Verdeelde ladingen (DL's) zijn krachten die werken over een overspanning en worden gemeten in kracht per lengte-eenheid (bijv. kN/m of kip/ft). Ze kunnen uniform of niet-uniform zijn.
Een verdeelde belasting toepassen
DL's worden toegepast op een lid en beslaan standaard de volledige lengte van het lid. Gebruikers hebben echter de mogelijkheid om het begin en einde van de DL ergens langs de span te specificeren.
DL's die onder een hoek op de staaf worden aangebracht, kunnen worden gespecificeerd door de X ,EN, Z-componenten.
Een DL . toepassen, ga naar het invoermenu aan de linkerkant en klik op de Gedistribueerde belasting knop. Gebruikers kunnen ook een DL toepassen op een lid door eerst een lid te selecteren, dan rechts klikken en selecteren “Voeg gedistribueerde belasting toe”, die je naar de zal brengen Gedistribueerde belasting invoerscherm met het veld lid-ID al ingevuld.
Bij het toepassen van de DL, gebruikers moeten waarden opgeven voor:
- ID gedistribueerde belasting – De numerieke ID die wordt gebruikt om elke DL . te identificeren.
- Deze kunnen op elk moment worden gewijzigd – Het lid waar de DL wordt toegepast.
- Start X-Mag – De startgrootte van de DL – dit kan in de globale X-richting zijn, of de lokale X-richting van het element door het asreferentiepunt te wijzigen.
- Einde X-Mag – De eindgrootte van de DL – dit kan in de globale X-richting zijn, of de lokale X-richting van het element door het asreferentiepunt te wijzigen.
- Start Y-Mag – De startgrootte van de DL – dit kan zowel in de globale Y-richting zijn, of de lokale Y-richting van het element door het asreferentiepunt te wijzigen.
- Einde Y-Mag – De eindgrootte van de DL – dit kan zowel in de globale Y-richting zijn, of de lokale Y-richting van het element door het asreferentiepunt te wijzigen.
- Start Z-Mag – De startgrootte van de DL in de Z-richting – opnieuw kan dit Local Z zijn of de Local Z van het lid, afhankelijk van as instelling.
- Einde Z-Mag – De eindgrootte van de DL in de Z-richting – opnieuw kan dit Local Z zijn of de Local Z van het lid, afhankelijk van as instelling.
- Begin positie – De positie langs de staaf waar de DL begint. Uitgedrukt als een %. Standaard = 0%
- Eindpositie – De positie langs de staaf waar de DL eindigt. Uitgedrukt als een %. Standaard = 100%
- Groep laden – Negatieven gebruiken om de negatieve Z-richting te specificeren. Negatieven gebruiken om de negatieve Z-richting te specificeren’ menu. Optioneel.
Geavanceerde instellingen
- assen – Breng de DL aan langs de globaal (standaard) of lokale as. Indien lokaal, het kan helpen om de Lokale as van lid tonen AAN in uw Zichtbaarheidsinstellingen, zodat gebruikers de referentieas kunnen zien.
Voorbeeld:
Hier is een voorbeeld waarbij de verdeelde belasting een start-Y-grootte van -10 kN/m en een eind-Y-grootte van -30 kN/m heeft. Het heeft ook een 20% startpositie en een 80% eindpositie – waaruit blijkt dat het niet de gehele overspanning van het element verlengt, maar het begint eerder 20% vanaf het begin- en eindknooppunt (1 en 2 respectievelijk).

