A guide on the Direct Strength Method for Cold Formed Steel
Cold-formed steel member design is challenging due to the complex stability behavior of the thin-walled members. 为了解决这个问题,已经开发了几种方法, 就像直接强度法一样 (帝斯曼), 最灵活、最现代的方法. SkyCiv is committed to help supporting DSM, through resources such as this and software that supports cold formed steel design through this approach.
DSM 无需计算有效宽度即可预测冷弯构件强度 [1] (有效宽度计算通常是一个复杂的过程,对于分析复杂的几何形状有很多限制). 用这种方法, the calculation of critical buckling strength can be carried out in various approaches, 主要是有限条法 (有限状态机) 和有限元法 (五). 在本指南中, 我们将探索:
- 什么是直接强度法
- Acceptance and Adoption in the Industry
- 传统有限条法
- Buckling Mode Types
- What are the DSM Factors?
- SkyCiv 剖面生成器中的有限条法
什么是直接强度法 (帝斯曼)
的 直接强度法 (帝斯曼) is a design approach used predominately for the analysis and design of cold-formed steel members. Unlike traditional methods (such as the Effective Width Method) that rely on calculating effective section properties to account for local buckling, the DSM directly computes the member’s strength using its full, unreduced cross-sectional properties.
Pros and Cons of Direct Strength Method
| 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|
| Simplifies Design Process: Reduces complexity by eliminating effective width calculations. | Learning Curve: Requires engineers to become familiar with new concepts and formulations. |
| Enhanced Accuracy: Directly accounts for various buckling modes for precise strength predictions. | Limited Historical Data: Less empirical data available for some specific applications compared to traditional methods. |
| Versatile Application: Suitable for complex and unconventional cross-sections. | Software Dependence: May require advanced software tools not readily available to all practitioners. |
| Unified Methodology: Provides a consistent approach across different buckling behaviors. | Standard Compliance: Not all regional codes may fully incorporate DSM provisions yet. |
| Facilitates Innovation: Encourages the use of new materials and shapes due to its adaptable framework. | Resistance to Change: Industry inertia can slow adoption as practitioners stick to familiar methods. |
Adoption and Acceptance:
The DSM is recognized and incorporated into major international design standards, 如:
- AISI S100: 北美冷弯型钢结构构件设计规范.
- AS / NZS 4600: Australian/New Zealand Standard for Cold-Formed Steel Structures.
DSM is also being prioritised as a future method by being taught in universities and becoming a more common method taught in cold formed design courses. We’re also seeing an increase in it’s support by structural analysis and design software packages who are integrating DSM into their design modules.
然而, there are still some obstacles and challenges in the DSM being widely-adopted, since it is a relatively new/untaught method. Transitioning from traditional methods requires training and adaptation, which some practitioners can be reluctant to undertake.
传统有限条法
FSM 是作为 FEM 的简化而创建的, 两种方法具有相同的理论背景, and the FSM is also a matrix method. By defining the nodes and elements of a section it is possible to analyze any complex shape. 这鼓励部分优化并简化分析过程.
几种选择, 包括开源工具, 目前可用于执行有限带分析. 然而, integrating these tools with general analysis and design software has proved challenging due to their complex nature. SkyCiv has recently built a Finite Strip Method analysis tool which is fully integrated into our 分区生成器 软件. This tool automates calculation of DSM factors for standard and custom cold-formed sections, allowing for DSM steel design in accordance with AISI S100, 如 4600 and other international standards.
The FSM discretizes the section’s transversal shape into longitudinal strips [3]. This simplifies the traditional 3D analysis problem with 6 degrees of freedom to a problem with 4 自由程度. The strips are analyzed for different lengths called half-wavelength.
Using the geometrical section properties, 材料, the stresses, and the load condition, two global matrices are constructed, the elastic stiffness matrix (Ke) and the geometric stiffness matrix (Kg).
