Introduction
In the following tutorial, we will explore how to create and analyze a structure using dynamic frequency in SkyCiv 3D Structural Analysis Software. We will go step by step showing how to create nodes, members, plates, sections, materials, supports, loads, diaphragms, nodal masses and spectral loads.
You have to open Structural 3D from your SkyCiv dashboard and create a new project, in this tutorial, we will be working on meters, so you can modify the units by going to settings > unit system and selecting metric
Member creation
There are different ways to create members, using the form, and datasheet, but in this example, we will be using the pen tool for the member creation, you can activate the pen tool going to the right panel > pen > pen tool.
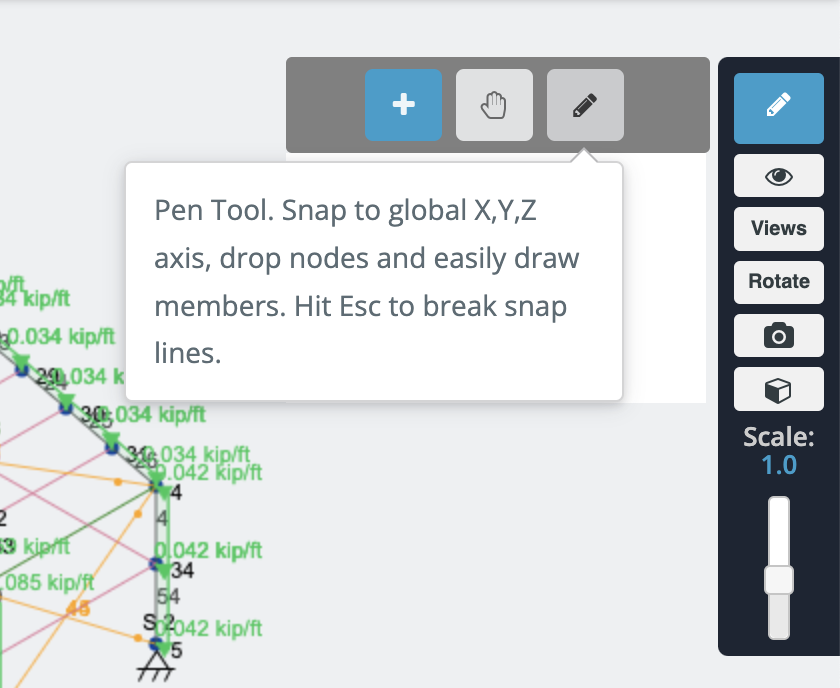
After we have the pen tool selected we can start to create all the frame members we will create a column member of 4.5m and beams of 7m. In the middle of the structure we will create x-bracing truss members. we will repeat the same process until we complete three floors.
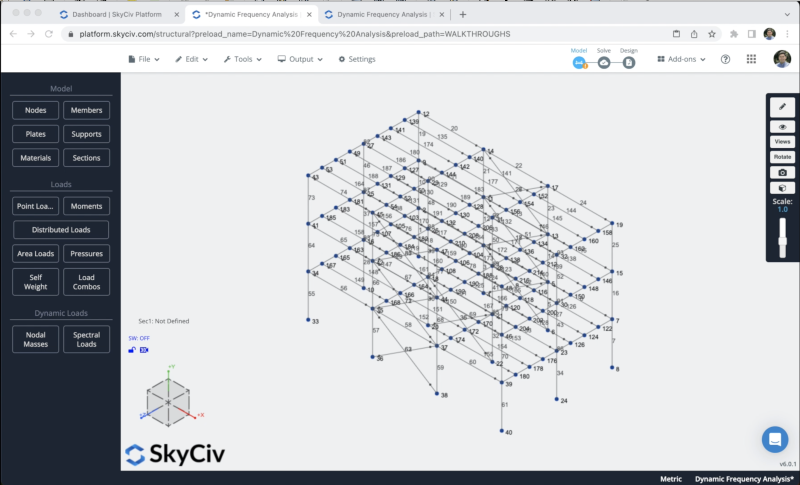
To avoid the creation of more nodes and members we will duplicate the frame that we created in the previous steps in the Z axis. To achieve this we need to select the whole structure by doing right click on the canvas > Select all or hit Ctrl + A on your keyboard. After we select the whole frame we can go to Edit > Operations > Repeat or hit Ctrl + D.
