A guide on the Direct Strength Method for Cold Formed Steel
Cold-formed steel member design is challenging due to the complex stability behavior of the thin-walled members. Bu sorunu çözmek için çeşitli yöntemler geliştirilmiştir, Doğrudan Mukavemet Yöntemi gibi (DSM), en esnek ve modern yaklaşım. SkyCiv is committed to help supporting DSM, through resources such as this and software that supports cold formed steel design through this approach.
DSM, etkin genişlikleri hesaplamadan soğuk şekillendirilmiş eleman mukavemetine ilişkin tahminler sağlar [1] (Etkin genişliklerin hesaplanması genellikle karmaşık geometrik şekillerin analiz edilmesinde birçok sınırlamanın bulunduğu karmaşık bir süreçtir.). Bu yöntemde, the calculation of critical buckling strength can be carried out in various approaches, esas olarak Sonlu Şerit Yöntemi (FSM) ve Sonlu Elemanlar Yöntemi (BEŞ). Bu kılavuzda, keşfedeceğiz:
- Doğrudan Mukavemet Yöntemi Nedir?
- Acceptance and Adoption in the Industry
- Geleneksel Sonlu Şerit Yöntemi
- Buckling Mode Types
- What are the DSM Factors?
- SkyCiv Bölüm Oluşturucuda Sonlu Şerit Yöntemi
Doğrudan Mukavemet Yöntemi Nedir? (DSM)
NS Doğrudan Mukavemet Yöntemi (DSM) is a design approach used predominately for the analysis and design of cold-formed steel members. Unlike traditional methods (such as the Effective Width Method) that rely on calculating effective section properties to account for local buckling, the DSM directly computes the member’s strength using its full, unreduced cross-sectional properties.
Pros and Cons of Direct Strength Method
| Artıları | Eksileri |
|---|---|
| Simplifies Design Process: Reduces complexity by eliminating effective width calculations. | Learning Curve: Requires engineers to become familiar with new concepts and formulations. |
| Enhanced Accuracy: Directly accounts for various buckling modes for precise strength predictions. | Limited Historical Data: Less empirical data available for some specific applications compared to traditional methods. |
| Versatile Application: Suitable for complex and unconventional cross-sections. | Software Dependence: May require advanced software tools not readily available to all practitioners. |
| Unified Methodology: Provides a consistent approach across different buckling behaviors. | Standard Compliance: Not all regional codes may fully incorporate DSM provisions yet. |
| Facilitates Innovation: Encourages the use of new materials and shapes due to its adaptable framework. | Resistance to Change: Industry inertia can slow adoption as practitioners stick to familiar methods. |
Adoption and Acceptance:
The DSM is recognized and incorporated into major international design standards, gibi:
- AISI S100: Soğuk Şekillendirilmiş Çelik Yapı Elemanlarının Tasarımına İlişkin Kuzey Amerika Şartnamesi.
- AS / NZS 4600: Australian/New Zealand Standard for Cold-Formed Steel Structures.
DSM is also being prioritised as a future method by being taught in universities and becoming a more common method taught in cold formed design courses. We’re also seeing an increase in it’s support by structural analysis and design software packages who are integrating DSM into their design modules.
ancak, there are still some obstacles and challenges in the DSM being widely-adopted, since it is a relatively new/untaught method. Transitioning from traditional methods requires training and adaptation, which some practitioners can be reluctant to undertake.
Geleneksel Sonlu Şerit Yöntemi
FSM, FEM'in basitleştirilmesi olarak oluşturuldu, her iki yöntem de aynı teorik altyapıya sahiptir, and the FSM is also a matrix method. By defining the nodes and elements of a section it is possible to analyze any complex shape. Bu, bölüm optimizasyonunu teşvik eder ve analiz sürecini basitleştirir.
Çeşitli seçenekler, açık kaynak araçları dahil, şu anda Sonlu Şerit analizi gerçekleştirmek için kullanılabilir. ancak, integrating these tools with general analysis and design software has proved challenging due to their complex nature. SkyCiv has recently built a Finite Strip Method analysis tool which is fully integrated into our Bölüm Oluşturucu yazılım. This tool automates calculation of DSM factors for standard and custom cold-formed sections, allowing for DSM steel design in accordance with AISI S100, GİBİ 4600 and other international standards.