最后, this represents an eigenvalue decomposition problem, 其中特征值代表负载因子, 特征向量包含变形的形状.
![]()
Buckling Mode Types
屈曲类别分为三个主要组, 全球的, 当地的, 和扭曲的, 取决于故障类型.
局部屈曲: 涉及横截面严重变形的屈曲, 但这种扭曲只包括旋转, 不是翻译, 在内部折叠线处 [2].
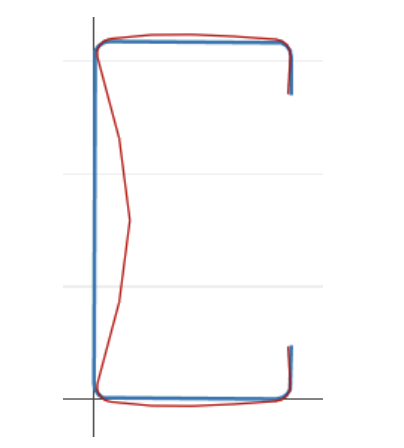
扭曲屈曲: 涉及横截面严重变形的屈曲, 但这种变形包括在构件的一个或多个内部折叠线处的旋转和平移 [2].
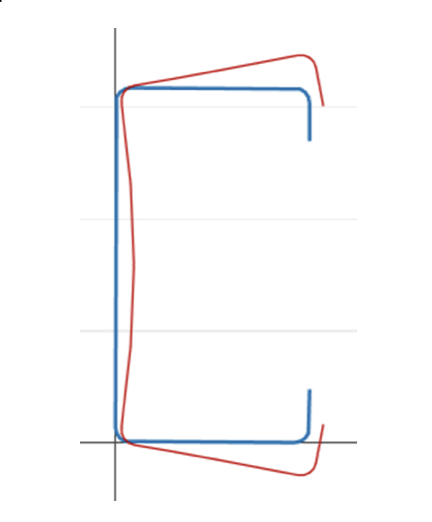

全局屈曲: 不涉及横截面扭曲的屈曲, 而是翻译 (弯曲) 和/或旋转 (扭力) 整个横截面发生 [2].
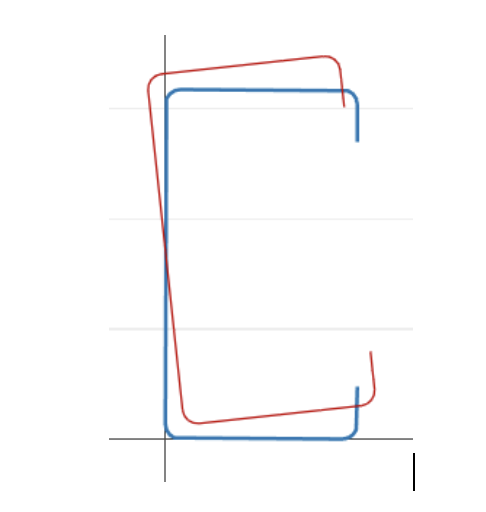
通过这个定义我们可以推断屈曲分类和变形形状之间存在很强的几何相关性, 我们显示了签名曲线每个点的变形.