We will repeat the structure 2 times every 6m along the z-axis. Then we can connect the structures by creating beams along the z direction every 1.5m in all the floors
Sections and Materials
The next step will be the creation of sections and materials, in this example, we will be using the Section Builder module to create our sections, to access the Section Builder module we need to go to Sections > Builder. Once the section builder is opened, we can select sections from Shape Templates, in this case, we will select Database Shapes and we will look for the following sections:
- W10 x 49: Will be used for all the columns
- W12x26: Will be used for all the beams in the X direction
- HSS4x4x1/4: Will be used for the X bracing members
- W16x36: Will be used for all the beams in the Z direction
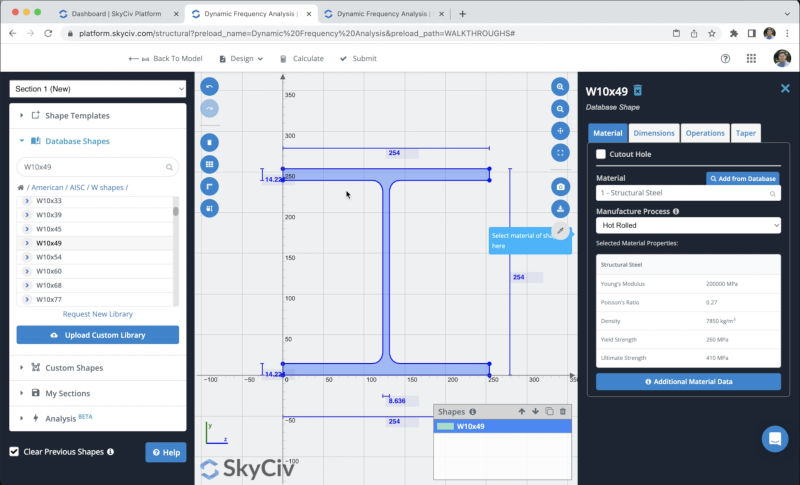
After we select our section we can click on Submit. By default, when we have members without sections defined, the new section will be assigned to them.
The result of our sections should look like this:
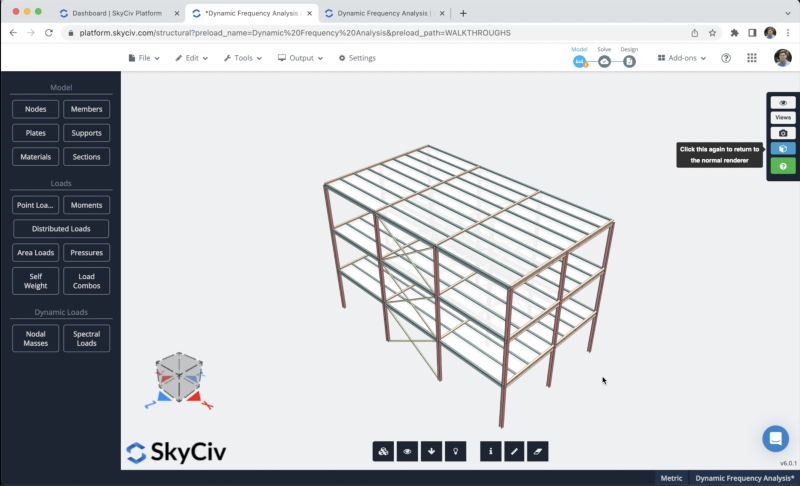
Plates and Rigid Diaphragms
We can create our plates by clicking in Plates > Fill the Node IDs information > Apply. We have to repeat the same process for all the floors. The result should look like this:
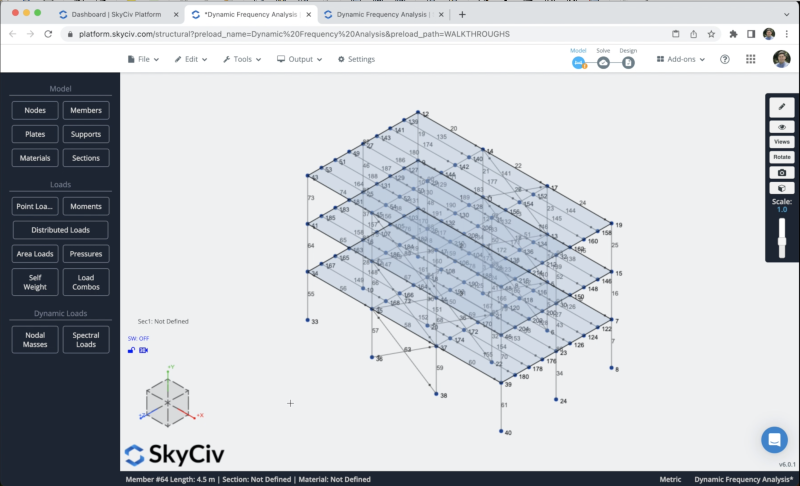
After we finish the process, we need to convert these plates into rigid diaphragms, we can select our plates and click in Advanced > Diaphragm > Rigid > Apply.