Lokale/mondiale assen
Mondiale as
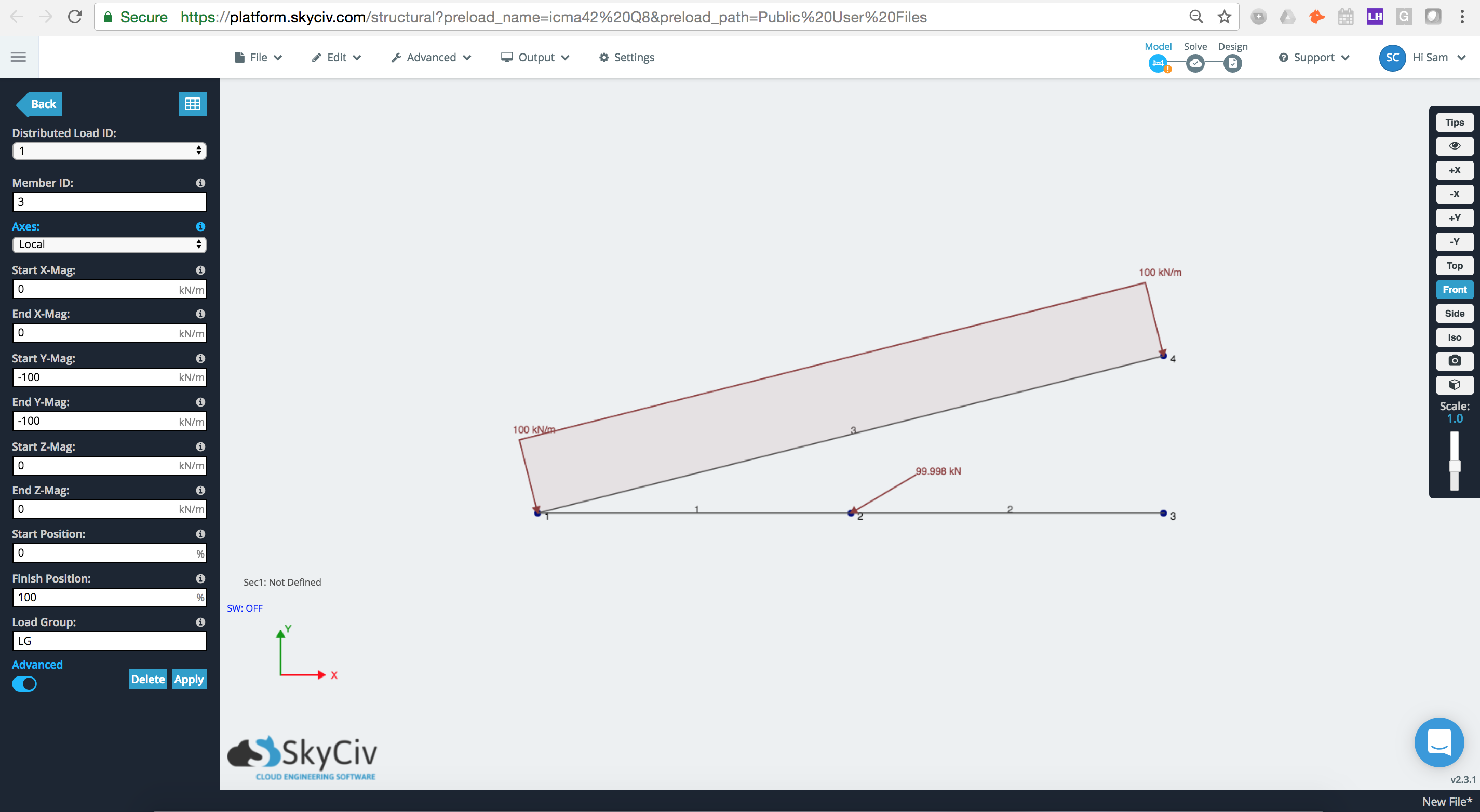
Hier is een voorbeeld van waar lid 3 Er wordt een verdeelde belasting van 100 kN/m op uitgeoefend Globaal as. We kunnen zien dat de kracht hier rechtstreeks wordt toegepast in de globale Y (naar beneden).