The FSM discretizes the section’s transversal shape into longitudinal strips [3]. This simplifies the traditional 3D analysis problem with 6 degrees of freedom to a problem with 4 özgürlük derecesi. The strips are analyzed for different lengths called half-wavelength.
Using the geometrical section properties, malzeme, the stresses, and the load condition, two global matrices are constructed, the elastic stiffness matrix (Ke) and the geometric stiffness matrix (Kg).
En sonunda, this represents an eigenvalue decomposition problem, where the eigenvalues represent the load factors, and the eigenvectors contain the deformed shape.
![]()
Buckling Mode Types
The buckling classes are organized into three main groups, küresel, yerel, and distortional, depending on the failure type.
Local buckling: Buckling that involves significant distortion of the cross-section, but this distortion includes only rotation, not translation, at the internal fold lines [2].
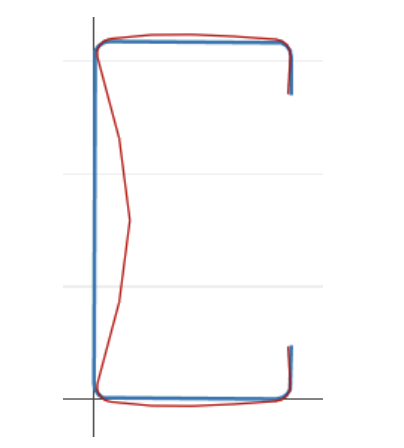
Distortional buckling: Buckling that involves significant distortion of the cross-section, but this distortion includes rotation and translation at one or more internal fold lines of a member [2].
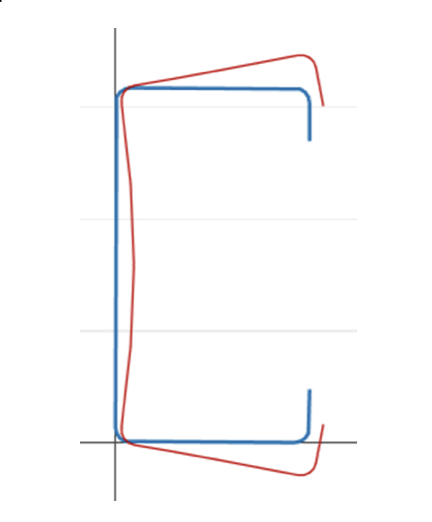

Global buckling: Enine kesitin bozulmasına neden olmayan bükülme, bunun yerine çeviri (eğilme) ve/veya rotasyon (burulma) tüm kesitin meydana gelmesi [2].
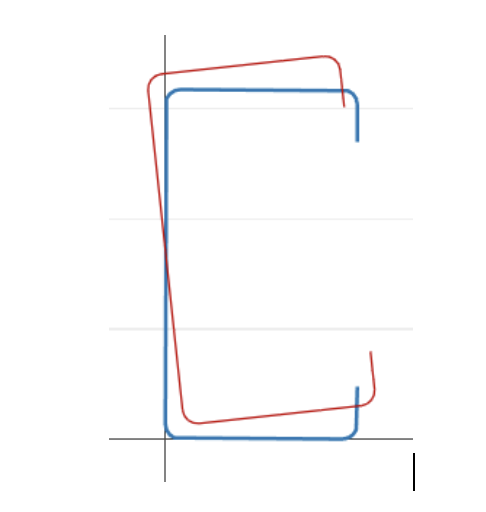
Bu tanımdan, burkulma sınıflandırması ile deforme olmuş şekil arasında güçlü bir geometrik korelasyon olduğu sonucunu çıkarabiliriz., imza eğrisinin her noktası için deforme olanı gösteriyoruz.