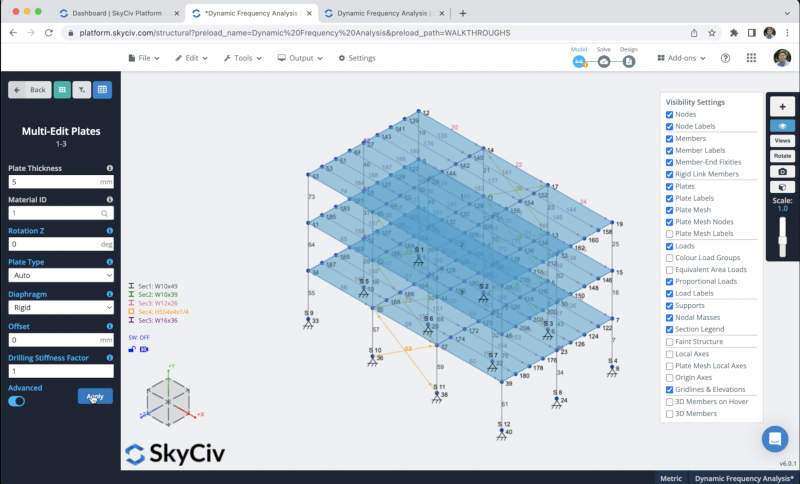
Static Loads Assignment
We will apply some area loads to our structure, we will use live loads of -2 kPa and superimposed loads of 2.5 kPa on all the floors. To apply area loads you can go to Area Loads and select the 4 nodes where you want to apply your area load
We will repeat the same process with the remaining floors. The final result should look like this:
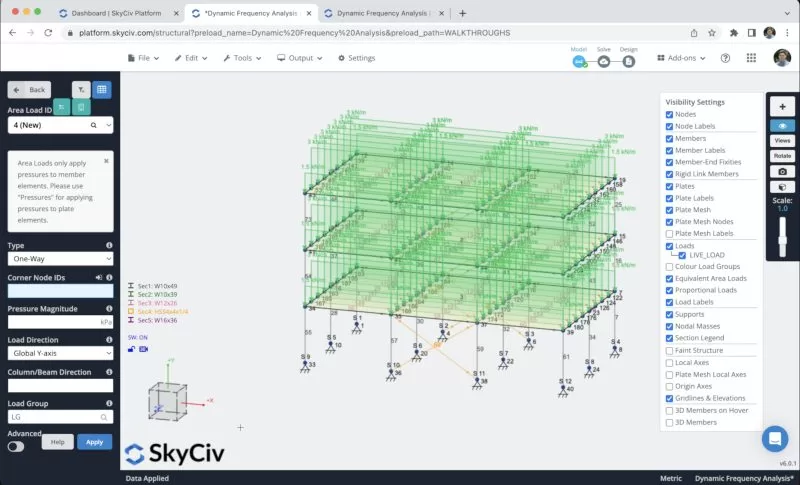
We will activate the self-weight of our members so when we solve our structure the load of the elements will be considered, to do this we just need to click on Self Weight > Click on On > Apply. We need to verify that the value in our vertical axis is equal to -1.
Supports Assignment
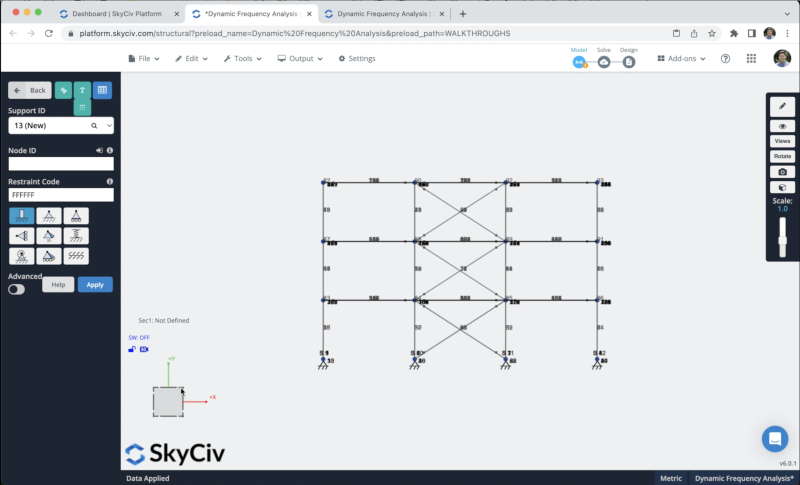
To add supports to our structure we have to select all the ground nodes, then go to Supports > Double Click on the Node ID field (If you have your nodes selected) > Select 3D Pin Support > Apply. After you create all your supports they should appear on your model.