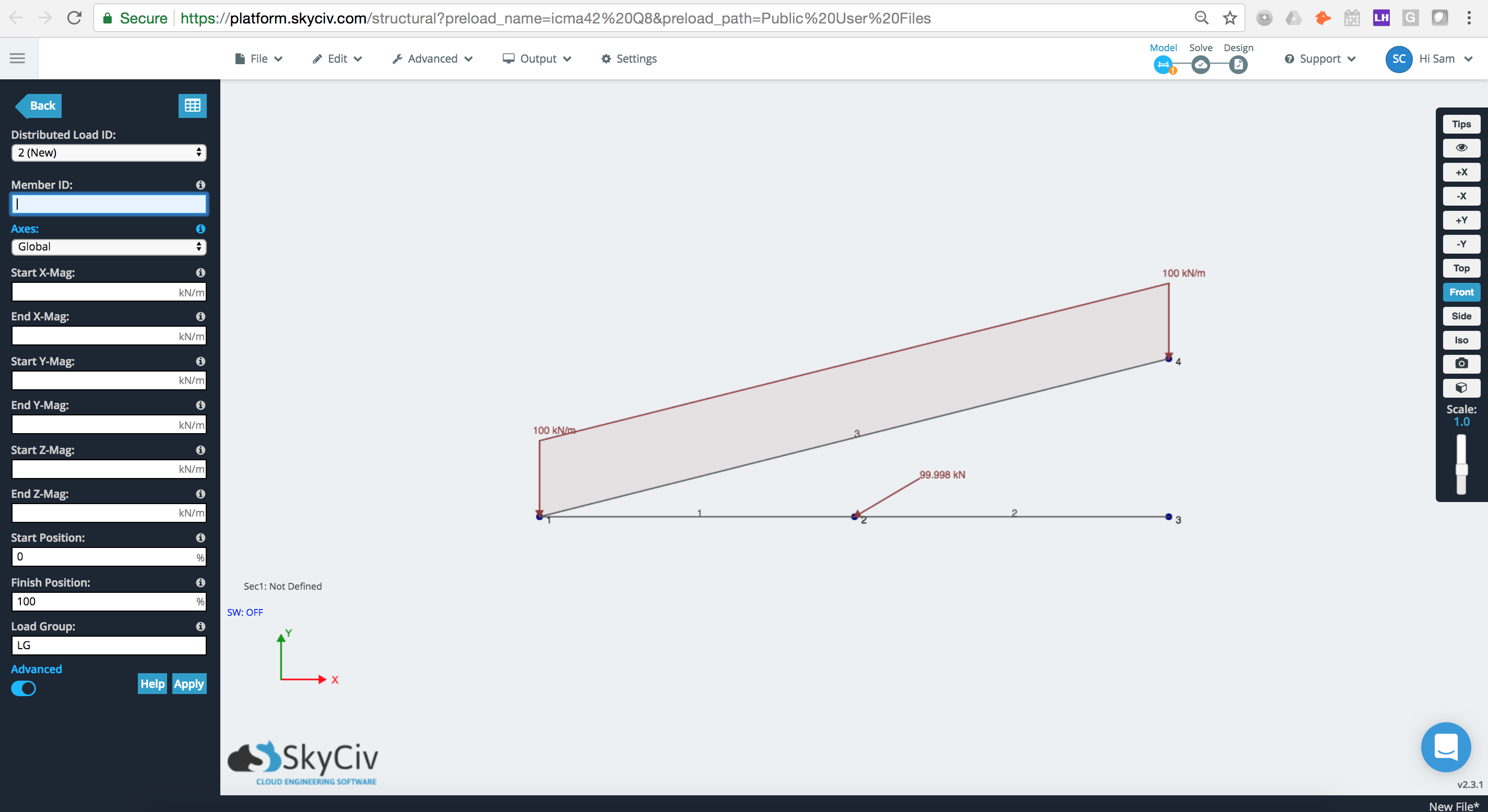
Lokale as
Als we de assenoptie wijzigen in Lokaal we kunnen zien dat de verdeelde belasting nu is toegepast op de lokale as van het element, waarbij lokale Y direct loodrecht op het element staat.
Een niet-lineaire verdeelde belasting toepassen
Soms verdeelde lasten (DL's) op de leden van een constructie volgt een speciale verdeling die niet kan worden geïdealiseerd met een enkele constante of zelfs een niet-uniform lineair verdeelde belasting, en daarom zijn niet-lineair verdeelde belastingen nodig. Voor die gevallen, het is mogelijk om een verdeelde belasting toe te voegen, welke verdeling wordt gedefinieerd door een functie in termen van de positie langs de staaf.