DSM Factors
SkyCiv 剖面生成器中的有限条法
SkyCiv has a Direct Strength Method Calculator built into our Section Analysis Software (SkyCiv版块生成器) which can automatically calculate the key DSM factors for any custom cold formed steel shape. Simply start from the Section Builder module by loading in a CFS section and clicking Design -> 冷弯钢:
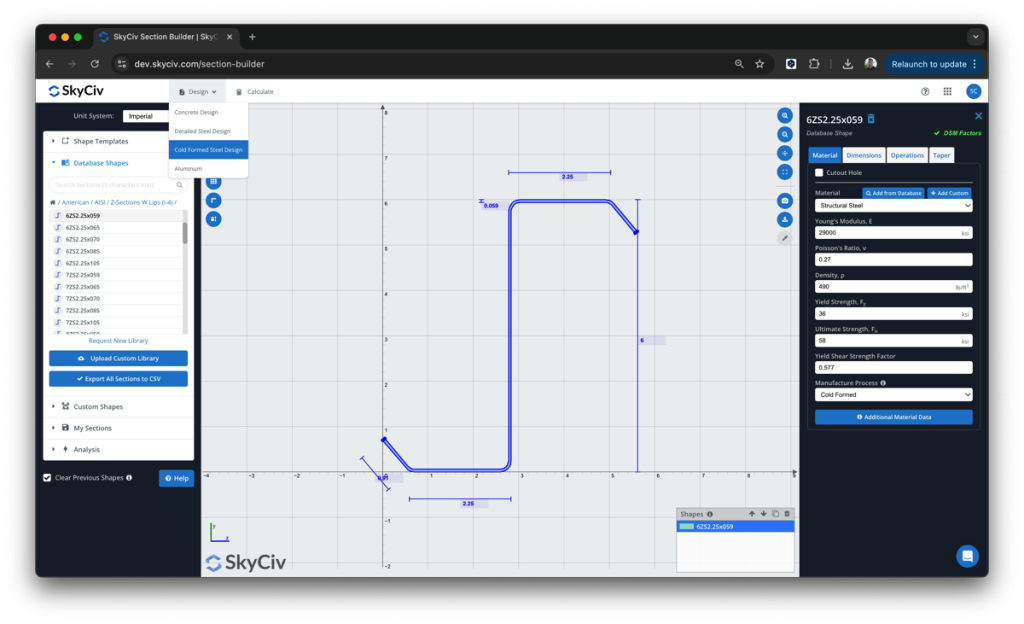
从这里, the DSM factors will be automatically calculated, ready for the user to review and submit:
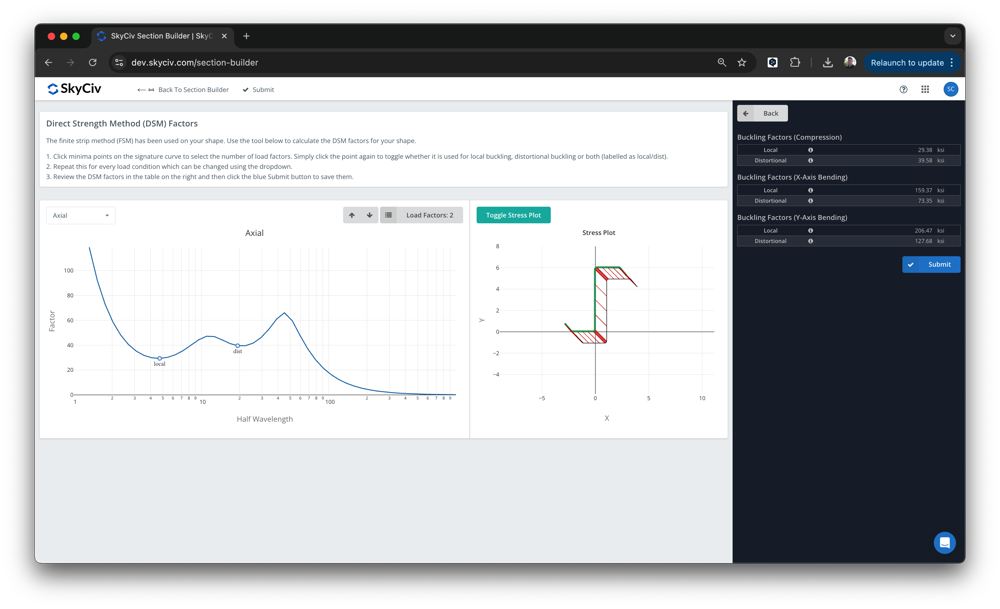
该软件构建在 SkyCiv Section Builder 之上, 下 设计 – 冷成型. 将自动检测局部和扭曲屈曲最小值, 但是用户可以覆盖这些值. 一旦提交, 这些因素将用于 SkyCiv AISI 的设计 (2016) 和AS4600 (2018) 集成设计模块.