Nodal Masses
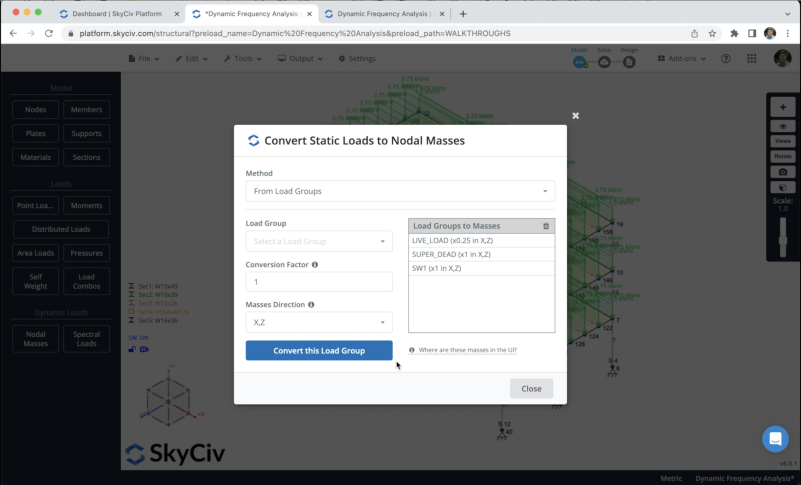
We can create the nodal masses by clicking on Nodal Masses > Convert Loads to Masses, then choose the load groups and put the Conversion factor based on the standard that you’re using, in this example we will use the following factors:
- LIVE_LOAD: 0.25 in X, Z
- SUPER_DEAD: 1 in X, Z
- SW1: 1 in X, Z
Spectral Loads
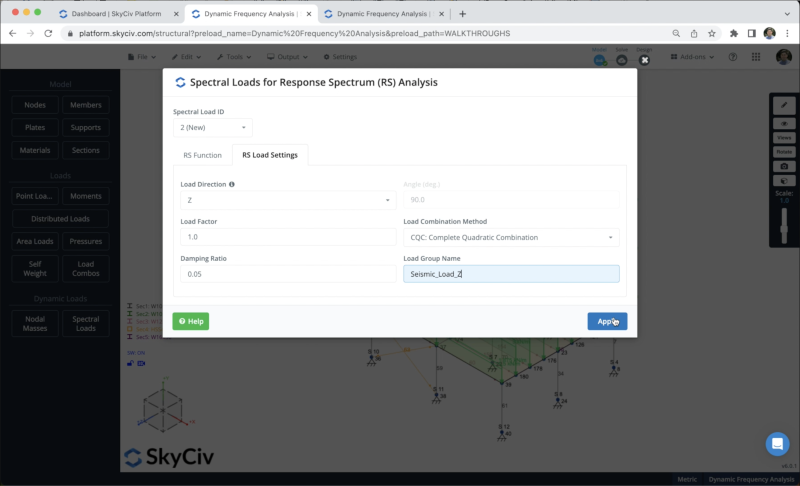
We can define the spectral loads by clicking on Spectral Loads, we can choose a design code to define the input values, however, in this example, we will use the user input to define the Periods and Spectral Values.
