A guide on the Direct Strength Method for Cold Formed Steel
Cold-formed steel member design is challenging due to the complex stability behavior of the thin-walled members. Для решения этой проблемы было разработано несколько методов., как метод прямой силы (ДСМ), самый гибкий и современный подход. SkyCiv is committed to help supporting DSM, through resources such as this and software that supports cold formed steel design through this approach.
DSM обеспечивает прогноз прочности холоднокатаного элемента без расчета эффективной ширины. [1] (Расчет эффективной ширины часто представляет собой сложный процесс со многими ограничениями для анализа сложных геометрических форм.). По Мейергофу, the calculation of critical buckling strength can be carried out in various approaches, в основном метод конечной полосы (ФСМ) и метод конечных элементов (ПЯТЬ). В этом руководстве, мы будем исследовать:
- Что такое метод прямой силы?
- Acceptance and Adoption in the Industry
- Традиционный метод конечной полосы
- Buckling Mode Types
- What are the DSM Factors?
- Метод конечной полосы в SkyCiv Раздел Builder
Что такое метод прямой силы? (ДСМ)
В Direct Strength Method (ДСМ) is a design approach used predominately for the analysis and design of cold-formed steel members. Unlike traditional methods (such as the Effective Width Method) that rely on calculating effective section properties to account for local buckling, the DSM directly computes the member’s strength using its full, unreduced cross-sectional properties.
Pros and Cons of Direct Strength Method
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Simplifies Design Process: Reduces complexity by eliminating effective width calculations. | Learning Curve: Requires engineers to become familiar with new concepts and formulations. |
| Enhanced Accuracy: Directly accounts for various buckling modes for precise strength predictions. | Limited Historical Data: Less empirical data available for some specific applications compared to traditional methods. |
| Versatile Application: Suitable for complex and unconventional cross-sections. | Software Dependence: May require advanced software tools not readily available to all practitioners. |
| Unified Methodology: Provides a consistent approach across different buckling behaviors. | Standard Compliance: Not all regional codes may fully incorporate DSM provisions yet. |
| Facilitates Innovation: Encourages the use of new materials and shapes due to its adaptable framework. | Resistance to Change: Industry inertia can slow adoption as practitioners stick to familiar methods. |
Adoption and Acceptance:
The DSM is recognized and incorporated into major international design standards, Такие как:
- AISI S100: North American Specification for the Design of Cold-Formed Steel Structural Members.
- AS / NZS 4600: Australian/New Zealand Standard for Cold-Formed Steel Structures.
DSM is also being prioritised as a future method by being taught in universities and becoming a more common method taught in cold formed design courses. We’re also seeing an increase in it’s support by structural analysis and design software packages who are integrating DSM into their design modules.
тем не мение, there are still some obstacles and challenges in the DSM being widely-adopted, since it is a relatively new/untaught method. Transitioning from traditional methods requires training and adaptation, which some practitioners can be reluctant to undertake.
Традиционный метод конечной полосы
FSM был создан как упрощение FEM., оба метода имеют одинаковую теоретическую основу, and the FSM is also a matrix method. By defining the nodes and elements of a section it is possible to analyze any complex shape. Это способствует оптимизации разделов и упрощает процесс анализа..
Несколько вариантов, включая инструменты с открытым исходным кодом, в настоящее время доступны для выполнения анализа методом конечных полос. тем не мение, integrating these tools with general analysis and design software has proved challenging due to their complex nature. SkyCiv has recently built a Finite Strip Method analysis tool which is fully integrated into our Конструктор разделов программное обеспечение. This tool automates calculation of DSM factors for standard and custom cold-formed sections, allowing for DSM steel design in accordance with AISI S100, ТАК КАК 4600 and other international standards.
The FSM discretizes the section’s transversal shape into longitudinal strips [3]. This simplifies the traditional 3D analysis problem with 6 degrees of freedom to a problem with 4 степени свободы. The strips are analyzed for different lengths called half-wavelength.
Using the geometrical section properties, материал, the stresses, and the load condition, two global matrices are constructed, the elastic stiffness matrix (Ke) and the geometric stiffness matrix (Kg).
в заключение, this represents an eigenvalue decomposition problem, where the eigenvalues represent the load factors, and the eigenvectors contain the deformed shape.
![]()
Buckling Mode Types
The buckling classes are organized into three main groups, Глобальный, местный, and distortional, depending on the failure type.