DSM Factors
SkyCiv Bölüm Oluşturucuda Sonlu Şerit Yöntemi
SkyCiv has a Direct Strength Method Calculator built into our Section Analysis Software (SkyCiv Bölüm Oluşturucu) which can automatically calculate the key DSM factors for any custom cold formed steel shape. Simply start from the Section Builder module by loading in a CFS section and clicking Design -> Soğuk Şekillendirilmiş Çelik:
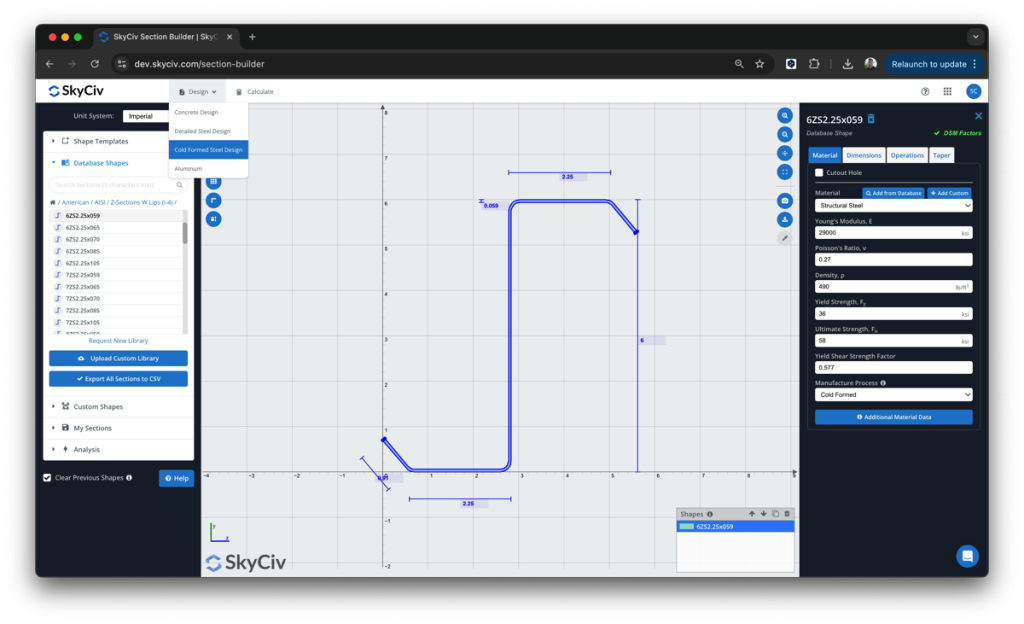
Buradan, the DSM factors will be automatically calculated, ready for the user to review and submit:
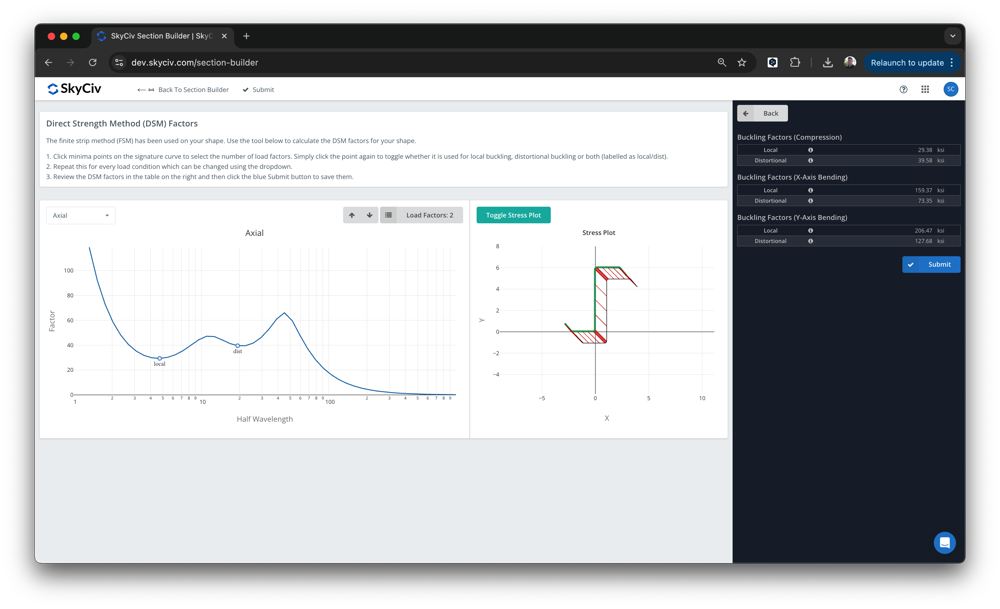
The software is built on top of the SkyCiv Section Builder, altında Tasarım – Soğuk Şekillendirilmiş. The local and distortional buckling minima will automatically be detected, however users can override these values. Bir kez gönderildi, these factors will then be used in the design for the SkyCiv AISI (2016) and AS4600 (2018) integrated design modules.
In SkyCiv elastic buckling analysis module, there are some important hypotheses and considerations that we clarify here. Bunları aşağıda inceleyeceğiz:
Mesh of elements
The mesh of the elements is produced automatically and can be viewed in the right chart, the fillets are split into 4 elementler, and the straight line into 4 elements too.