SkyCiv 弹性屈曲分析模块中, 我们在此澄清一些重要的假设和考虑因素. 我们将在下面探讨这些:
元素网格
The mesh of the elements is produced automatically and can be viewed in the right chart, 鱼片被分成 4 元素, 和直线进入 4 元素也.
分析长度
用于执行有限带分析的长度默认定义为对数空间: 0 到英制单位系统中的 10^3 以及从 0 公制为 10^3.5.
负载条件
我们计算签名曲线 5 不同的负载条件:
- 轴向载荷
- X轴弯矩, 积极的
- X轴弯矩, 消极的
- Y轴弯矩, 积极的
- Y轴弯矩, 消极的
边界条件
假设模型被固定并在两端自由扭曲来进行分析.
特征曲线
使用传统的有限条带法构建签名曲线, Fy 标准化 (风 = 1) 因此负载系数以压力单位表示 (MPa 或 ksi 根据单位制).
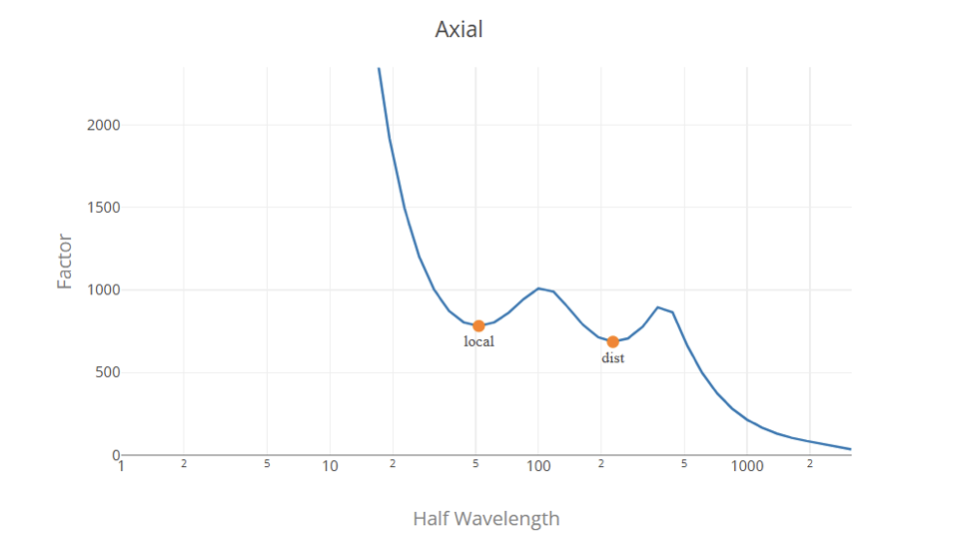
负载系数选择
通常, 负载因子是特征曲线中的局部最小点, 第一个代表局部屈曲的临界载荷系数,第二个代表扭曲屈曲的临界载荷系数. 从特征曲线确定全局负载因子是一项艰巨的任务,因为特征曲线中没有局部最小值点. 所以, 最合适的解决方案是使用有限带分析中的局部和扭曲屈曲载荷因子以及使用经典公式的全局屈曲因子.
我们使用算法来查找和分类签名曲线中的负载因子. 然而, this does not ensure a correct classification in all the cases, and this does not replace the engineering judgment, 我们鼓励用户在提交之前检查这些值并在必要时进行修改.
参考资料
- 北美冷弯型钢结构构件设计规范, 2016 版, 美国钢铁协会.
- 直接强度法 (帝斯曼) 设计指南, 2006, 冷弯型钢结构构件设计规范委员会.
- 使用 CUFSM 进行冷弯型钢构件的屈曲分析: 传统和约束有限条法, 体重. 谢弗和S. 阿达尼, 2006, 18第六届国际冷弯型钢结构专业会议.

