Dans la mise à jour la plus récente du générateur de combinaisons de charges, nous avons simplifié le fonctionnement interne du module et ajouté la fonctionnalité suivante:
- La génération de combinaisons de charges est définie par un seul fichier .json (Schéma) pour chaque norme.
- Des groupes et combinaisons de charges peuvent être créés sans avoir à attribuer des charges au préalable dans l'espace de modélisation S3D..
- Motifs, qui sont basés sur les anciens “Augmenter les charges de vent” case à cocher, fonctionne maintenant avec tous les cas de charge.
Nomenclature
Dans la dernière version du générateur de combinaison de charges, le nom du cas de charge qui a été utilisé pour beaucoup de choses:
- Agir comme un identifiant unique.
- Faire la différence entre la charge super cas et est la distance horizontale entre l'avant-toit et le faîte, et nécessitent toujours une valeur dans chaque (menant à des bizarres comme Morte: mort).
- Rester lisible par l'homme, tout en restant suffisamment petit pour des menus déroulants en contractant des mots (Habitent: Q-dist-toit-plancher).
Dans la mise à jour la plus récente, nous avons divisé les noms de cas de charge en symboles, qui sont compacts et utilisés lorsque l’espace est limité (lors de la dénomination des combinaisons de charges par exemple: 1.25D1 + 1.5La formule de moment statique + 1.5Ld + 0.5SL + 0.5T), et étiquettes, qui sera descriptif (utilisé par exemple dans les listes déroulantes). Les deux symboles et étiquettes devra être unique au sein d’une norme donnée. Nous autoriserons également cas de charge porter le même nom que la charge super cas, généralement pour le cas de charge par défaut (le plus couramment utilisé). Les deux exemples utilisés ci-dessus seraient divisés comme ceci:
{"D": "Mort"}
{"Ldr": "En direct - Concentré, Toits, Sol"}
Ce logiciel symbole doit être composé au minimum d'une lettre majuscule, qui définit le super cas. Ce logiciel super cas est un nouveau concept, utilisé pour regrouper des cas de charge similaires qui agissent généralement ensemble. Ce logiciel super cas l'étiquette est donnée au début de l'étiquette du cas de charge (avant le sprint). Dans l'exemple ci-dessus (Eurocode) le cas de charge Ldr ferait partie du super cas L (nommé Live dans le label), aux côtés d'autres cas de charge comme Ldd et Ldo. Dans les coulisses, l' super cas est principalement utilisé pour appliquer les règles de filtrage, c'est-à-dire déterminer quelles lignes de schéma doivent être conservées et lesquelles doivent être supprimées.
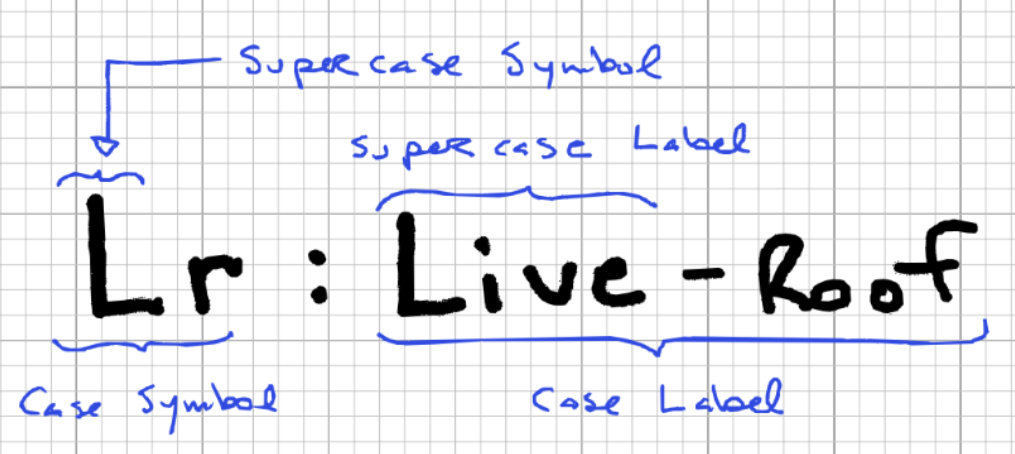
La première partie de l'étiquette (avant le sprint) est le nom du super cas. La deuxième partie est une description, utiliser des virgules pour séparer les catégories des sous-catégories. La deuxième partie est facultative, mais un seul cas de charge peut prendre la valeur par défaut super cas place.
