Flujo de trabajo de diseño de zapata extendida
Las zapatas son miembros estructurales utilizados para soportar columnas y otros elementos verticales para transmitir sus cargas de superestructura a los suelos subyacentes..
Figura 1 ilustra el proceso de flujo de trabajo de diseño, que la Fundación SkyCiv adapta el proceso de flujo de trabajo. Donde estos controles tales como (1) Rodamiento del suelo, (2) corte, (3) Flexural, (4) Longitud de desarrollo, (5) Edificación, y (6) Las comprobaciones de estabilidad son parámetros importantes necesarios para satisfacer el resultado sin exceder el índice de utilidad permitido..
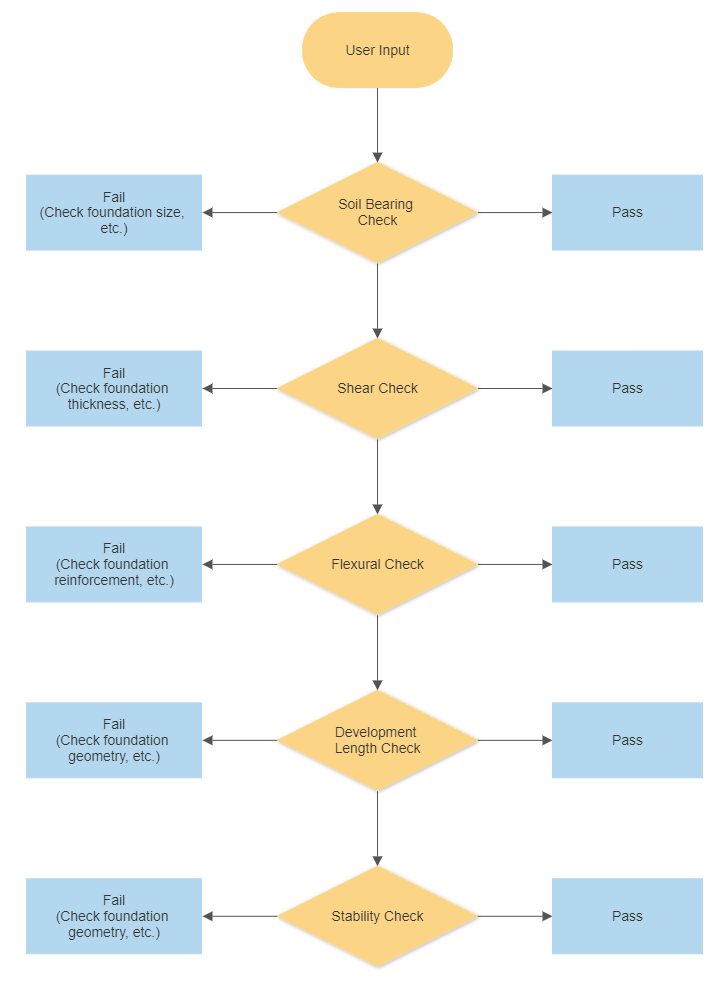
Figura 1: flujo de trabajo de Fundación SkyCiv.
Cómo diseñar una zapata extendida
Esta sección analiza el procedimiento de diseño de zapatas extendidas en referencia al Instituto Americano del Concreto 318-2014.
Los controles de longitud de desarrollo y estabilidad son parámetros importantes que se requieren para satisfacer el resultado sin exceder un valor de
La Comprobación de carga del suelo determina principalmente las dimensiones geométricas de una zapata aislada de la superestructura. (servicio o sin factorizar) cargas. La presión real del rodamiento determinada principalmente por la siguiente ecuación:
Cuando las excentricidades superan el kern, Se explica el artículo detallado sobre el patrón de presión de los rodamientos. aquí.
Para satisfacer las dimensiones geométricas de la fundación., La capacidad de carga permitida del suelo debe ser mayor que la presión base gobernante debajo de la zapata..
\( \texto{Capacidad de carga permitida} > \texto{ Actual (Gobernante) Presión sobre los cimientos} \)
Nota: Sin tensión en la presión de apoyo en el diseño de la cimentación.