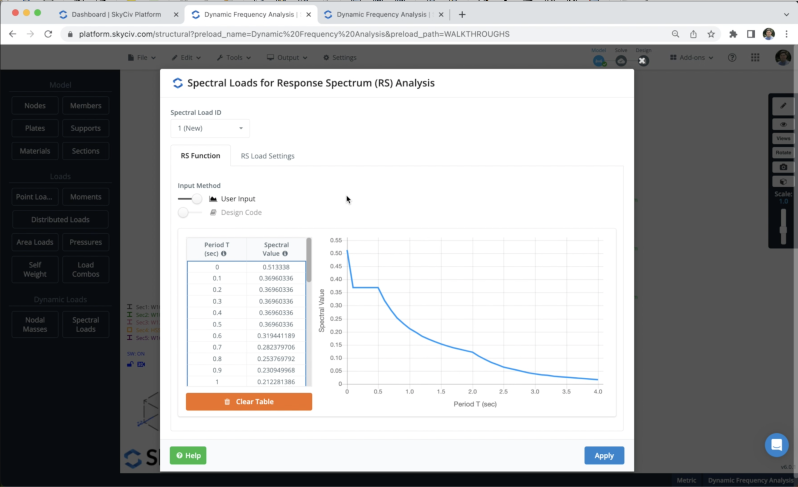
In this example, we have two different lateral resistance systems: braced and moment frames. Both systems respond inelastically in different modes so that, ductility and strength factors will modify the Reduced Design Spectrum to be used in each main direction, we can define these values in X and Z direction as shown in the following image.
Solving the Model
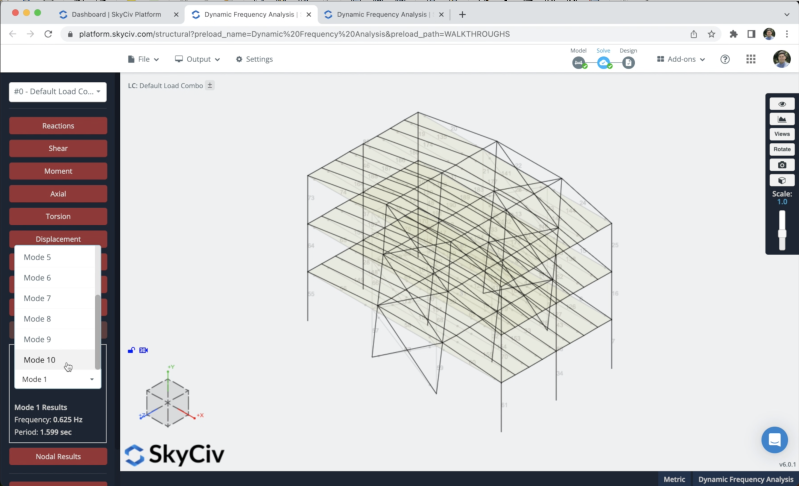
After we finished the modeling of the structure, we can proceed to solve our Structure, we can do this by clicking on Solve > Dynamic Frequency, and it will take us to a new window where we will be able to see all the results of the structure, we can go to Dynamic Frequency and we will see all the natural vibration periods or frequencies for all modes considered in the analysis.
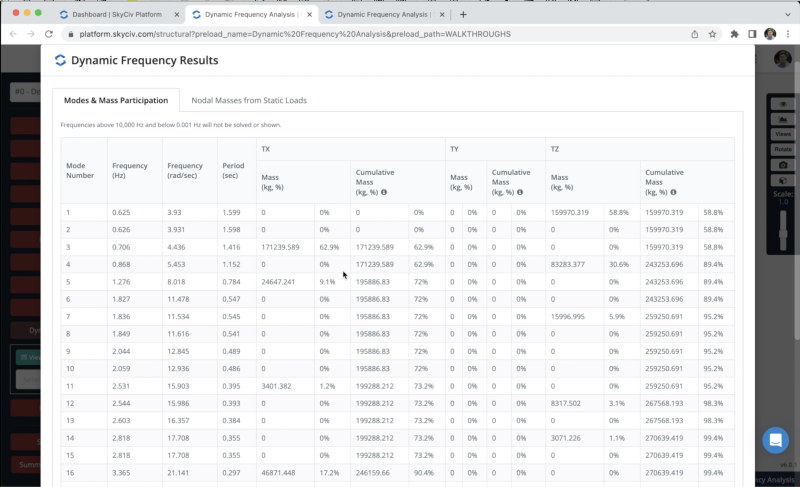
We can also access tables with the RSA results by clicking on View All Results. We will be able to see the frequencies and participation masses for all modes of vibration in the analysis.
FAQ
Yes, you have to go to Spectral Loads > Activate Design Code and you can choose between any of the following design codes: Eurocode 8, AASHTO LRFD / ASCE, NBCC 2020
Yes, you can use the load generator module to calculate seismic loads. Also, you can check the seismic loads articles in the documentation.
Yes, refer to the following articles where we explain the different options of solving.