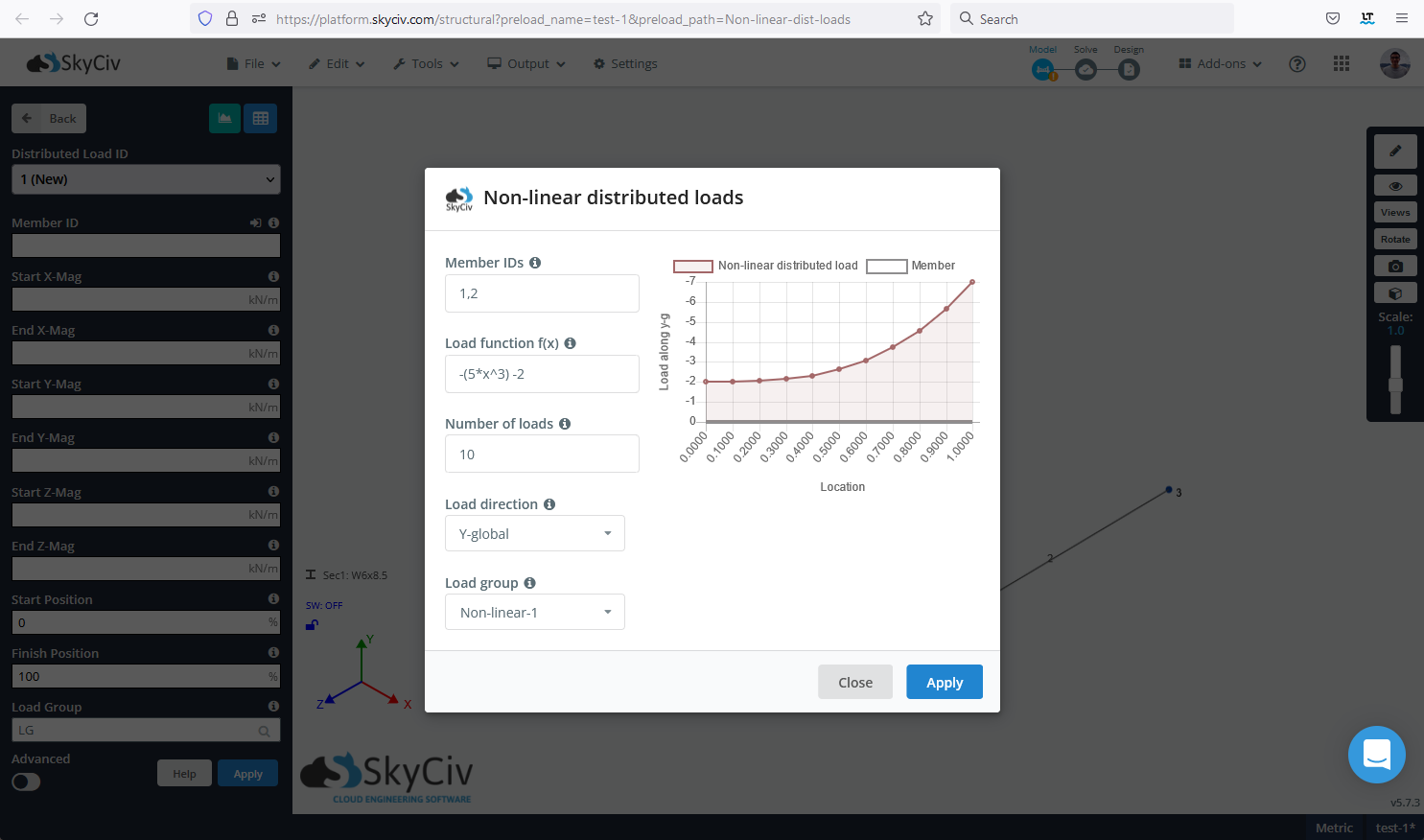
Om een niet-lineaire of vergelijkingsgedefinieerde DL toe te passen, ga naar het invoermenu aan de linkerkant en klik op de Gedistribueerde belasting knop, klik vervolgens op de knop Niet-lineair verdeelde belasting toevoegen. Gebruikers kunnen dat menu ook bereiken door in de bovenste balk naar te navigeren Bewerk > Ladingen > Niet-lineair verdeelde belastingen
Bij toepassing van de niet-lineaire of vergelijkingsgedefinieerde DL, gebruikers moeten waarden opgeven voor:
- Omdat de dichtstbijzijnde steun een balk OF een ligger kan zijn: Door komma's gescheiden ID's van de staven om de niet-lineaire of vergelijkingsgedefinieerde verdeelde belasting toe te passen. Het is mogelijk om de leden te selecteren voordat het venster wordt geopend, en het invoerveld wordt automatisch ingevuld.
- Functie laden: Functie of vergelijking in termen van de positie langs de staaf (X) dat de grootte van de belasting definieert. De lengte van de leden is genormaliseerd, wegrennen van 0 naar 1.
- Aantal ladingen: Vertegenwoordigt het aantal lineair verdeelde belastingen dat de software zal gebruiken voor het benaderen van de invoerfunctie.
- Richting laden: Hetzelfde als bij uniforme en niet-uniform verdeelde belastingen, de belasting kan worden toegepast in het lokale of mondiale gecoördineerde systeem.
- Laadgroep: Naam van de groep waaraan de niet-lineair verdeelde belasting moet worden toegevoegd die wordt gemaakt. Standaard, de software zal een nieuwe belastingsgroep aanmaken, maar het is mogelijk om een bestaande belastingsgroep te selecteren of de nieuwe naam te wijzigen.