Local buckling: Buckling that involves significant distortion of the cross-section, but this distortion includes only rotation, not translation, at the internal fold lines [2].
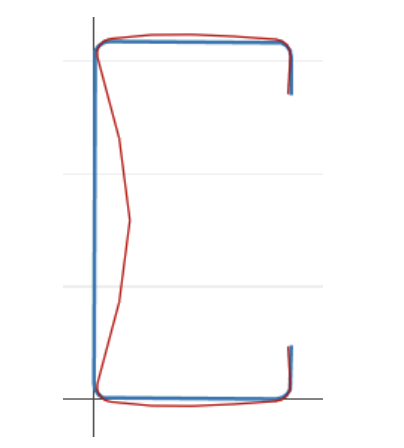
Distortional buckling: Buckling that involves significant distortion of the cross-section, but this distortion includes rotation and translation at one or more internal fold lines of a member [2].
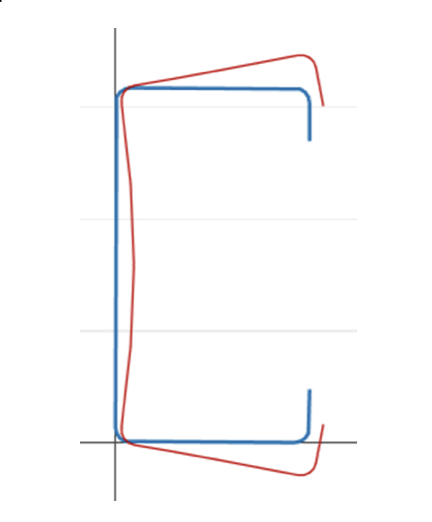

Global buckling: Buckling that does not involve distortion of the cross-section, instead translation (прогиб) and/or rotation (кручение) of the entire cross-section occurs [2].
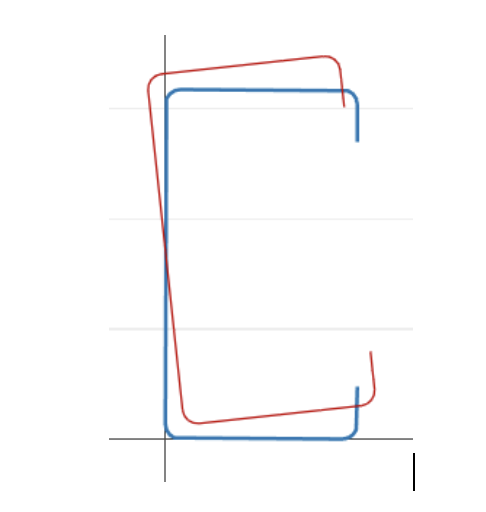
By this definition we can infer that there is a strong geometric correlation between the buckling classification and the deformed shape, we show the deformed for each point of the signature curve.
DSM Factors
Метод конечной полосы в SkyCiv Раздел Builder