Lignes de schémas standard
Chaque norme a un schéma qui définit complètement toutes les combinaisons de charges possibles pour cette norme. Ce logiciel Schéma.json le fichier est assez simple, mais ça peut devenir assez long, surtout dans les normes (comme l'Eurocode) qui nécessitent une multitude de permutations. Pour prendre un exemple simple, prenons l'exemple d'exigence suivant.
1.2*D + 1.5*L + (0.5*S ou 0,5*W ou 0,5*T)
Pour convertir cela en notre schéma, nous devons le décomposer en chaque permutation possible:
1.2*D + 1.5*L 1.2*D + 1.5*L + 0.5*S 1.2*D + 1.5*L + 0.5*W 1.2*D + 1.5*L + 0.5*T 1.2*D + 1.5*L + 0.5*S + 0.5*W 1.2*D + 1.5*L + 0.5*W + 0.5*T 1.2*D + 1.5*L + 0.5*T + 0.5*S 1.2*D + 1.5*L + 0.5*S + 0.5*W + 0.5*T
Une fois que chaque combinaison de charges est répertoriée de cette manière, vous pouvez créer le schéma en suivant ces étapes:
- Utilisez chaque clé et coefficient de cas de charge pour créer un objet de ligne de schéma.
- Nommez chaque ligne avec un identifiant unique (puisque ça va être un objet). La convention est d'utiliser des tirets pour séparer les différents éléments du nom.
- Un niveau au dessus, regrouper les lignes en critères (force, facilité d'entretien, accidentel, etc.)
Le résultat final devrait ressembler à ceci:
"Lignes": {
"force":{
"A-1-u": {"D": 1.40},
"A-2a-u":{"D": 1.25, "L": 1.50, "Ls": 1.50},
"A-2b-u":{"D": 1.25, "L": 1.50, "Ls": 1.50, "S": 1.00},
"A-2c-u":{"D": 1.25, "S": 1.50, "W": 0.40},
"A-3a-u":{"D": 1.25, "S": 1.50}
}
}
Algorithme de génération de combinaison de charges
L'algorithme passe par plusieurs étapes pour générer l'objet de combinaison de charge final:
- Ce logiciel schéma as defined above is needed. It will be passed to the main load combination generation function.
- An object is created to group the number of cas de charge par pattern. Par exemple, let’s look into a request for the load cases below:
2 Dead load case, with a merge pattern 4 Wind load cases, with an individual pattern 1 Snow load cases, with an individual pattern 2 Dead load cases, with a merge pattern
Grouping the motifs par est la distance horizontale entre l'avant-toit et le faîte will give the following object, which will be passed to the main load combination generation function.
input_by_case =
{
"D": {"fusionner": [2, 2], "individuel": []},
"W": {"fusionner": [], "individuel": [4]},
"S": {"fusionner": [], "individuel": [1]}
}
- The last two arguments are filtering objects, which allow for filtering by criteria ou par clé de schéma.
- Une fois qu'il a tous les arguments requis, la fonction principale de génération de combinaison de charge est appelée. Cette fonction parcourt plusieurs boucles imbriquées pour générer chaque combinaison requise, qui sont expliqués dans les puces suivantes, et illustré dans la figure suivante.
- Au plus haut niveau, il parcourt les lignes du schéma. Chaque ligne est vérifiée pour voir si elle doit être conservée ou ignorée à cette étape, en utilisant les objets de filtrage et la logique spécifique décrite dans la section ci-dessous.
- Dans la première boucle se trouve une seconde, qui parcourt chaque demande est la distance horizontale entre l'avant-toit et le faîte dans la ligne du schéma. Si la demande est la distance horizontale entre l'avant-toit et le faîte existe également la ligne du schéma (les requêtes sont résumées dans l'objet input_by_case), puis nous passons au niveau suivant.