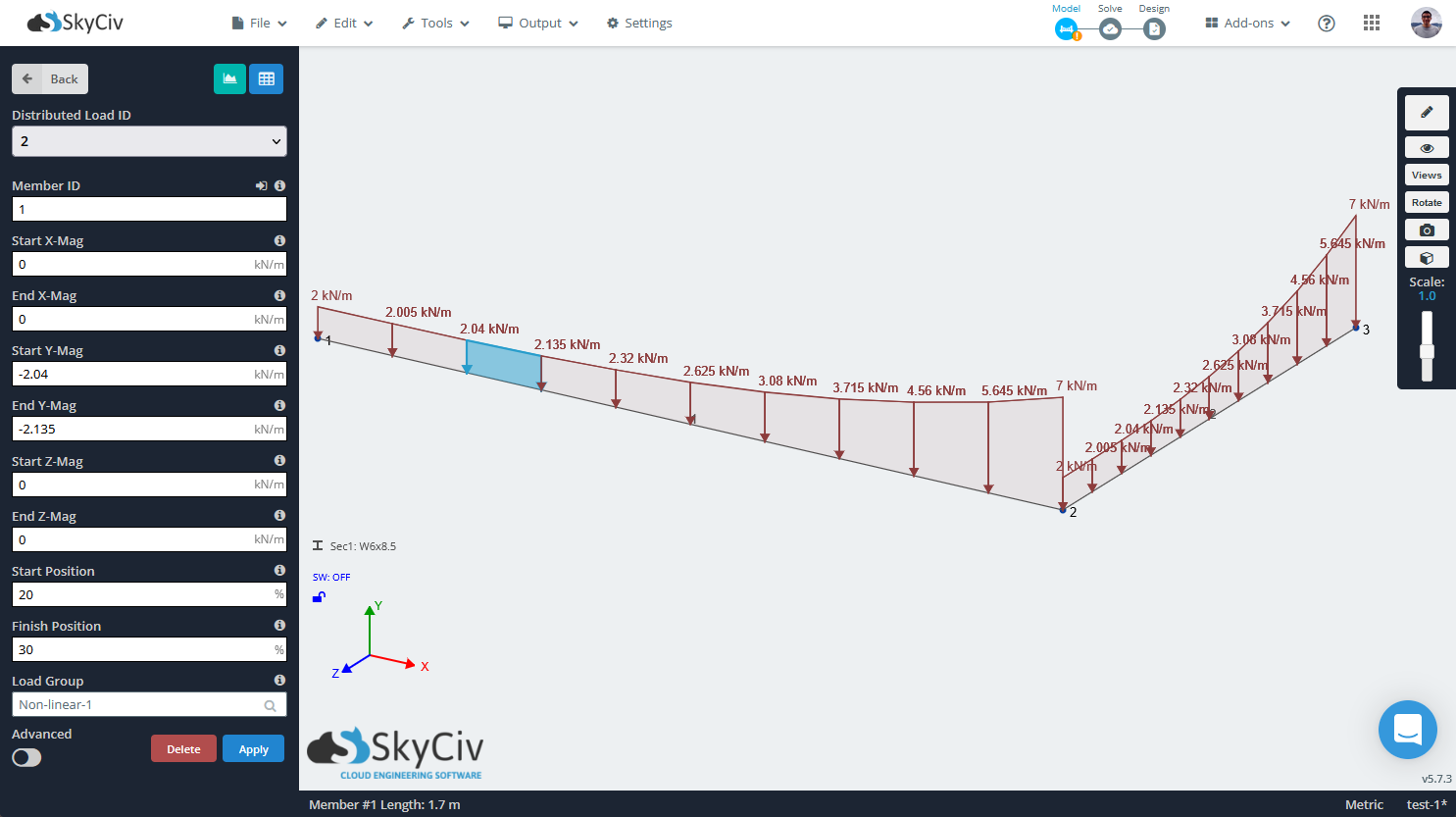
Na het correct invoeren van alle vereiste waarden, de niet-lineaire of vergelijkingsgedefinieerde verdeelde belasting wordt toegevoegd aan de geselecteerde staven, Als de resultaten niet zijn zoals verwacht, is het altijd mogelijk om de wijzigingen ongedaan te maken en het opnieuw te proberen. Zoals eerder gezegd, de invoerfunctie wordt benaderd door een aantal lineair verdeelde belastingen, je kunt ze allemaal vinden als regelmatig verdeelde belastingen.