Comprobación de corte
Shear Check determina el grosor o la profundidad de la cimentación en función de la carga de corte inducida por las cargas de la superestructura. Hay dos controles de cortante primarios, como sigue:
- De una sola mano (o Haz) corte
- Bidireccional (o punzonado) corte
De una sola mano (o Haz) corte
La sección crítica para cortante en una dirección se extiende a lo ancho de la zapata y está ubicada a una distancia d de la cara de una columna..
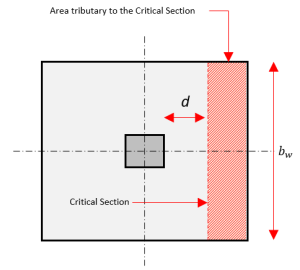
Figura 2: Cizalla unidireccional
Imperial (psi)
\( V_{c} = 2 \lambda sqrt{ f ^{"}_ _{c} } B_{w} d \)
Métrico (MPa)
\( V_{c} = 0.17 \lambda sqrt{ f ^{"}_ _{c} } B_{w} d \)
Para satisfacer el One Way (o Haz) corte, la \( V_{c} \) no debe ser mayor que \( V_{tu} \).
\( \no V_{c} > V_{tu} = text{ Actual (Gobernante) Cizalla de la Fundación} \)
Bidireccional (o punzonado) corte
La sección crítica para el diseño de cortante en dos direcciones se encuentra en \( \frac{d}{2} \) lejos de la cara de una columna de concreto. Dónde \( V_{c} \) la ecuación se define de la siguiente manera:
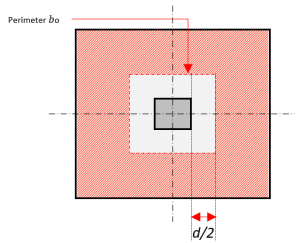
Figura 3: Cizalla bidireccional
Imperial (psi)
\( V_{c} = left( 2 + \frac{4}{\beta} \verdad) \lambda sqrt{ f ^{"}_ _{c} } B_{los} d \)
\( V_{c} = left( \frac{\alfa_{s} d }{ B_{los} } + 2 \verdad) \lambda sqrt{ f ^{"}_ _{c} } B_{los} d \)
\( V_{c} = 4 \lambda sqrt{ f ^{"}_ _{c} } B_{los} d \)
Métrico (MPa)
\( V_{c} = 0.17 \izquierda( 1 + \frac{2}{\beta} \verdad) \lambda sqrt{ f ^{"}_ _{c} } B_{los} d \)
\( V_{c} = 0.083 \izquierda( \frac{ \alfa_{s} d }{ B_{los} } + 2 \verdad) \lambda sqrt{ f ^{"}_ _{c} } B_{los} d \)
\( V_{c} = 0.33 \lambda sqrt{ f ^{"}_ _{c} } B_{los} d \)
el gobernante \( V_{c} \) se tomará como el valor mínimo.
Para satisfacer el Two Way (o punzonado) corte, la \( V_{c} \) no debe ser mayor que \( V_{tu} \).
\( \no V_{c} > V_{tu} = text{ Actual (Gobernante) Cizalla de la Fundación} \)
Comprobación de flexión
La comprobación de flexión determina el refuerzo necesario de la cimentación en función del momento o la carga de flexión inducida por las cargas de la superestructura.. El procedimiento de diseño para resistencia a momento considera un elemento de flexión unidireccional primero en una dirección principal.
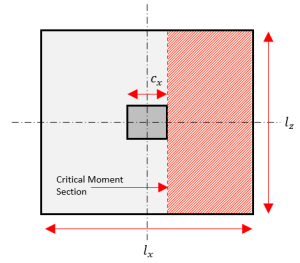
Figura 4: Línea de sección de momento crítico
Paso 1. Calcular el Momento Real en la cimentación \( METRO_{tu} \).
\( METRO_{tu} = q_{tu} \izquierda( \frac{ l_{x} – c }{ 2 } \verdad) l_{z} \frac{ l_{x} – c }{ 2 } \)
Paso 2. Calcule el refuerzo mínimo requerido de la cimentación.
Paso 3. Calculó la profundidad del bloque de tensión rectangular equivalente, a.
\( a = frac{ UNA_{s} F_{y} }{ 0.85 F_{c}^{"} l_{z} } \)
Paso 4. Calcular la capacidad de momento de la cimentación \( \película_{norte} \).
