SkyCiv样本报告
查看 SkyCiv 底板设计报告的详细程度和清晰度. 该报告包括所有关键的设计检查, 方程式, 并以清晰易读的格式呈现结果. 完全符合设计标准. 单击下面查看使用 SkyCiv 底板计算器生成的示例报告.
(样本报告即将添加)
购买基板软件
单独购买基本板设计模块的完整版本,而没有任何其他SkyCiv模块. 这为您提供了底板设计的完整结果, 包括详细报告和更多功能.