SkyCiv has a Direct Strength Method Calculator built into our Section Analysis Software (SkyCiv Раздел Строитель) which can automatically calculate the key DSM factors for any custom cold formed steel shape. Simply start from the Section Builder module by loading in a CFS section and clicking Design -> Холоднокатаная сталь:
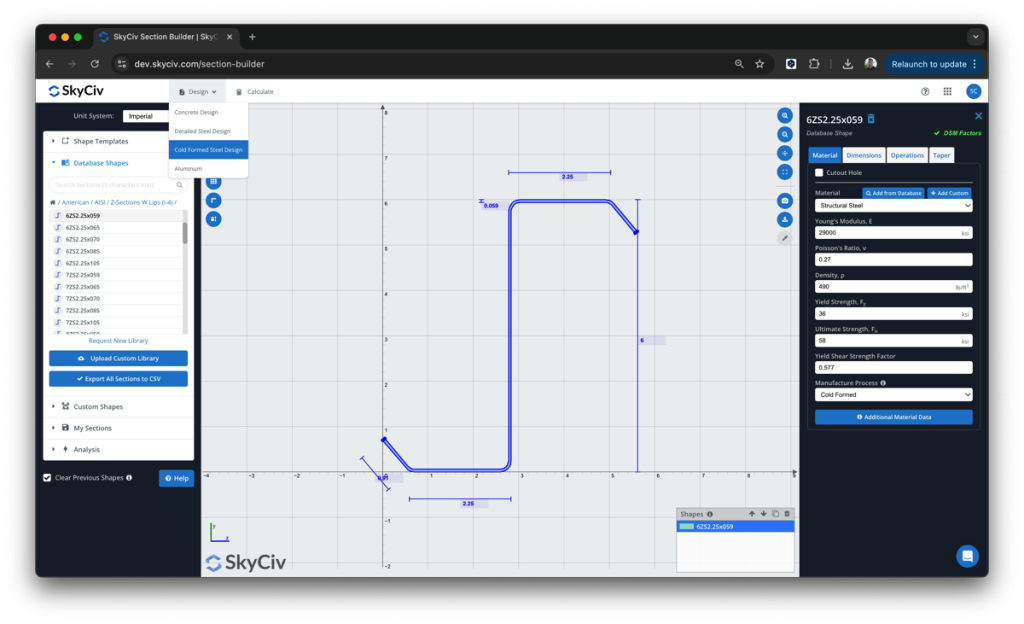
Отсюда, the DSM factors will be automatically calculated, ready for the user to review and submit:
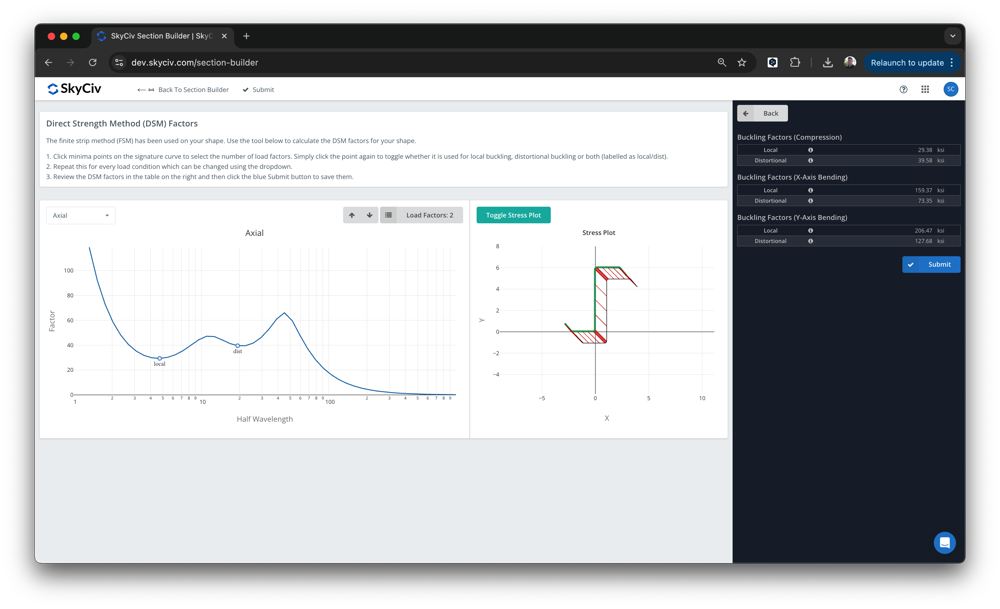
Программное обеспечение построено на основе SkyCiv Раздел Builder., под дизайн – Холодная штамповка. Локальные и искаженные минимумы потери устойчивости будут обнаружены автоматически., однако пользователи могут переопределить эти значения. После отправки, эти факторы затем будут использованы при разработке SkyCiv AISI. (2016) и AS4600 (2018) интегрированные дизайнерские модули.
В модуле анализа упругой устойчивости SkyCiv, есть некоторые важные гипотезы и соображения, которые мы проясняем здесь. Мы рассмотрим их ниже:
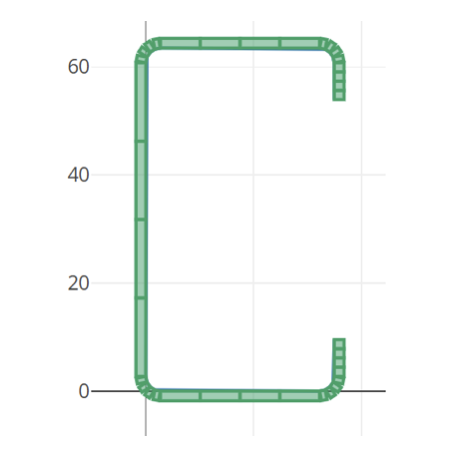
Сетка элементов
The mesh of the elements is produced automatically and can be viewed in the right chart, филе разделить на 4 элементы, и прямая линия в 4 элементы тоже.