\( \película_{norte} = phi A_{s} F_{y}\izquierda( d – \frac{a}{2} \verdad) \)
Para satisfacer el requisito de flexión, la \( \película_{norte} \) no debe ser mayor que \( METRO_{tu} \)..
\( \película_{norte} > METRO_{tu} \)
Comprobación de longitud de desarrollo
La verificación de longitud de desarrollo determina la longitud de empotramiento más corta requerida para que una barra de refuerzo desarrolle su límite elástico completo en concreto..
Comprobación de estabilidad
Hay dos tipos principales de controles de estabilidad en la base., como sigue:
- Volcarse
- Corredizo
Cheque anulado
La verificación de vuelco es una verificación de estabilidad contra el momento de la carga de la superestructura. Generalmente, este factor de seguridad para el momento de vuelco es 1.5-3.0.
\( \texto{Factor de seguridad de vuelco} < \frac{ \ESTOY{R} }{ \ESTOY{Antiguo Testamento} } \)
Nota:
- \( \ESTOY{R} \) – Momento resistente
- \( \ESTOY{Antiguo Testamento} \) – Momento de vuelco
Cheque deslizante
Sliding Check es un control de estabilidad contra la fuerza horizontal inducida por la carga de la superestructura. Generalmente, este factor de seguridad para el momento de vuelco es 1.5-3.0.
\( \texto{Factor deslizante de seguridad} < \texto{Fuerza de deslizamiento} \)
Verificación de elevación
Comprueba la carga axial gobernante que actúa sobre la zapata.. Suma todas las cargas verticales, incluida la carga del usuario y los pesos propios de la columna., losa de zapata, suelo, y fuerza de flotación. Si la columna experimenta una fuerza hacia arriba, Los pesos propios especificados deben contrarrestar la fuerza ascendente.; de lo contrario, El diseño corre el riesgo de fallar debido a la inestabilidad..
Este artículo explica el ajuste primario cuando el Fundación SkyCiv los usuarios encuentran esta verificación de falla.
- Los controles de longitud de desarrollo y estabilidad son parámetros importantes que se requieren para satisfacer el resultado sin exceder un valor de está influenciada principalmente por la dimensión de la zapata extendida que está sujeta a la superestructura (sin factorizar) cargas y presión de suelo permisible.
- Comprobación de corte está influenciado principalmente por la profundidad de la zapata extendida donde la zapata extendida realiza comprobaciones en un sentido y en dos sentidos.