- Dans la deuxième boucle se trouve une troisième, qui parcourt chaque possible pattern pour voir s'il y a des groupes de charges à générer en leur sein, et exécute la fonction pour les nommer et les générer quand ils le font.
- Une fois que tous les cas de charge de la ligne du schéma ont été générés et nommés, ils sont recombinés (à côté de leurs coefficients) en une ou plusieurs combinaisons de charges.

- Ce processus est répété pour chaque ligne du schéma, pousser toutes les combinaisons de charges générées dans l'objet de combinaison de charges finale.
Cela ne vaut rien que toute la logique liée aux modèles se déroule à l'intérieur d'une seule ligne de schéma.. Il est important de savoir cela pour comprendre le comportement des modèles. Le modèle de fusion, par exemple, ne permet pas de fusionner autre chose que le cas de charge auquel il est affecté. Cela signifie que vous ne pouvez pas:
- Fusionner différents cas de charge ensemble, comme essayer de fusionner les groupes de charge D1 et L1.
- Fusionner les cas de charge identiques sur différentes lignes de la table d'entrée. Par exemple, dans l'exemple donné au point #2 au dessus, on nous demande de générer 2 charges mortes utilisant le modèle de fusion sur deux lignes distinctes. Les combinaisons de résultats finaux ressembleraient alors à quelque chose comme ceci:
1.2*D1 + 1.2*D2 + 1.5*L 1.2*D3 + 1.2*D4 + 1.5*L 1.2*D1 + 1.2*D2 + 1.5*L + 0.5*S 1.2*D3 + 1.2*D4 + 1.5*L + 0.5*S 1.2*D1 + 1.2*D2 + 1.5*L + 0.5*W 1.2*D3 + 1.2*D4 + 1.5*L + 0.5*T
Filtrage automatique des combinaisons de charges inutiles
Alors que l'algorithme ci-dessus est fonctionnel sans aucun filtrage, cela peut conduire à des combinaisons de charges redondantes, ce qui entraîne un temps de calcul supplémentaire et des résultats redondants. Prenez les combinaisons de charges suivantes:
1.2*D + 1.5*L 1.2*D + 1.5*L + 0.5*S 1.2*D + 1.5*L + 0.5*W 1.2*D + 1.5*L + 0.5*T
Si nous avons un seul cas de charge morte, ces quatre combinaisons de charges donneront lieu à des combinaisons de charges identiques:
1.2*ré 1.2*D 1.2*D 1.2*D
Pour éviter cette situation, quatre règles sont utilisées, chacune contenant quelques légères exceptions. Première, jetons un oeil aux règles. L'état par défaut est que la combinaison soit conservée et les règles sont utilisées pour déterminer laquelle exclure.
Filtrage par critères
Ce cas est assez explicite. Si la criteria is not requested, toutes les lignes de schéma associées à cela criteria sont rejetés.
Filtrage par caractères dans la clé de schéma
Les clés de schéma sont généralement des pointeurs séparés par des virgules vers la référence d'origine. Par exemple, dans l'exemple du NBCC ci-dessous, la clé a trois composants:
- A: Le premier terme est généralement la référence principale, référencer le tableau dans lequel cette partie des charges est prise.
- 2b: Le deuxième terme est généralement un identifiant unique pour la combinaison de charges à l'intérieur du tableau..
- u: The third term is usually reserved to indicate when a large number of load combinations are permuted with a slight modification. Par exemple, it can indicate if the dead loads in the load combination are favorable ( F ) or unfavorable ( u ).
{
"force":{
"A-2b-u":{"D": 1.25, "L": 1.50, "Ls": 1.50, "S": 1.00},
}
}
Le filtrage dans la clé de schéma peut être effectué pour n'importe lequel de ces termes. Par exemple, si on veut filtrer par le troisième terme, nous pouvons ajouter le filtre suivant, ce qui créera une liste déroulante de filtrage pour ce terme:
"nom_filtres": {
"Force": {
"Poids mort": {
"positionner": 2,
"info-bulle": "",
"articles": {
"Favorable": "F",
"Défavorable": "u"
},
"valeurs par défaut": ["Favorable", "Défavorable"]
}
}
}
Tous les noms de listes déroulantes possibles et les termes associés doivent être répertoriés sous « éléments ». Seules les lignes du schéma avec les symboles correspondants seront conservées. S'il est nécessaire de conserver une ligne de schéma indépendamment de ce qui est saisi dans le filtre, le terme peut rester vide. Toute clé de schéma qui ne contient pas tous les termes déroulants correspondants sera ignorée..