Analysis lengths
The lengths used to perform the Finite Strip analysis are defined by default as a logarithmic space from 0 to 10^3 in the imperial unit system and from 0 to 10^3.5 in the metric system.
Load conditions
We calculate the signature curve for 5 different load conditions:
- Axial load
- Bending moment in X axis, pozitif
- Bending moment in X axis, olumsuz
- Bending moment in Y axis, pozitif
- Bending moment in Y axis, olumsuz
Sınır şartları
The analysis is performed assuming the model is pinned and free to warp at both ends.
Signature Curve
İmza eğrisi geleneksel Sonlu Şerit Yöntemi kullanılarak oluşturulur, Fy normalleştirildi (Fy = 1) böylece yük faktörleri basınç birimlerinde sunulur (Birim sistemine göre MPa veya ksi).
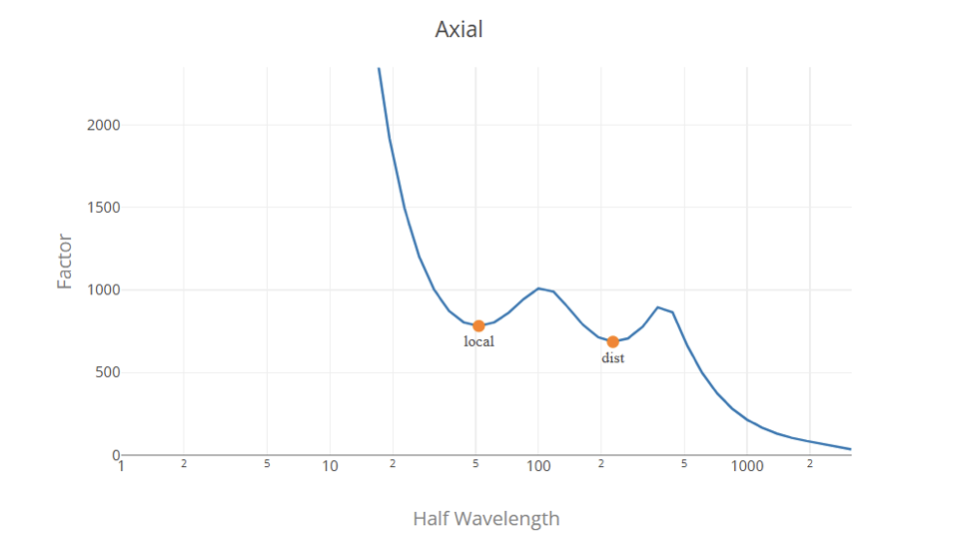
Yük Faktörü Seçimi
Genel olarak, yük faktörleri imza eğrisindeki yerel minimum noktalardır, birincisi yerel burkulma için kritik yük faktörünü temsil eder ve ikincisi çarpılma burkulması için kritik yük faktörünü temsil eder. İmza eğrisinde yerel minimum nokta olmadığından küresel yük faktörünün imza eğrisinden belirlenmesi zor bir iştir.. Yani, en uygun çözüm, Sonlu Şerit analizinden yerel ve distorsiyonlu burkulma yük faktörlerini ve klasik formülleri kullanarak global burkulma faktörünü kullanmaktır..
İmza eğrisindeki yük faktörlerini bulmak ve sınıflandırmak için bir algoritma kullanıyoruz. ancak, this does not ensure a correct classification in all the cases, and this does not replace the engineering judgment, Kullanıcının değerleri gözden geçirmesini ve gerekirse göndermeden önce bunları değiştirmesini öneririz..
Referanslar
- Soğuk Şekillendirilmiş Çelik Yapı Elemanlarının Tasarımına İlişkin Kuzey Amerika Şartnamesi, 2016 C'yi dikkate alacak, Amerikan Demir ve Çelik Enstitüsü.
- Doğrudan Mukavemet Yöntemi (DSM) Tasarım Kılavuzu, 2006, Soğuk Şekillendirilmiş Çelik Yapı Elemanlarının Tasarımına İlişkin Şartnameler Komitesi.
- CUFSM kullanılarak soğuk şekillendirilmiş çelik elemanların burkulma analizi: geleneksel ve kısıtlı sonlu şerit yöntemleri, siyah beyaz. Schafer ve S. Adany, 2006, 18Soğuk Şekillendirilmiş Çelik Yapılar Uluslararası Özel Konferansı.