- Comprobación de flexión está influenciado principalmente por el programa de refuerzo de la zapata extendida.
- Longitud de desarrollo Cheque y
- Comprobaciones de estabilidad están influenciados principalmente por las dimensiones de la zapata extendida.
Basado en la información anterior, esos ajustes aumentarán la capacidad de diseño por controles de la zapata extendida.
Tenga en cuenta que algunos parámetros como la resistencia de los materiales, factor, y las cargas sometidas también son parte de la influencia de una mayor capacidad de diseño.
Módulos de código de diseño
El Fundación SkyCiv tener estos códigos de diseño actualmente disponibles:
- Código americano : ACI 318-14
- Estándar australiano : AS 3600 (2009 & 2018)
- Europa : Eurocódigo
- canadiense: CSA 2014
Última actualización
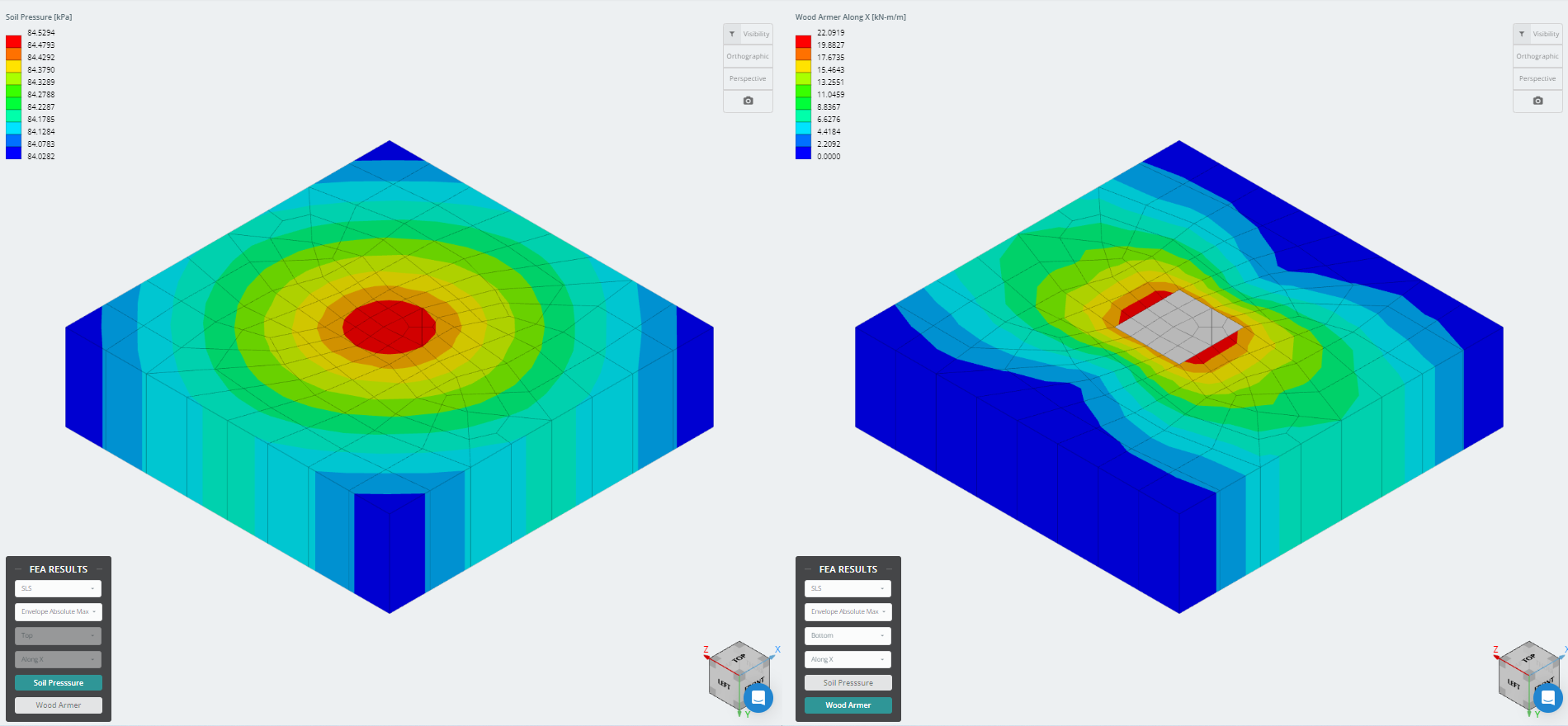
La última versión del módulo básico ahora está integrada con el Análisis de elementos finitos (FEA), que ofrece un análisis de presión del suelo más potente e introduce un análisis de armer de madera que se utilizará para una verificación de flexión mucho más detallada.. Los resultados de FEA para la presión del suelo y los momentos de armado de la madera se pueden ver en 3D y se agregaron a los informes..
Referencias
- Requisitos del Código de Construcción para Hormigón Estructural (ACI 318-14) Comentario sobre los requisitos del código de construcción para hormigón estructural (ACI 318R-14). Instituto Americano del Concreto, 2014.
- McCormac, Jack C., y Russell H. marrón. Diseño de hormigón armado ACI 318-11 Edición de código. Wiley, 2014.
- Taylor, Andrés, et al. El manual de diseño de hormigón armado: un compañero a ACI-318-14. Instituto Americano del Concreto, 2015.
- La zapata extendida se puede clasificar como zapatas de pared y columna., david y dolan, Charles. Diseño de Estructuras de Hormigón 16 Edición. mcgrawhill, 2021.
Comience con la Fundación SkyCiv hoy!
Nuestra herramienta gratuita permite a los usuarios realizar cálculos de carga sin descargar ni instalar! Inicie el Diseño de Cimientos y pruébalo hoy! Es fácil empezar, pero si necesitas más ayuda, asegúrese de visitar nuestro documentación o ponte en contacto con nosotros!
No es un usuario de SkyCiv?
Regístrese para un Gratis 14 Day Trial para empezar hoy!
Desarrollador de producto
licenciatura (Civil), maestría (Civil)