Combinaisons redondantes
Si une ligne de schéma n'est pas filtrée par les deux premières étapes, on passe à l'étape numéro trois. Dans cette étape, le problème de redondance de l'exemple ci-dessus est résolu. Pour faire ça, we need to look at two objects simultaneously, schema row and the sorted input_by_case object (see description above), which describes which load cases have been requested. If the schema row contains any super case which the input_by_case object does not, the load combination is removed. Take, par exemple, the following schema row:
"A-2a-u":{"D": 1.25, "L": 1.50, "S": 1.50}
and the following input_by_case object:
input_by_case =
{
"D": {"fusionner": [], "individuel": [1]},
"L": {"fusionner": [], "individuel": [4]}
}
Dans cet exemple, the schema row contains a super cas S which has not been requested. Keeping this row would lead to a load combination that would be identical to the load combination associated with the schema row below, donc il est supprimé.
"A-1a-u":{"D": 1.25, "L": 1.50}
Exceptions
Bien que ce comportement soit généralement souhaitable, il y a des cas où NE PAS supprimer une ligne lorsque le cas de charge est absent conduit à un schéma beaucoup plus simple. Par exemple, si nous avons des charges de terre horizontales qui devraient être ajoutées à chaque combinaison de schéma, mais ne sont pas toujours présents, we could copy and paste all of the load combinations and modify the schema key for the new rows with a suffix like “h” for horizontal earth loads. Aussi, we can simply add the horizontal earth load to all of the cases and add a keep exception to the load case in the meta data. That way, if the load case is not requested, it will not show up, but the row will still be kept. The result looks something like this in the schema’s meta property:
"H": {
"dimension gousset": "Lateral earth - Défavorable",
"rank": 1,
"exceptions": ["keep"],
"old_labels": []
},
Superfluous combinations
If a schema row is not filtered out by the first three steps, it moves on to step number four. Dans cette étape, the issue of matching specific load cases between the schema and what is requested. If a schema row and a request have matching super cases, but the specific load case requested is not in the schema, the row will not be kept. Take, par exemple, the following schema row:
"A-2a-u":{"D": 1.25, "SL": 1.50}
and the following input_by_case:
input_by_case = { "D": {"fusionner": [], "individuel": [1]}, "Sh": {"fusionner": [], "individuel": [1]} }
Dans cet exemple, both the schema row and the request have matching super cases. Par contre, la demande nécessite une combinaison avec Sh, ce que la ligne du schéma ne fournit pas. C'est à dire, la ligne du schéma n'est pas conservée.
Exceptions
Encore une fois, ce comportement est généralement souhaitable, mais peut entraîner des problèmes. L'un de ces problèmes est lorsque les normes ont des cas de charge qui partagent un super cas, mais n'agissez pas simultanément. Par exemple, en ASCE, les charges de vent W et les charges de tornade Wt n'agissent pas simultanément, bien qu'ils partagent le même super cas W. Quand nous rencontrons ce problème, on peut ajouter une exception pour passer à une autre super cas avant que le code ne s'exécute dans les métadonnées. Dans les coulisses, le symbole qui suit le “->” les caractères seront attribués au cas de charge, qui simulera les cas de charge agissant dans ce super cas. The result looks something like this in the schema’s meta property:
"Poids" : {
"dimension gousset": "Vent - Tornade",
"rank": 8,
"exceptions": ["supercase->X"],
"old_labels": []
},
Dans le cas ci-dessus, l' super cas “W” sera échangé contre “X” avant que le code ne s'exécute. Cette fonctionnalité peut également être utilisée pour envoyer des cas de charge de groupe ayant des caractéristiques uniques. super cas symboles ensemble.