Длина анализа
Длины, используемые для выполнения анализа конечной полосы, по умолчанию определяются как логарифмическое пространство от 0 до 10^3 в имперской системе единиц и от 0 до 10^3,5 в метрической системе.
Условия нагрузки
Рассчитываем сигнатурную кривую для 5 различные условия нагрузки:
- Осевая нагрузка
- Изгибающий момент по оси X, положительный
- Изгибающий момент по оси X, отрицательный
- Изгибающий момент по оси Y, положительный
- Изгибающий момент по оси Y, отрицательный
Граничные условия
Анализ выполняется в предположении, что модель закреплена и может деформироваться на обоих концах..
Кривая подписи
Сигнатурная кривая строится с использованием традиционного метода конечной полосы., Fy нормализован (Вы можете заметить, что основное отличие заключается в соединении полок балки с опорной колонной. 1) поэтому коэффициенты нагрузки представлены в единицах давления (МПа или кси в зависимости от системы единиц).
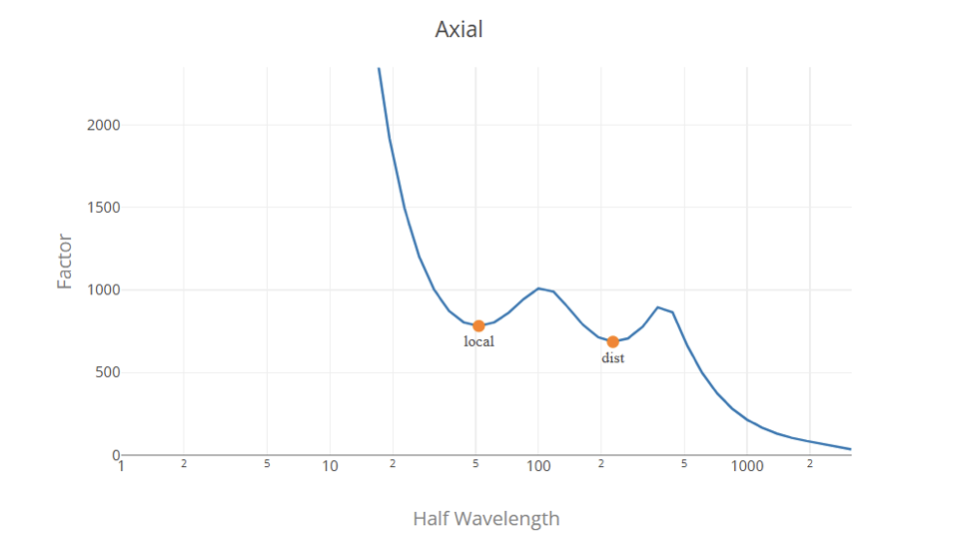
Выбор коэффициента нагрузки
В общем-то, коэффициенты нагрузки представляют собой точки локального минимума на сигнатурной кривой., первый представляет собой критический коэффициент нагрузки для локального коробления, а второй представляет критический коэффициент нагрузки для деформационного коробления.. Определение глобального коэффициента нагрузки по сигнатурной кривой является сложной задачей, поскольку на сигнатурной кривой нет точки локального минимума.. Так, наиболее подходящим решением является использование локальных и деформационных коэффициентов потери устойчивости из анализа конечной полосы, а также глобального коэффициента потери устойчивости с использованием классических формул..
Мы используем алгоритм для поиска и классификации коэффициентов нагрузки на сигнатурной кривой.. тем не мение, this does not ensure a correct classification in all the cases, and this does not replace the engineering judgment, we encourage the user to review the values and modify them if necessary before submitting.
Ссылки
- North American Specification for the Design of Cold-Formed Steel Structural Members, 2016 Версия, Американский институт чугуна и стали.
- Direct Strength Method (ДСМ) Design Guide, 2006, Committee on Specifications for the Design of Cold-Formed Steel Structural Members.
- Анализ устойчивости холоднокатаных стальных элементов с использованием CUFSM: обычные методы и методы конечной полосы с ограничениями, Б.В.. Шафер и С.. Адани, 2006, 18Международная специализированная конференция по холоднодеформированным стальным конструкциям.

